|
Florisbad Skull
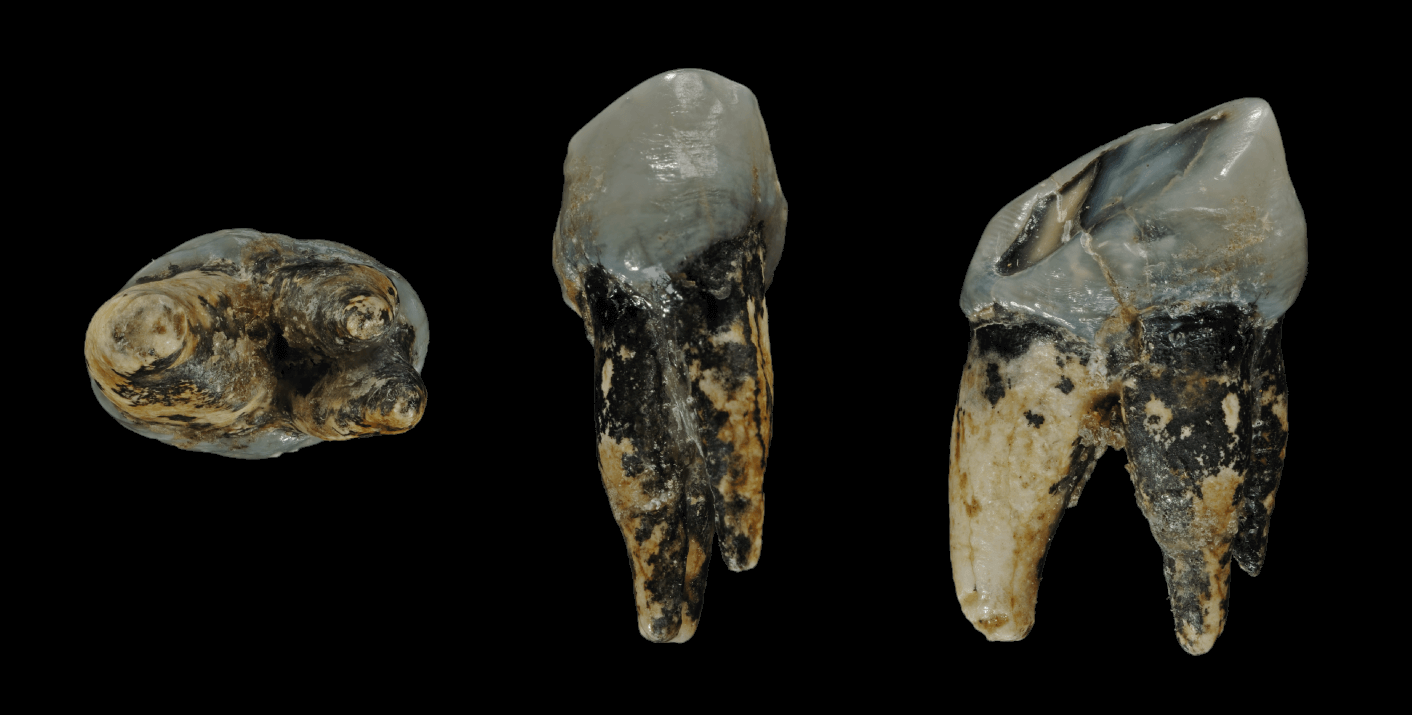
The Florisbad Skull is an important human fossil of the early Middle Stone Age, representing either late ''Homo heidelbergensis'' or early ''Homo sapiens''. It was discovered in 1932 by T. F. Dreyer at the Florisbad site, Free State Province, South Africa. Classification The Florisbad Skull was classified as ''Homo (Africanthropus) helmei'' by Dreyer (1935), after the sponsor of Dreyer's expedition, R. E. Helme. The ''Africanthropus'' generic name proposed by Dreyer was taken up by Weinert (1938) to refer to early African human fossils. In a note to Dreyer's 1935 publication, C. U. Ariëns Kappers mentioned the close resemblance of the fossil to ''Homo sapiens fossilis'' (Cro-Magnon Man). M. R. Drennan (1935, 1937) emphasized resemblance to ''Homo neanderthalensis'', proposing his classification as ''Homo florisbadensis (helmei)''. A. Galloway (1937) proposed classification as ''Homo sapiens'', specifically noting a resemblance to modern Australoids. Commentators of the 1950s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus '' Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chris Stringer
Christopher Brian Stringer (born 1947) is a British physical anthropologist noted for his work on human evolution. Biography Growing up in a working-class family in the East End of London, Stringer's interest in anthropology began in primary school, where he undertook a project on Neanderthals. Stringer studied anthropology at University College London, holds a PhD in Anatomical Science and a DSc in Anatomical Science (both from Bristol University). Stringer joined the permanent staff of the Natural History Museum in 1973. He is currently Research Leader in Human Origins. Research Stringer is one of the leading proponents of the recent African origin hypothesis or ″Out of Africa″ theory, which hypothesizes that modern humans originated in Africa over 100,000 years ago and replaced, in some way, the world's archaic humans, such as '' Homo floresiensis'' and Neanderthals, after migrating within and then out of Africa to the non-African world within the last 50,000 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Fossils
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related to modern humans (depending on the species), most notably ''Homo erectus'' and ''Homo neanderthalensis''. The genus emerged with the appearance of ''Homo habilis'' just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus ''Paranthropus'', is probably sister to ''Australopithecus africanus'', which itself had previously split from the lineage of '' Pan'', the chimpanzees. ''Homo erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and, in several early migrations, spread throughout Africa (where it is dubbed ''Homo ergaster'') and Eurasia. It was likely that the first human species lived in a hunter-gatherer society and was able to control fire. An adaptive and successful species, ''Homo erectus'' persisted for more than a million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Natural History
The National Museum of Natural History is a natural history museum administered by the Smithsonian Institution, located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., United States. It has free admission and is open 364 days a year. In 2021, with 7.1 million visitors, it was the eighteenth most visited museum in the world and the second most visited natural history museum in the world after the Natural History Museum in London."The World's most popular museums", CNN.com, 22 June 2017. Opened in 1910, the museum on the National Mall was one of the first Smithsonian buildings constructed exclusively to hold the national collections and research facilities. The main building has an overall area of with of exhibition and public space and houses over 1,000 employees. The museum's collections contain over 145 million specimens of plants, animals, fossils, minerals, rocks, meteorites, human remains, and human cultural artifacts, the largest natural history collection in the world. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. Called "the nation's attic" for its eclectic holdings of 154 million items, the institution's 19 museums, 21 libraries, nine research centers, and zoo include historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in the District of Columbia. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York, and Virginia. More than 200 institutions and museums in 45 states,States without Smithsonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Evolution Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of hominin fossils and remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but show some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million years ago (extinction of ''Paranthropus''), all fossils sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedetes
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa. Species A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. They include: * South African springhare or ''springhaas'' (''Pedetes capensis'') * East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster'') * ''Pedetes laetoliensis'' (Davies, 1987) (Pliocene fossil) Throughout the 20th century, the living species (and occasionally the prehistoric one) were merged into ''P. capensis'', making the genus monotypic. Ecology These rodents are generally nocturnal and sleep through the day in burrows they dig. They feed on foliage, roots and other vegetable matter, and occasionally arthropods. Outside the burrow they usually move around by hopping on their hind legs. When only one springhare species was recognized, it was listed as vulnerable by the IUCN in 1996 due to an approximately 20% decrease in the populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Spin Resonance Dating
Electron spin resonance dating, or ESR dating, is a technique used to date materials which radiocarbon dating cannot, including minerals ( e.g., carbonates, silicates, sulphates), biological materials (e.g., tooth enamel), archaeological materials (e.g., ceramics) and food (e.g., potato chips). Electron spin resonance dating was first introduced to the science community in 1975, when Japanese nuclear physicist Motoji Ikeya dated a speleothem in Akiyoshi Cave, Japan. ESR dating measures the amount of unpaired electrons in crystalline structures that were previously exposed to natural radiation. The age of substance can be determined by measuring the dosage of radiation since the time of its formation. Applications Electron spin resonance dating is being used in fields like radiation chemistry, biochemistry, and as well as geology, archaeology, and anthropology. ESR dating is used instead of radiocarbon dating or radiometric dating because ESR dating can be applied on materials diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Spin Resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a method for studying materials that have unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but the spins excited are those of the electrons instead of the atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes and organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford. Theory Origin of an EPR signal Every electron has a magnetic moment and spin quantum number s = \tfrac , with magnetic components m_\mathrm = + \tfrac or m_\mathrm = - \tfrac . In the presence of an external magnetic field with strength B_\mathrm , the electron's magnetic moment aligns itself either antiparallel ( m_\mathrm = - \tfrac ) or parallel ( m_\mathrm = + \tfrac ) to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porotic Hyperostosis
Porotic hyperostosis, is a pathological condition that affects bones of the cranial vault, and is characterized by localized areas of spongy or porous bone tissue.El-Najjar M and Robertson Jr AL. 1976Spongy bones in prehistoric MARICOTAS.''Science'' Volume 193, Issue 4248, Pages 141-143. Retrieved on July 9, 2007. The diploë, or spongy tissue within the bones of the cranium, swells and the tissue of the outer surface becomes thinner and more porous in appearance.Angel JL. 1966.Porotic Hyperostosis, Anemias, Malarias, and Marshes in the Prehistoric Eastern Mediterranean.''Science'' Volume 153, Number 3737, Pages 760-763. Retrieved on July 9, 2007.Cule J and Evans IL. 1968Porotic hyperostosis and the Gelligaer skull ''Journal of Clinical Pathology'', Volume 21, Issue 6, Pages 753–758. Retrieved on July 9, 2007. This condition was widely accepted as a result of anemia, which is typically due to an iron deficient diet,Stuart-Macadam P. 1992 Porotic hyperostosis: a new perspective. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national "newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Communications
''Nature Communications'' is a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio since 2010. It is a multidisciplinary journal and it covers the natural sciences, including physics, chemistry, earth sciences, medicine, and biology. The journal has editorial offices in London, Berlin, New York City, and Shanghai. The founding editor-in-chief was Lesley Anson, followed by Joerg Heber, Magdalena Skipper, and Elisa De Ranieri. As of 2022, the editors are Nathalie Le Bot for health and clinical sciences, Stephane Larochelle for biological sciences, Enda Bergin for chemistry and biotechnology, and Prabhjot Saini for physics and earth sciences. Starting October 2014, the journal only accepted submissions from authors willing to pay an article processing charge. Until the end of 2015, part of the published submissions were only available to subscribers. In January 2016, all content became freely accessible. Starting from 2017, the journal offers a depositio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)