|
Flotation (other)
Flotation (also spelled floatation) involves phenomena related to the relative buoyancy of objects. The term may also refer to: *Flotation (archaeology), a method for recovering very small artefacts from excavated sediments *Flotation (shares), an initial public offering of stocks or shares in a company *Floating exchange rate – changing policy to make a fixed currency have a floating rate may be called 'flotation'. *Flotation, any material added to the hull of a watercraft to keep the hull afloat *Flotation, the ability (as of a tire or snowshoes) to stay on the surface of soft ground or snow *"Floatation", a 1990 electronic music song by The Grid *Flotation process, in process engineering, a method for the separation of mixtures **Dissolved air flotation (DAF), a water treatment process **Froth flotation, a process for separating hydrophobic from hydrophilic materials **Induced gas flotation, a water treatment process that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the remova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
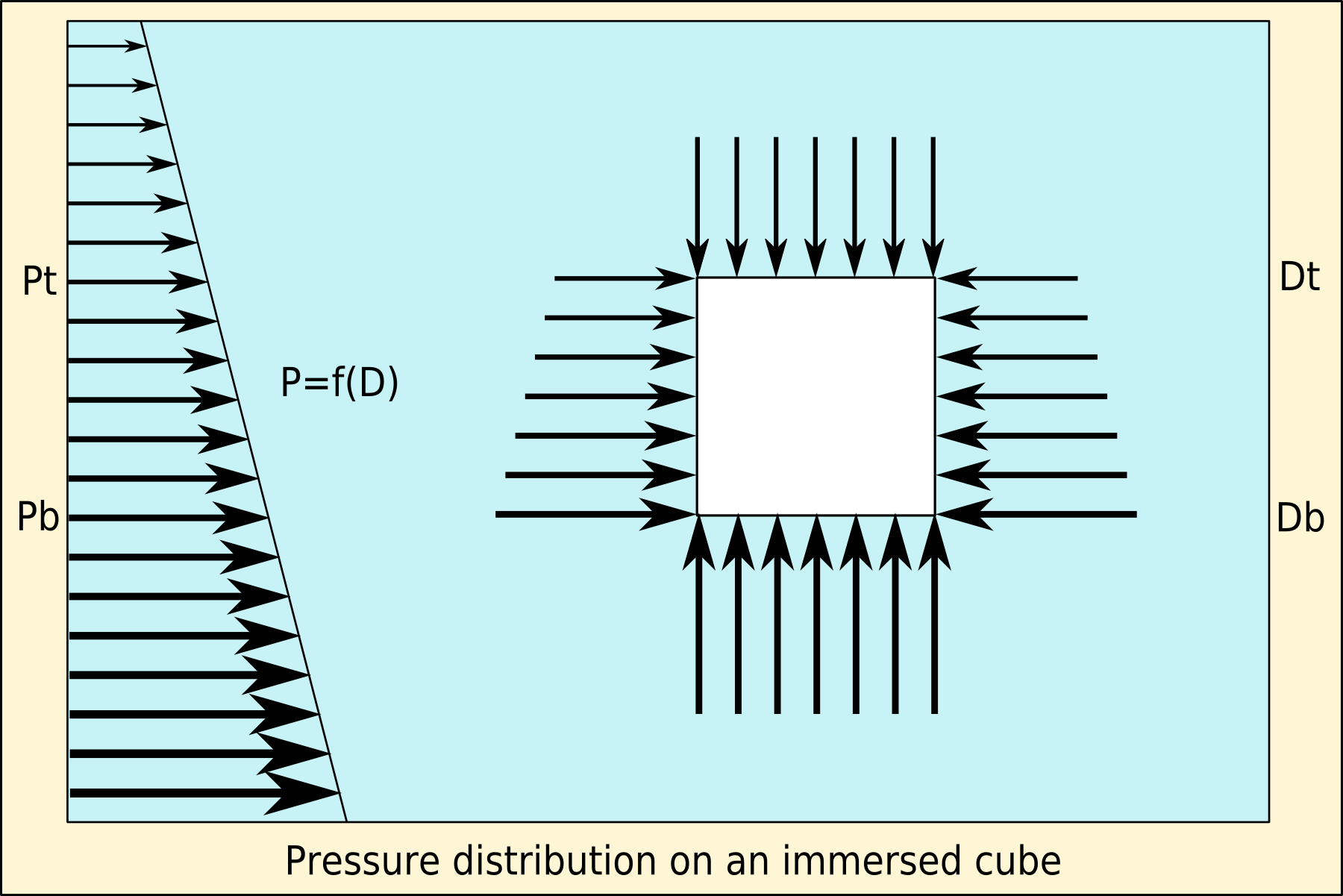
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flotation (archaeology)
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains. A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also * Outline of archaeology * Table of years in archaeology * Glossary of history References Bibliography * * * * * * * External links About.com Archaeology Glossary {{Glossaries of science and engineering Archaeology Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flotation (shares)
An initial public offering (IPO) or stock launch is a public offering in which shares of a company are sold to institutional investors and usually also to retail (individual) investors. An IPO is typically underwritten by one or more investment banks, who also arrange for the shares to be listed on one or more stock exchanges. Through this process, colloquially known as ''floating'', or ''going public'', a privately held company is transformed into a public company. Initial public offerings can be used to raise new equity capital for companies, to monetize the investments of private shareholders such as company founders or private equity investors, and to enable easy trading of existing holdings or future capital raising by becoming publicly traded. After the IPO, shares are traded freely in the open market at what is known as the free float. Stock exchanges stipulate a minimum free float both in absolute terms (the total value as determined by the share price multiplied by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating Exchange Rate
In macroeconomics and economic policy, a floating exchange rate (also known as a fluctuating or flexible exchange rate) is a type of exchange rate regime in which a currency's value is allowed to fluctuate in response to foreign exchange market events. A currency that uses a floating exchange rate is known as a ''floating currency'', in contrast to a ''fixed currency'', the value of which is instead specified in terms of material goods, another currency, or a set of currencies (the idea of the last being to reduce currency fluctuations). In the modern world, most of the world's currencies are floating, and include the most widely traded currencies: the United States dollar, the euro, the Swiss franc, the Indian rupee, the pound sterling, the Japanese yen, and the Australian dollar. However, even with floating currencies, central banks often participate in markets to attempt to influence the value of floating exchange rates. The Canadian dollar most closely resembles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline. General features There is a wide variety of hull types that are chosen for suitability for different usages, the hull shape being dependent upon the needs of the design. Shapes range from a nearly perfect box in the case of scow barges to a needle-sharp surface of revolution in the case of a racing multihull sailboat. The shape is chosen to strike a balance between cost, hydrostatic considerations (accommodation, load carrying, and stability), hydrodynamics (speed, power requirements, and motion and behavior in a seaway) and special considerations for the ship's role, such as the rounded bow of an icebreaker or the flat bottom of a landing craft. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Grid
The Grid is an English electronic dance group, consisting of David Ball (formerly of Soft Cell) and Richard Norris, with guest contributions from other musicians. They are best known for the hits "Swamp Thing", "Texas Cowboys", "Crystal Clear", "Rollercoaster" and "Floatation". Band members * Richard Norris – keyboards, drum programming * David Ball – keyboards, programming * Sacha Rebecca Souter – vocals History The Grid formed in 1988, after both Ball and Norris had worked with Psychic TV on the ''Jack the Tab – Acid Tablets Volume One'' album. They recorded the track "Meet Every Situation Head On" together as "M.E.S.H.". The Grid had their first success with their debut single, "Floatation", released on East West Records in 1990. They went on to release a string of ten UK hit singles and four albums, and toured the UK, Europe, Asia and Australia. The group's 1994 album '' Evolver'' reached No. 14 in the UK Albums Chart. The lead single from this album, "Swamp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flotation Process
Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, where it was one of the great enabling technologies of the 20th century. It has been described as "the single most important operation used for the recovery and upgrading of sulfide ores". The development of froth flotation has improved the recovery of valuable minerals, such as copper- and lead-bearing minerals. Along with mechanized mining, it has allowed the economic recovery of valuable metals from much lower grade ore than previously. Industries Froth flotation is applied to a wide range of separations. An estimated 1B tons of materials are processed in this manner annually. Mineral processing Froth flotation is a process for separating minerals from gangue by exploiting differences in their hydrophobicity. Hydrophobicity differenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolved Air Flotation
Dissolved air flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the removal of suspended matter such as oil or solids. The removal is achieved by dissolving air in the water or wastewater under pressure and then releasing the air at atmospheric pressure in a flotation tank basin. The released air forms tiny bubbles which adhere to the suspended matter causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where it may then be removed by a skimming device. Dissolved air flotation is very widely used in treating the industrial wastewater effluents from oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical plants, natural gas processing plants, paper mills, general water treatment and similar industrial facilities. A very similar process known as '' induced gas flotation'' is also used for wastewater treatment. ''Froth flotation'' is commonly used in the processing of mineral ores. In the oil industry, '' dissolved gas flotation'' (DGF) unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Froth Flotation
Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, where it was one of the great enabling technologies of the 20th century. It has been described as "the single most important operation used for the recovery and upgrading of sulfide ores". The development of froth flotation has improved the recovery of valuable minerals, such as copper- and lead-bearing minerals. Along with mechanized mining, it has allowed the economic recovery of valuable metals from much lower grade ore than previously. Industries Froth flotation is applied to a wide range of separations. An estimated 1B tons of materials are processed in this manner annually. Mineral processing Froth flotation is a process for separating minerals from gangue by exploiting differences in their hydrophobicity. Hydrophobicity diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Gas Flotation
Induced gas flotation (IGF) is a water treatment process that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the removal of suspended matter such as oil or solids. The removal is achieved by injecting gas bubbles into the water or wastewater in a flotation tank or basin. The small bubbles adhere to the suspended matter causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where it may then be removed by a skimming device. Induced gas flotation is very widely used in treating the industrial wastewater effluents from oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical plants, natural gas processing plants and similar industrial facilities. A very similar process known as '' dissolved air flotation'' is also used for waste water treatment. ''Froth flotation'' is commonly used in the processing of mineral ores. IGF units in the oil industry do not use air as the flotation medium due to the explosion risk. These IGF units use natural gas or nitrogen to create the bubbles. Process descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolation Tank
An isolation tank, sensory deprivation tank, float tank, float pod, float cabin, flotation tank, or sensory attenuation tank is a water filled, pitch-black, light-proof, soundproof environment heated to the same temperature as the skin, developed in 1954 by John C. Lilly. Flotation tanks are widely advertised as a form of alternative medicine but beneficial health effects are unproven. Method The tank is filled with 10 inches of water which contains enough dissolved Epsom salt to create a specific gravity of approximately 1.25–1.26. This environment allows an individual to float effortlessly on the surface of the water. History The isolation tank was developed in 1954 by John C. Lilly, a medical practitioner and neuropsychiatrist. During his training in psychoanalysis at the US National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), Lilly experimented with sensory deprivation. Widespread commercial interest and use of the isolation tank did not occur until 1972, when Glenn Perry, a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_model_Biosow-FB2.jpg)

