|
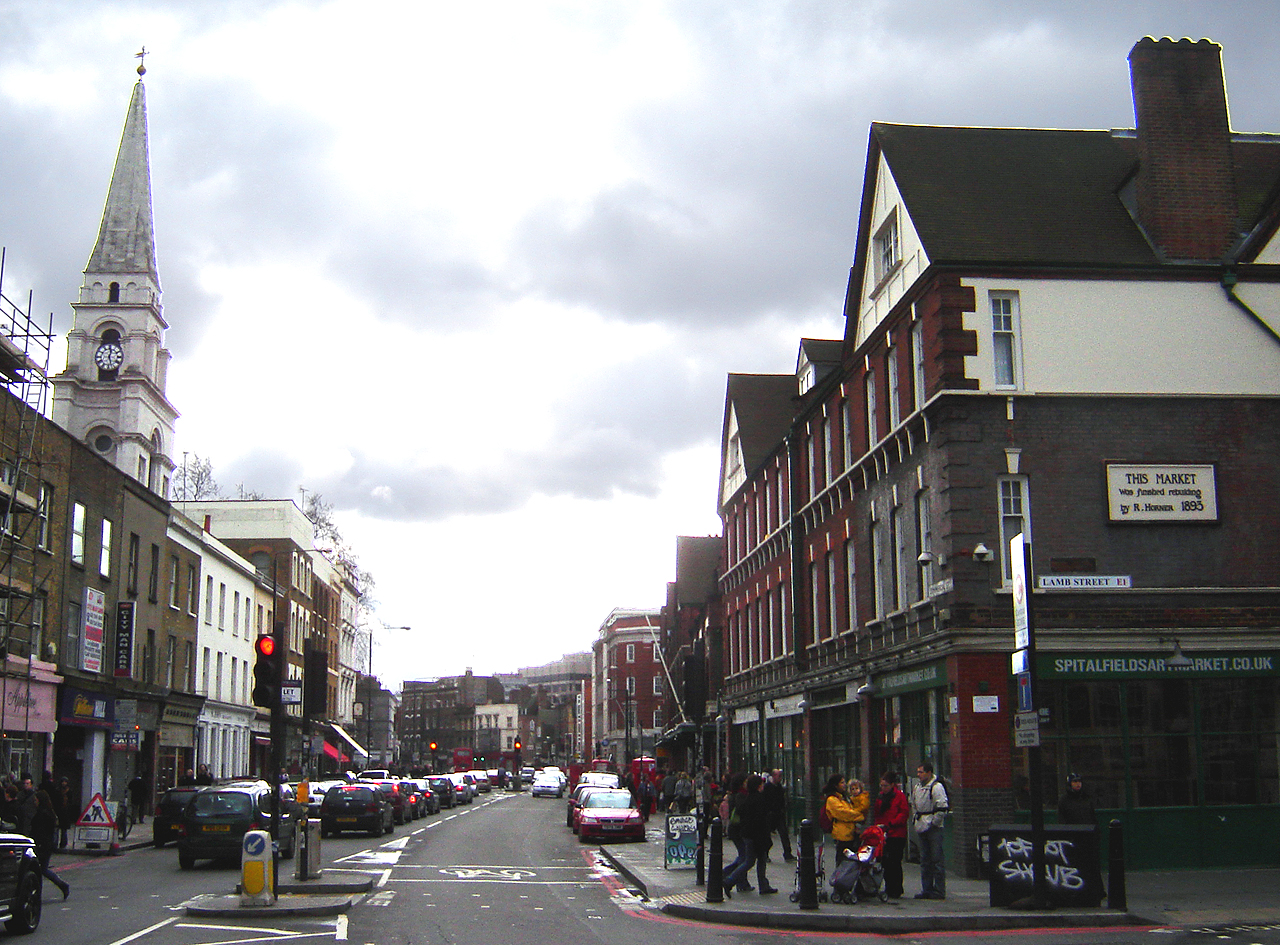
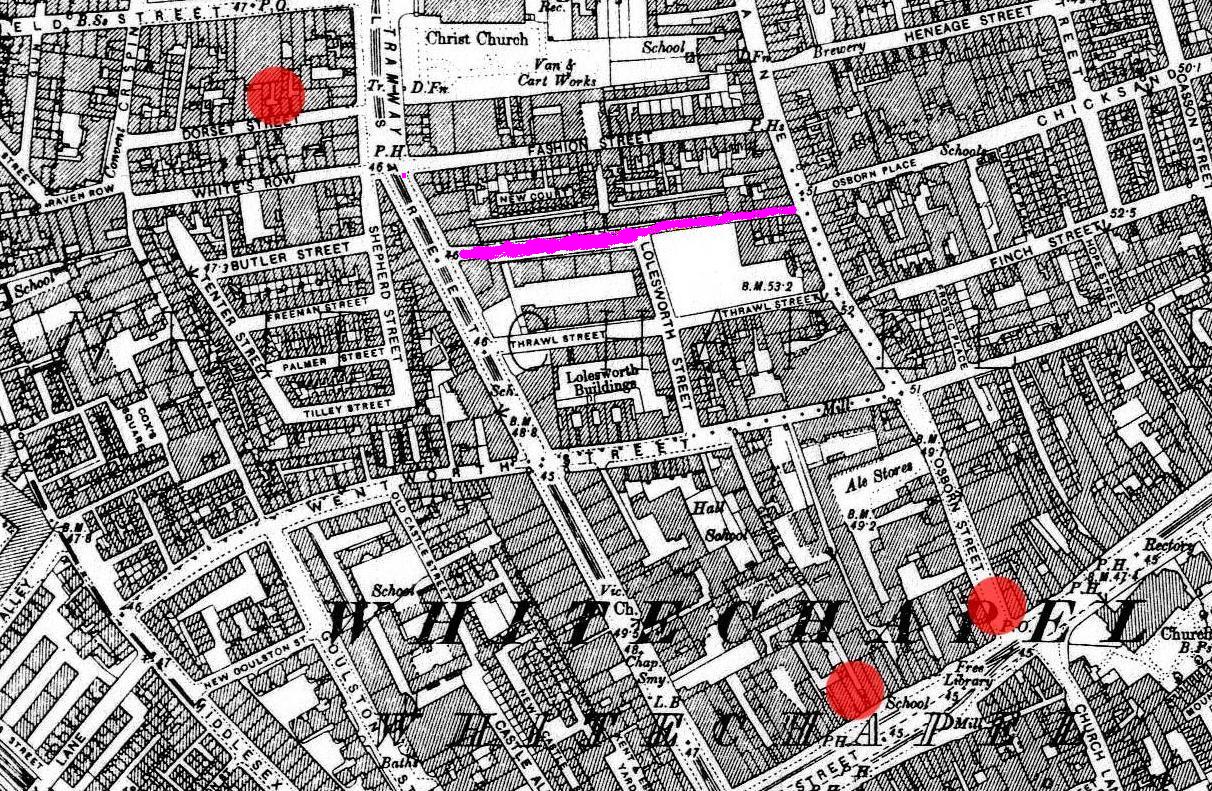
Flower And Dean Street
Flower and Dean Street was a road at the heart of the Spitalfields rookery in the East End of London. It was one of the most notorious slums of the Victorian era, being described in 1883 as "perhaps the foulest and most dangerous street in the whole metropolis", and was closely associated with the victims of Jack the Ripper. Land was acquired by the Fossan brothers in the mid 17th century. At that time it consisted of the southern part of Lolesworth Field, a tenterground to its south and a spinning and twisting ground with gardens to the south of that. The brothers built a street through the field which was named after them, which became Fashion Street. They split the tenterground into two long parcels and employed two bricklayers, John Flower and Gowan Dean, to build houses along its length. By the nineteenth century the back gardens of the original tenements had been built on for narrow courts and alleys and the area had become a slum. The poverty and deprivation of the area was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitechapel Flower And Dean St
Whitechapel is a district in East London and the future administrative centre of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is a part of the East End of London, east of Charing Cross. Part of the historic county of Middlesex, the area formed a civil and ecclesiastical parish after splitting from the ancient parish of Stepney in the 14th century. It became part of the County of London in 1889 and Greater London in 1965. Because the area is close to the London Docklands and east of the City of London, it has been a popular place for immigrants and the working class. The area was the centre of the London Jewish community in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Whitechapel, along with the neighbouring district of Spitalfields, were the location of the infamous 11 Whitechapel murders (1888–91), some of which were attributed to the mysterious serial killer known as Jack the Ripper. In the latter half of the 20th century, Whitechapel became a significant settlement for the British Ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work (painting)
''Work'' (1852–1865) is a painting by Ford Madox Brown that is generally considered to be his most important achievement. It exists in two versions. The painting attempts to portray, both literally and analytically, the totality of the Victorian social system and the transition from a rural to an urban economy. Brown began the painting in 1852 and completed it in 1865, when he set up a special exhibition to show it along with several of his other works. He wrote a detailed catalogue explaining the significance of the picture. The painting was commissioned by Thomas Plint, a well-known collector of Pre-Raphaelite art, who died before its completion.Dianne Sachko Macleod, "Plint, Thomas Edward (1823–1861)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, Sept 2004 A second version, smaller at 684 × 990 mm, was commissioned in 1859 and completed in 1863. This is now in the Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery. It is closely similar, though for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Street, London
