|
Flight Instruments
Flight instruments are the instruments in the cockpit of an aircraft that provide the pilot with data about the flight situation of that aircraft, such as altitude, airspeed, vertical speed, heading and much more other crucial information in flight. They improve safety by allowing the pilot to fly the aircraft in level flight, and make turns, without a reference outside the aircraft such as the horizon. Visual flight rules (VFR) require an airspeed indicator, an altimeter, and a compass or other suitable magnetic direction indicator. Instrument flight rules (IFR) additionally require a gyroscopic pitch-bank (artificial horizon), direction (directional gyro) and rate of turn indicator, plus a slip-skid indicator, adjustable altimeter, and a clock. Flight into instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) require radio navigation instruments for precise takeoffs and landings. The term is sometimes used loosely as a synonym for cockpit instruments as a whole, in which context it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slingsby
Slingsby may refer to: * Slingsby (surname) * Slingsby, North Yorkshire * Slingsby Aviation Slingsby Aviation was a British aircraft manufacturer based in Kirkbymoorside, North Yorkshire, England. The company was founded to design and build gliders and sailplanes. From the early 1930s to around 1970 it built over 50% of all British ..., formerly Slingsby Sailplanes, a manufacturer of gliders and other aircraft * Slingsby Channel, a strait in the Queen Charlotte Strait region of the Central Coast of British Columbia, Canada * Slingsby Baronets * HC Slingsby PLC, a historical British company started in 1893 {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitot-static System
A pitot-static system is a system of pressure-sensitive instruments that is most often used in aviation to determine an aircraft's airspeed, Mach number, altitude, and altitude trend. A pitot-static system generally consists of a pitot tube, a static port, and the pitot-static instruments. Other instruments that might be connected are air data computers, flight data recorders, altitude encoders, cabin pressurization controllers, and various airspeed switches. Errors in pitot-static system readings can be extremely dangerous as the information obtained from the pitot static system, such as altitude, is potentially safety-critical. Several commercial airline disasters have been traced to a failure of the pitot-static system. Pitot-static pressure The pitot-static system of instruments uses the principle of air pressure gradient. It works by measuring pressures or pressure differences and using these values to assess the speed and altitude. These pressures can be measured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Speed Indicator
In aviation, a variometer – also known as a rate of climb and descent indicator (RCDI), rate-of-climb indicator, vertical speed indicator (VSI), or vertical velocity indicator (VVI) – is one of the flight instruments in an aircraft used to inform the pilot of the rate of descent or climb.Federal Aviation Administration, ''Glider Flying Handbook'', Skyhorse Publishing Inc., 2007 pages 4-7 and 4-8 It can be calibrated in metres per second, feet per minute (1 ft/min = 0.00508 m/s) or knots (1 kn ≈ 0.514 m/s), depending on country and type of aircraft. It is typically connected to the aircraft's external static pressure source. In powered flight, the pilot makes frequent use of the VSI to ascertain that level flight is being maintained, especially during turning maneuvers. In gliding, the instrument is used almost continuously during normal flight, often with an audible output, to inform the pilot of rising or sinking air. It is usual for gliders to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flap (aeronautics)
A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the stalling speed of an aircraft wing at a given weight. Flaps are usually mounted on the wing trailing edges of a fixed-wing aircraft. Flaps are used to reduce the take-off distance and the landing distance. Flaps also cause an increase in drag so they are retracted when not needed. The flaps installed on most aircraft are partial-span flaps; spanwise from near the wing root to the inboard end of the ailerons. When partial-span flaps are extended they alter the spanwise lift distribution on the wing by causing the inboard half of the wing to supply an increased proportion of the lift, and the outboard half to supply a reduced proportion of the lift. Reducing the proportion of the lift supplied by the outboard half of the wing is accompanied by a reduction in the angle of attack on the outboard half. This is beneficial because it increases the margin above the stall of the outboard half, maintaining aileron effectiveness and redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Airspeed
The true airspeed (TAS; also KTAS, for ''knots true airspeed'') of an aircraft is the speed of the aircraft relative to the air mass through which it is flying. The true airspeed is important information for accurate navigation of an aircraft. Traditionally it is measured using an analogue TAS indicator, but as the Global Positioning System has become available for civilian use, the importance of such air-measuring instruments has decreased. Since ''indicated'', as opposed to ''true'', airspeed is a better indicator of margin above the stall, true airspeed is not used for controlling the aircraft; for these purposes the indicated airspeed – IAS or KIAS (knots indicated airspeed) – is used. However, since indicated airspeed only shows true speed through the air at standard sea level pressure and temperature, a TAS meter is necessary for navigation purposes at cruising altitude in less dense air. The IAS meter reads very nearly the TAS at lower altitude and at lower s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicated Airspeed
Indicated airspeed (IAS) is the airspeed of an aircraft as measured by its pitot-static system and displayed by the airspeed indicator (ASI). This is the pilots' primary airspeed reference. This value is not corrected for installation error, instrument error, or the actual encountered air density, being instead calibrated to always reflect the adiabatic compressible flow of the International Standard Atmosphere at sea level. It uses the difference between total pressure and static pressure, provided by the system, to either mechanically or electronically measure dynamic pressure. The dynamic pressure includes terms for both density and airspeed. Since the airspeed indicator cannot know the density, it is by design calibrated to assume the sea level standard atmospheric density when calculating airspeed. Since the actual density will vary considerably from this assumed value as the aircraft changes altitude, IAS varies considerably from true airspeed (TAS), the relative vel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
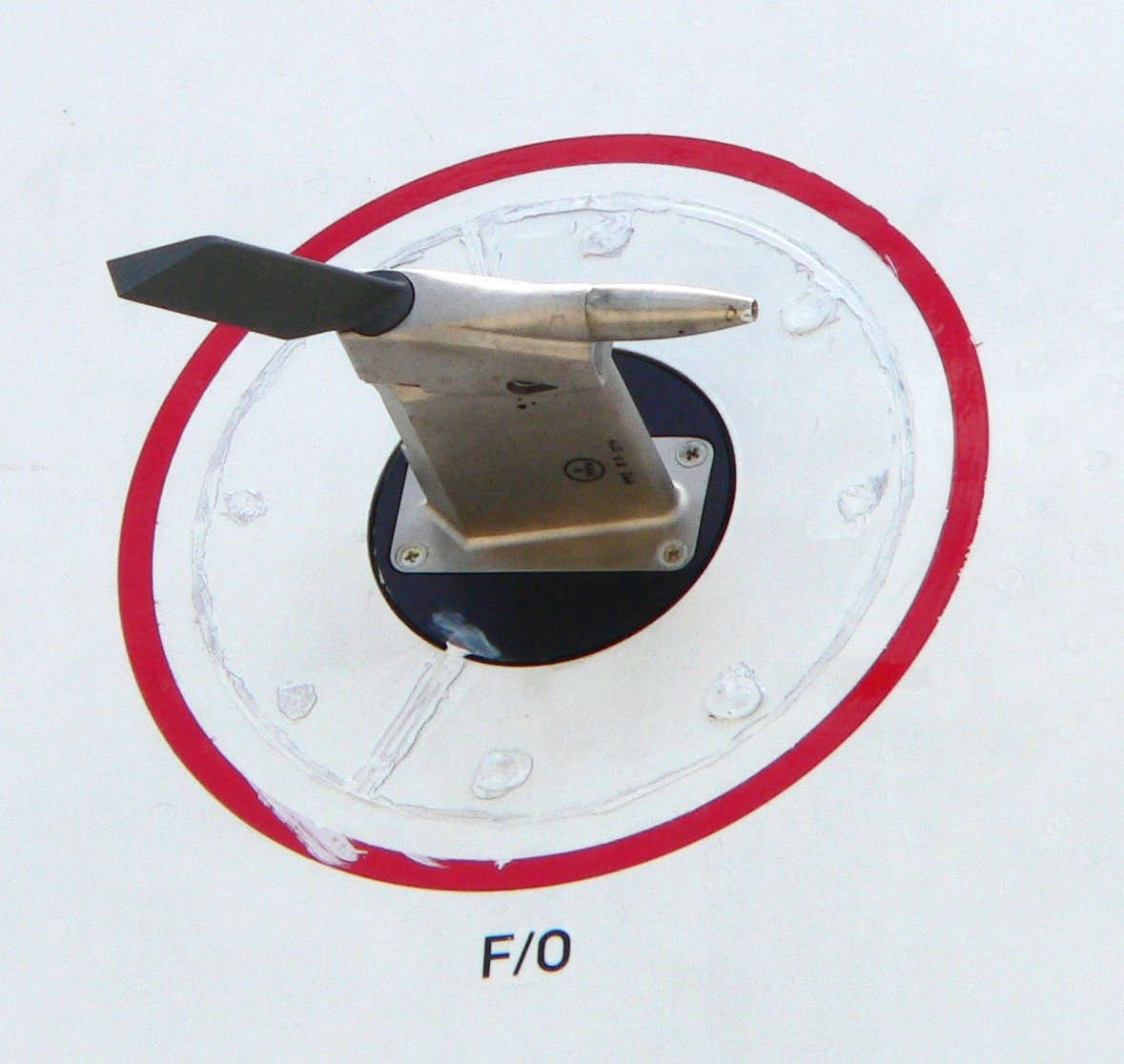
Pitot Tube
A pitot ( ) tube (pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by a French engineer, Henri Pitot, in the early 18th century, and was modified to its modern form in the mid-19th century by a French scientist, Henry Darcy. It is widely used to determine the airspeed of aircraft; the water speed of boats; and the flow velocity of liquids, air, and gases in industry. Theory of operation The basic pitot tube consists of a tube pointing directly into the fluid flow. As this tube contains fluid, a pressure can be measured; the moving fluid is brought to rest (stagnates) as there is no outlet to allow flow to continue. This pressure is the stagnation pressure of the fluid, also known as the total pressure or (particularly in aviation) the pitot pressure. The measured stagnation pressure cannot itself be used to determine the fluid flow velocity (airspeed in aviation). However, Bernoulli's equation states: :Stagnation pressure = static pressure + dynamic pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (unit)
The knot () is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly (approximately or ). The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ( IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). The knot is a non- SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour. Definitions ;1 international knot = :1 nautical mile per hour (by definition), : (exactly), : (approximately), : (approximately), : (approximately) : (approximately). The length of the internationally agreed nautical mile is . The US adopted the international definition in 1954, having previously used the US nautical mile (). The UK adopted the international nautical mile definition in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspeed Indicator
The airspeed indicator (ASI) or airspeed gauge is a flight instrument indicating the airspeed of an aircraft in kilometers per hour (km/h), knots (kn), miles per hour (MPH) and/or meters per second (m/s). The recommendation by ICAO is to use km/h, however knots is currently the most used unit. The ASI measures the pressure differential between static pressure from the static port, and total pressure from the pitot tube. This difference in pressure is registered with the ASI pointer on the face of the instrument. Color-coded speeds and ranges The ASI has standard color-coded markings to indicate safe operation within the limitations of the aircraft. At a glance, the pilot can determine a recommended speed (V speeds) or if speed adjustments are needed. Single and multi-engine aircraft have common markings. For instance, the green arc indicates the normal operating range of the aircraft, from ''V''S1 to ''V''NO. The white arc indicates the flap operating range, ''V'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inches Of Mercury
Inch of mercury (inHg and ″Hg) is a non- SI unit of measurement for pressure. It is used for barometric pressure in weather reports, refrigeration and aviation in the United States. It is the pressure exerted by a column of mercury in height at the standard acceleration of gravity. Conversion to metric units depends on the temperature of mercury, and hence its density; typical conversion factors are: In older literature, an "inch of mercury" is based on the height of a column of mercury at .Barry N. Taylor, ''Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI),'' 1995, NIST Special Publication 811, Appendix /ref> :1 inHg60 °F = In Imperial units: 1 inHg60 °F = 0.489 771 Pounds per square inch, psi, or 2.041 771 inHg60 °F = 1 psi. Applications Aircraft and automobiles Aircraft altimeters measure the relative pressure difference between the lower ambient pressure at altitude and a calibrated reading on the ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (unit)
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI), and is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is defined as one newton per square metre and is equivalent to 10 barye (Ba) in the CGS system. The unit of measurement called standard atmosphere (atm) is defined as 101,325 Pa. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Canada these reports are given in k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Pressure
In fluid mechanics the term static pressure has several uses: * In the design and operation of aircraft, ''static pressure'' is the air pressure in the aircraft's static pressure system. * In fluid dynamics, many authors use the term ''static pressure'' in preference to just ''pressure'' to avoid ambiguity. Often however, the word ‘static’ may be dropped and in that usage pressure is the same as static pressure at a nominated point in a fluid. * The term ''static pressure'' is also used by some authors in fluid statics. Static pressure in design and operation of aircraft An aircraft's static pressure system is the key input to its altimeter and, along with the pitot pressure system, also drives the airspeed indicator. The static pressure system is open to the aircraft's exterior through a small opening called the static port, which allows sensing the ambient atmospheric pressure at the altitude at which the aircraft is flying. In flight, the air pressure varies slightl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |