|
Florence And Cripple Creek Railroad
The Florence and Cripple Creek Railroad (F&CC) was a narrow-gauge railroad running northward from junctions with the Denver & Rio Grande Railroad at the mill towns of Florence and later moved to Cañon City, Colorado, on the banks of the Arkansas River, up steep and narrow Phantom Canyon to the Cripple Creek Mining District, west of Pikes Peak. It was founded in 1893 and went out of business in 1915 History Started in 1893, it was the first railroad to reach the new, booming mining district from the "outside world" and as a result it earned substantial profits in its first years. The railroad hauled people and goods into the mining district, and ore concentrates from the mines south for milling in either Florence, through a branch line to Canon City, or transfer to the D&RG for milling in Pueblo, Colorado. The F&CC's first main terminal was located in Victor, the "second city" of the district but its branch lines served many of the largest mines within the area. Ultimately, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide, Fremont County, Colorado
Adelaide, Colorado (formerly Robinson) is a former mining camp and railroad water stop along what is now known as Phantom Canyon Road in Fremont County, Colorado. The elevation of the ghost town is 6,950 feet (2,118 m). The Adelaide Bridge is located just north of the townsite. History Prior to the construction of the railroad bridge, the town was named "Robinson." A post office was established at Adelaide in 1894, and remained in operation until 1901. In 1894, the Adelaide Bridge was constructed as a 210-foot-long, 20-foot-wide narrow-gauge railroad passage for the Florence and Cripple Creek Railroad to carry gold mined in the region. The bridge and track were abandoned in 1912 and the railroad went out of business in 1915. The bridge was added to the National Register of Historic Places The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Belt Byway
The Gold Belt Tour Scenic and Historic Byway is a National Scenic Byway, a Back Country Byway, and a Colorado Scenic and Historic Byway located in Fremont and Teller counties, Colorado, USA. The byway is named for the Gold Belt mining region. The Cripple Creek Historic District is a National Historic Landmark. The byway forms a three-legged loop with the Phantom Canyon Road (narrow gravel), the Shelf Road (narrow unimproved), and the High Park Road (paved). Route The Gold Belt Byway contains many roads. Most of them are dirt roads that are narrow and run through canyons and other geological features. Phantom Canyon Road Phantom Canyon Road is a scenic road that connects Cañon City and Victor. The road goes through Phantom Canyon. The road has two tunnels and three elevated bridges. It has many camp locations. It was originally the route of a railroad that connected Florence and Cripple Creek. The route contains many narrow roads and high wooden bridges. The road is unpaved. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schenectady Locomotive Works
The Schenectady Locomotive Works built railroad locomotives from its founding in 1848 through its merger into American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in 1901. After the 1901 merger, ALCO made the Schenectady plant its headquarters in Schenectady, New York Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Yo .... One of the better-known locomotives to come out of the Schenectady shops was Central Pacific Railroad type 4-4-0 No. 60, the ''Jupiter (locomotive), Jupiter'' (built in September 1868), one of two steam locomotives to take part in the "Golden Spike Ceremony" to celebrate the completion of the First transcontinental railroad. Although the original was scrapped in 1909, a full-scale, operating replica was completed in 1979, and now is part of an operational display at the Golden Spike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the absence of trailing wheels. In the mid-19th century, this wheel arrangement became the second-most-popular configuration for new steam locomotives in the United States, where this type is commonly referred to as a ten-wheeler.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York, NY: Dover Publications. p. 57. As locomotives pulling trains of lightweight all-wood passenger cars from the 1890 to the 1920s, they were exceptionally stable at near speeds on the New York Central's New York-to-Chicago Water Level Route and on the Reading Railroad's line from Camden to Atlantic City, New Jersey. Overview Tender locomotives During the second half of the nineteenth and first half of the twentieth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
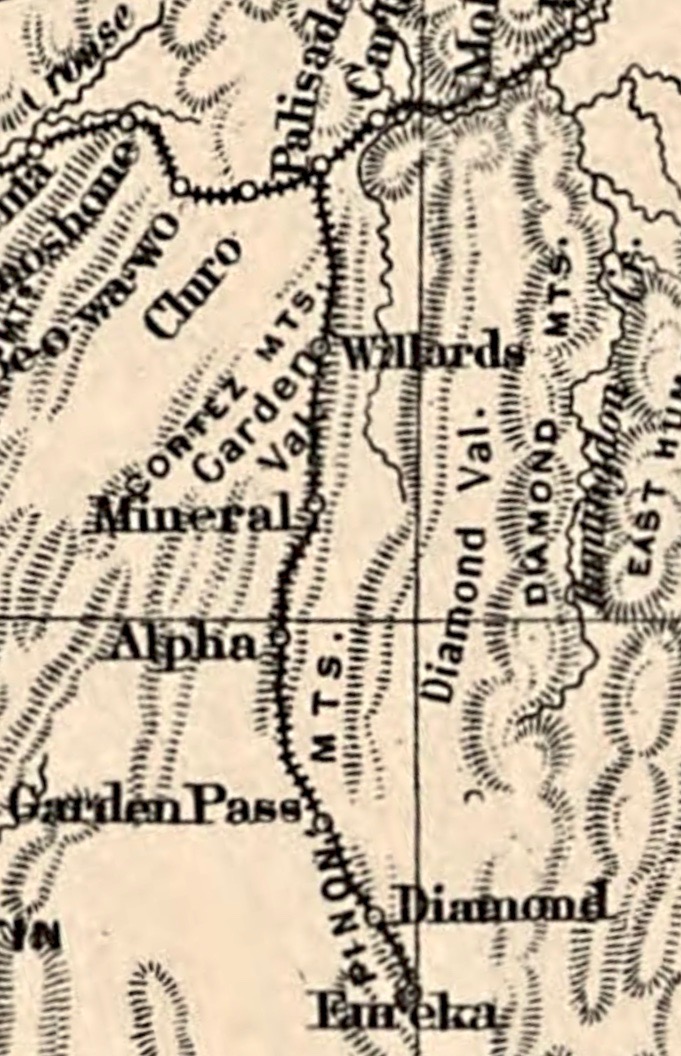
Eureka And Palisade Railroad
The Eureka & Palisade Railroad was a narrow gauge railroad constructed in 1873-1875 between Palisade and Eureka, Nevada, a distance of approximately . The railroad was constructed to connect Eureka, the center of a rich silver mining area, with the national railway network at Palisade. Later corporate reorganizations brought on by financial difficulties saw the line operated as the "Eureka and Palisade Railway" and the "Eureka Nevada Railway." The Eureka & Palisade Railroad was built in 1875 to carry silver-lead ore from Eureka, Nevada, to the Southern Pacific Railroad trunk line that ran through Palisade. Nevertheless, despite the determined and colorful management style of John Sexton, the line succumbed to the effects of flood, fire, competing road traffic, and dwindling amounts of ore extracted in Eureka. The rails and rolling stock of the last surviving narrow gauge railroad in Nevada were removed in 1938. The ''Eureka,'' one of the railroad's only surviving steam loco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uintah Railway
The Uintah Railway was a small narrow gauge railroad company in Utah and Colorado in the United States. It was constructed to carry Gilsonite which provided most of its operating revenues; but it operated as a common carrier from 1904 to 1939, also carrying passengers, mail, express, and other cargoes including sheep and wool. When a public library was built in Dragon in 1910, the Uintah Railway agreed to deliver library books free of charge to and from any borrower along its route. Many area ranchers and miners took advantage of the opportunity. Background The Uintah Basin includes seams of asphaltum remaining where petroleum from the Green River Formation oil shales seeped into fissures in the overlying sandstone where smaller hydrocarbon molecules were slowly evaporated or digested by aerobic microbes. The remaining large-molecular-weight hydrocarbons formed a lustrous black solid at ambient temperatures, resembling anthracite coal with a brownish dust. Following ignition, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denver And Rio Grande (film)
''Denver and Rio Grande'' is a 1952 American Technicolor Western film, directed by Byron Haskin and released by Paramount Pictures. The film is a dramatization of the building of the Denver and Rio Grande Railroad, which was chartered in 1870. It was filmed in the summer of 1951 on location on actual D&RG track (now the Durango and Silverton Narrow Gauge Railroad)This branch of the D&RG was used for filming of at least six movies, including the 1956 version of ''Around the World in 80 Days'' and '' Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid''. near Durango, Colorado.Agnew, Jeremy (2012). ''The Old West in Fact and Film: History Versus Hollywood''. McFarland & Company: Jefferson, North Carolina, , p.97 The film's storyline is a fictional account based on two factual right-of-way struggles in 1878-1879 between the D&RG and the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (here the Cañon City & San Juan RR The fictional CC&SJ bore the name of an actual company organized by the Santa Fe in 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden, Colorado
Golden is a home rule city that is the county seat of Jefferson County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 20,399 at the 2020 United States Census. Golden lies along Clear Creek at the base of the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains. Founded during the Pike's Peak Gold Rush on June 16, 1859, the mining camp was originally named Golden City in honor of Thomas L. Golden. Golden City served as the capital of the provisional Territory of Jefferson from 1860 to 1861, and capital of the official Territory of Colorado from 1862 to 1867. In 1867, the territorial capital was moved about east to Denver City. Golden is now a part of the Denver–Aurora–Lakewood, CO Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Front Range Urban Corridor. The Colorado School of Mines, offering programs in engineering and science, is located in Golden. In addition, it is also home to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, National Earthquake Information Center, Coors Brewing Company, CoorsTek, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado Railroad Museum