Commercial Street is an arterial road in Tower Hamlets, east London that runs north to south from Shoreditch High Street to Whitechapel High Street through the East End district of Spitalfields. The road is a section of the A1202 London Inner Ring Road and as such forms part of the boundary of the London congestion charge zone. As the name implies, Commercial Street has historically been dominated by industrial and commercial activity, which it maintains to this day. It is on the City fringes, and much industry that was seen as too noisome for the City was once exiled to such areas as this. However, since the early 1990s the street has grown increasingly fashionable, while maintaining its busy commercial feel. History Spitalfields was historically one of the poorest, most overcrowded and most crime-ridden districts in London: a parliamentary report of 1838 described this area as harbouring "an extremely immoral population; women of the lowest character, receivers of stolen go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical Profiling
Geographic profiling is a criminal investigative methodology that analyzes the locations of a connected series of crimes to determine the most probable area of offender residence. By incorporating both qualitative and quantitative methods, it assists in understanding spatial behaviour of an offender and focusing the investigation to a smaller area of the community. Typically used in cases of serial murder or rape (but also arson, bombing, robbery, terrorism and other crimes), the technique helps police detectives prioritize information in large-scale major crime investigations that often involve hundreds or thousands of suspects and tips. In addition to determining the offender's most likely area of residence, an understanding of the spatial pattern of a crime series and the characteristics of the crime sites can tell investigators other useful information, such as whether the crime was opportunistic and the degree of offender familiarity with the crime location. This is based on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Eddowes
Catherine Eddowes (14 April 1842 – 30 September 1888) was the fourth of the canonical five victims of the notorious unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, who is believed to have killed and mutilated a minimum of five women in the Whitechapel and Spitalfields districts of London from late August to early November 1888. Eddowes was murdered in the early hours of Sunday 30 September within the City of London. She was the second woman killed within an hour; the night having already seen the murder of Elizabeth Stride within the jurisdiction of the Metropolitan Police. These two murders are commonly referred to as the "double event";Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 114–140 a term which originates from the content of the "Saucy Jacky" postcard received at the Central News Agency on 1 October. Part of a left human kidney, accompanied by a letter addressed ''From Hell'' and postmarked 15 October, was later sent to the chairman of the Whitechapel Vigilance Committee, Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Stride
Elizabeth "Long Liz" Stride ( Gustafsdotter; 27 November 1843 – 30 September 1888) is believed to have been the third victim of the unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper, who killed and mutilated at least five women in the Whitechapel and Spitalfields districts of London from late August to early November 1888. Unlike the other four canonical Ripper victims, Stride had not been mutilated following her murder, leading some historians to suspect Stride had not actually been murdered by Jack the Ripper. However, Stride's murder occurred less than one hour before the murder of the Ripper's fourth canonical victim, Catherine Eddowes, within walking distance, and her act of murder is suspected to have been disturbed by an individual entering the crime scene upon a two-wheeled cart. In addition, both women had been murdered by slash wounds to the throat, leading most authors and researchers to consider Stride to be the third of the Ripper's canonical five victims. Stride ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitechapel Murders
The Whitechapel murders were committed in or near the largely impoverished Whitechapel district in the East End of London between 3 April 1888 and 13 February 1891. At various points some or all of these eleven unsolved murders of women have been ascribed to the notorious unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper. Most, if not all, of the victims— Emma Elizabeth Smith, Martha Tabram, Mary Ann "Polly" Nichols, Annie Chapman, Elizabeth Stride, Catherine Eddowes, Mary Jane Kelly, Rose Mylett, Alice McKenzie, Frances Coles, and an unidentified woman—were prostitutes. Smith was sexually assaulted and robbed by a gang. Tabram was stabbed 39 times. Nichols, Chapman, Stride, Eddowes, Kelly, McKenzie and Coles had their throats cut. Eddowes and Stride were murdered on the same night, within approximately an hour and less than a mile apart; their murders are known as the "double event", after a phrase in a postcard sent to the press by an individual claiming to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slum Clearance In The United Kingdom
Slum clearance in the United Kingdom has been used as an urban renewal strategy to transform low income settlements with poor reputation into another type of development or housing. Early mass clearances took place in the country's northern cities. Starting from 1930, councils were expected to prepare plans to clear slum dwellings, although progress stalled upon the onset of World War II. Clearance of slum areas resumed and increased after the war, while the 1960s saw the largest number of house renewal schemes pursued by local authorities, particularly in Manchester where it was reported around 27% 'may' have been unfit for human habitation - Although the majority were well built solid structures which could have been renovated or repurposed; housing, churches, schools and pubs which formed close-knit communities were devastated, with families dispersed across other areas. Towards the end of the decade, a housing act in 1969 provided financial encouragement for authorities and la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Madox Brown
Ford Madox Brown (16 April 1821 – 6 October 1893) was a British painter of moral and historical subjects, notable for his distinctively graphic and often William Hogarth, Hogarthian version of the Pre-Raphaelite style. Arguably, his most notable painting was ''Work (painting), Work'' (1852–1865). Brown spent the latter years of his life painting the twelve works known as ''The Manchester Murals'', depicting History of Manchester, Mancunian history, for Manchester Town Hall. Early life Brown was the grandson of the medical theorist John Brown (physician, born 1735), John Brown, founder of the Brunonian system of medicine. His great-grandfather was a Scottish labourer. His father Ford Brown served as a purser in the Royal Navy, including a period serving under Sir Isaac Coffin, 1st Baronet, Sir Isaac Coffin and a period on HMS Arethusa (1781), HMS ''Arethusa''. He left the Navy after the end of the Napoleonic Wars. In 1818, Ford Brown married Caroline Madox, of an ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitalfields
Spitalfields is a district in the East End of London and within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The area is formed around Commercial Street (on the A1202 London Inner Ring Road) and includes the locale around Brick Lane, Christ Church, Toynbee Hall and Commercial Tavern. It has several markets, including Spitalfields Market, the historic Old Spitalfields Market, Brick Lane Market and Petticoat Lane Market. It was part of the ancient parish of Stepney in the county of Middlesex and was split off as a separate parish in 1729. Just outside the City of London, the parish became part of the Metropolitan Board of Works area in 1855 as part of the Whitechapel District. It formed part of the County of London from 1889 and was part of the Metropolitan Borough of Stepney from 1900. It was abolished as a civil parish in 1921. Toponymy The name Spitalfields appears in the form ''Spittellond'' in 1399; as ''The spitel Fyeld'' on the "Woodcut" map of London of c.1561; and as ''Spy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Lodging-house
"Common lodging-house" is a Victorian era term for a form of cheap accommodation in which inhabitants are lodged together in one or more rooms in common with the rest of the lodgers, who are not members of one family, whether for eating or sleeping. The slang term flophouse is roughly the equivalent of common lodging-houses. The nearest modern equivalent is a hostel. There was no statutory definition of the class of houses in England intended to be included in the expression common lodging-house, but the definition used above was adopted to include those houses which, under the Public Health Act 1875 and other legislation, must be registered and inspected. The provisions of the Public Health Act were that every urban and rural district council must keep registers showing the names and residences of the keepers of all common lodging-houses in their districts, the location of every such house, and the number of lodgers authorized by them. The scandalous condition of the common lodgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenterground
A tenterground, tenter ground or teneter-field was an area used for drying newly manufactured cloth after fulling. The wet cloth was hooked onto frames called "tenters" and stretched taut using "tenter hooks", so that the cloth would dry flat and square. It is from this process that some have the expression "on tenterhooks", meaning in a state of nervous tension. There were tentergrounds wherever cloth was made, and as a result the word "tenter" is found in place names throughout the United Kingdom and its empire, for example several streets in Spitalfields, London and Tenterfield House in Haddington, East Lothian, Scotland, which in turn gave its name to Tenterfield in New South Wales, Australia. London The Spitalfields Tenterground was established in the 17th century by Flemish weavers, who were Huguenot refugees fleeing religious persecution. Their weaving industry led to the area becoming a centre of the garment industry (the rag trade as it became known colloquially) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
.png)