The Colorado Railroad Museum is a non-profit railroad museum. The museum is located on at a point where Clear Creek flows between North and South Table Mountains in Golden, Colorado. The museum was established in 1959 to preserve a record of Colorado's flamboyant railroad era, particularly the state's pioneering narrow-gauge mountain railroads. Facilities The museum building is a replica of an 1880s-style railroad depot. Exhibits feature original photographs by pioneer photographers such as William Henry Jackson and Louis Charles McClure, as well as paintings by Howard L Fogg, Otto Kuhler, Ted Rose and other artists. Locomotives and railroad cars modeled in the one inch scale by Herb Votaw are also displayed. A bay window contains a reconstructed depot telegrapher's office, complete with a working telegraph sounder. The lower level of the museum building contains an exhibition hall which features seasonal and traveling displays on railroading history. The lower level als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montana Southern Railway
The Montana Southern Railway, now defunct, was an American narrow gauge railroad constructed between Divide, Montana and the mining district of Coolidge, Montana. The short-lived line was noteworthy in that it was the last common carrier narrow gauge railroad to be constructed in the United States. History The Montana Southern Railway was largely the brainchild of William R. Allen, a politician and entrepreneur who had served as the lieutenant governor of Montana between 1909 and 1913. Allen was the president of the Boston-Montana Mining Company, which was developing a large silver-mining operation in the remote Pioneer Mountains of far southwestern Montana. Because of the site's remoteness and poor access, a railroad was considered to be a necessary component of the mining district's development. The railway was first incorporated in 1914 as the "Southern Montana Railway." Construction of the line began in earnest in 1917 after the company was reincorporated as the Montana S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chama, New Mexico
Chama is a village in Rio Arriba County, New Mexico, United States. The population was 1,022 at the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. The village is located in the Rocky Mountains about south of the Colorado-New Mexico border. Geography Chama is located at (36.894777, -106.584406), on the Rio Chama (Rio Grande), Rio Chama, south of the Colorado border. According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , all of it land. History Chama is the western terminus of the Cumbres and Toltec Scenic Railroad, a steam-driven, narrow gauge heritage railway which carries visitors to and from Osier, Colorado, and Antonito, Colorado, during the summer months. It is the remaining 64 mile portion of the Denver & Rio Grande Railroad's San Juan Extension built in the 1880s between Alamosa, Colorado, and Durango, Colorado. The route was abandoned in the late 1960s and the tracks from Chama westward to Durango were torn up soon afterwards. File:C&TS Chama Depot 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbres And Toltec Scenic Railroad
The Cumbres and Toltec Scenic Railroad, often abbreviated as the C&TSRR, is a narrow-gauge heritage railroad that operates on of track between Antonito, Colorado, and Chama, New Mexico, in the United States. The railroad is named for two geographical features along the route: the -high Cumbres Pass and the Toltec Gorge. Originally part of the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad's narrow-gauge network, the line has been jointly owned by the states of Colorado and New Mexico since 1970. Today, the C&TSRR is one of only two remaining parts of the former D&RGW narrow-gauge network, the other being the Durango and Silverton Narrow Gauge Railroad (D&SNG), which runs between the communities of Durango and Silverton, Colorado. The railroad has a total of ten narrow-gauge steam locomotives (six of which are operational) and two narrow-gauge diesel locomotives on its current roster. The railroad also operates two smaller former D&RGW steam locomotives, Nos. 315 and 168, for special eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |