|
Flight Deck Cruiser
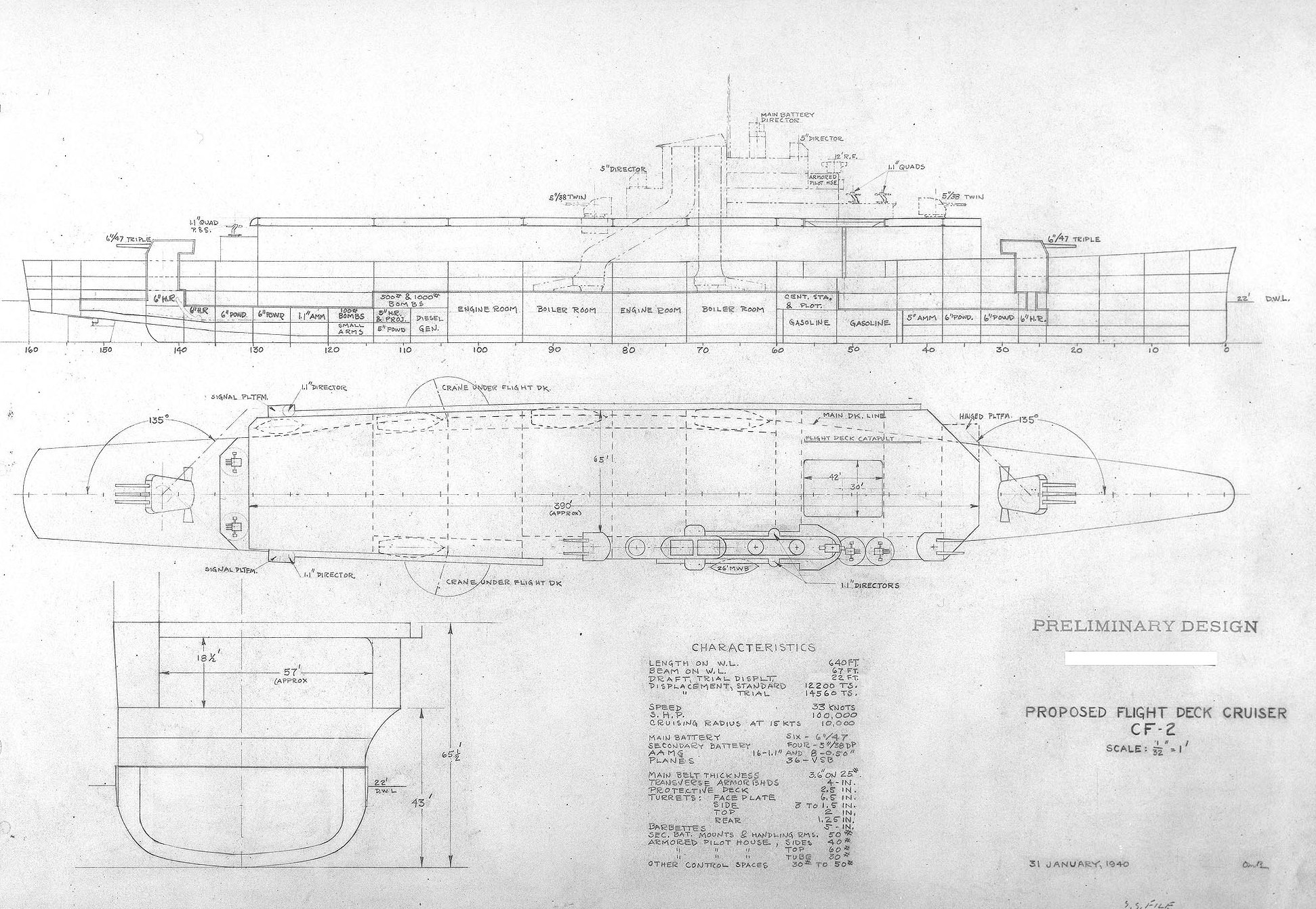
The flight-deck cruiser was a proposed type of aircraft cruiser, (warships combining features of aircraft carriers and light cruisers), designed by the United States Navy during the period between World War I and World War II. Several designs were proposed for the type, but none was approved for construction. The final design was developed just before World War II, and the entry of the United States into the war saw the project come to an end. Background In the 1920s, following the signing of the Washington Naval Treaty, the United States Navy converted two incomplete battlecruisers into aircraft carriers, and . These conversions proved to be extremely expensive, and designs were sought that would provide aircraft carrying capability for the fleet at a more reasonable cost.Adcock 1996, p.4. , America's first purpose-built aircraft carrier, was of a smaller, more economical design than the battlecruiser conversions, however the ship sacrificed the big-gun scouting capability of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Deck Cruiser Design CF-2 31 Jan 1940
Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere (i.e. air flight or aviation) or through the vacuum of outer space (i.e. spaceflight). This can be achieved by generating aerodynamic lift associated with gliding or propulsive thrust, aerostatically using buoyancy, or by ballistic movement. Many things can fly, from animal aviators such as birds, bats and insects, to natural gliders/parachuters such as patagial animals, anemochorous seeds and ballistospores, to human inventions like aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, airships, balloons, etc.) and rockets which may propel spacecraft and spaceplanes. The engineering aspects of flight are the purview of aerospace engineering which is subdivided into aeronautics, the study of vehicles that travel through the atmosphere, and astronautics, the study of vehicles that travel through space, and ballistics, the study of the flight of projectil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval War College
The Naval War College (NWC or NAVWARCOL) is the staff college and "Home of Thought" for the United States Navy at Naval Station Newport in Newport, Rhode Island. The NWC educates and develops leaders, supports defining the future Navy and associated roles and missions, supports combat readiness, and strengthens global maritime partnerships. The Naval War College is one of the senior service colleges including the Army War College, the Marine Corps War College, and the USAF Air War College. Additionally, the U.S. Department of Defense operates the National War College. History The college was established on October 6, 1884; its first president, Commodore Stephen B. Luce, was given the old building of the Newport Asylum for the Poor to house it on Coasters Harbor Island in Narragansett Bay. Among the first four faculty members were Tasker H. Bliss, a future Army Chief of Staff, James R. Soley, the first civilian faculty member and a future Assistant Secretary of the Navy, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Carriers Of The United States
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called '' aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abandoned Military Projects Of The United States
Abandon, abandoned, or abandonment may refer to: Common uses * Abandonment (emotional), a subjective emotional state in which people feel undesired, left behind, insecure, or discarded * Abandonment (legal), a legal term regarding property ** Child abandonment, the extralegal abandonment of children ** Lost, mislaid, and abandoned property, legal status of property after abandonment and rediscovery * Abandonment (mysticism) Art, entertainment, and media Film * Abandon (film), ''Abandon'' (film), a 2002 film starring Katie Holmes * Abandoned (1949 film), ''Abandoned'' (1949 film), starring Dennis O'Keefe * Abandoned (1955 film), ''Abandoned'' (1955 film), the English language title of the Italian war film ''Gli Sbandati'' * Abandoned (2001 film), ''Abandoned'' (2001 film), a Hungarian film * Abandoned (2010 film), ''Abandoned'' (2010 film), starring Brittany Murphy * Abandoned (2015 film), ''Abandoned'' (2015 film), a television movie about the shipwreck of the ''Rose-Noëlle'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Cruiser Vittorio Veneto (550)
''Vittorio Veneto'' was a helicopter cruiser that served with the Italian Navy. Originally intended to be a class of two ships specifically designed for anti-submarine warfare (ASW), only ''Vittorio Veneto'' entered into service in 1969, its sister ship ''Italia'' being cancelled. ''Vittorio Veneto'' was decommissioned in 2003. This ship has the same general layout as the smaller helicopter cruisers, but with two elevators in the flight deck and the hangar below, rather than with the hangar as part of the superstructure. It was named for the decisive Battle of Vittorio Veneto which ended World War I on the Italian front. History Although the ''Andrea Doria''-class helicopter cruisers proved a useful addition to the fleet, it was judged that a larger ship was necessary. Such a vessel would be able operate a larger airwing and provide helicopter support in bad weather conditions. These considerations led to the ''Vittorio Veneto'' class, of which two ships were originally planned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
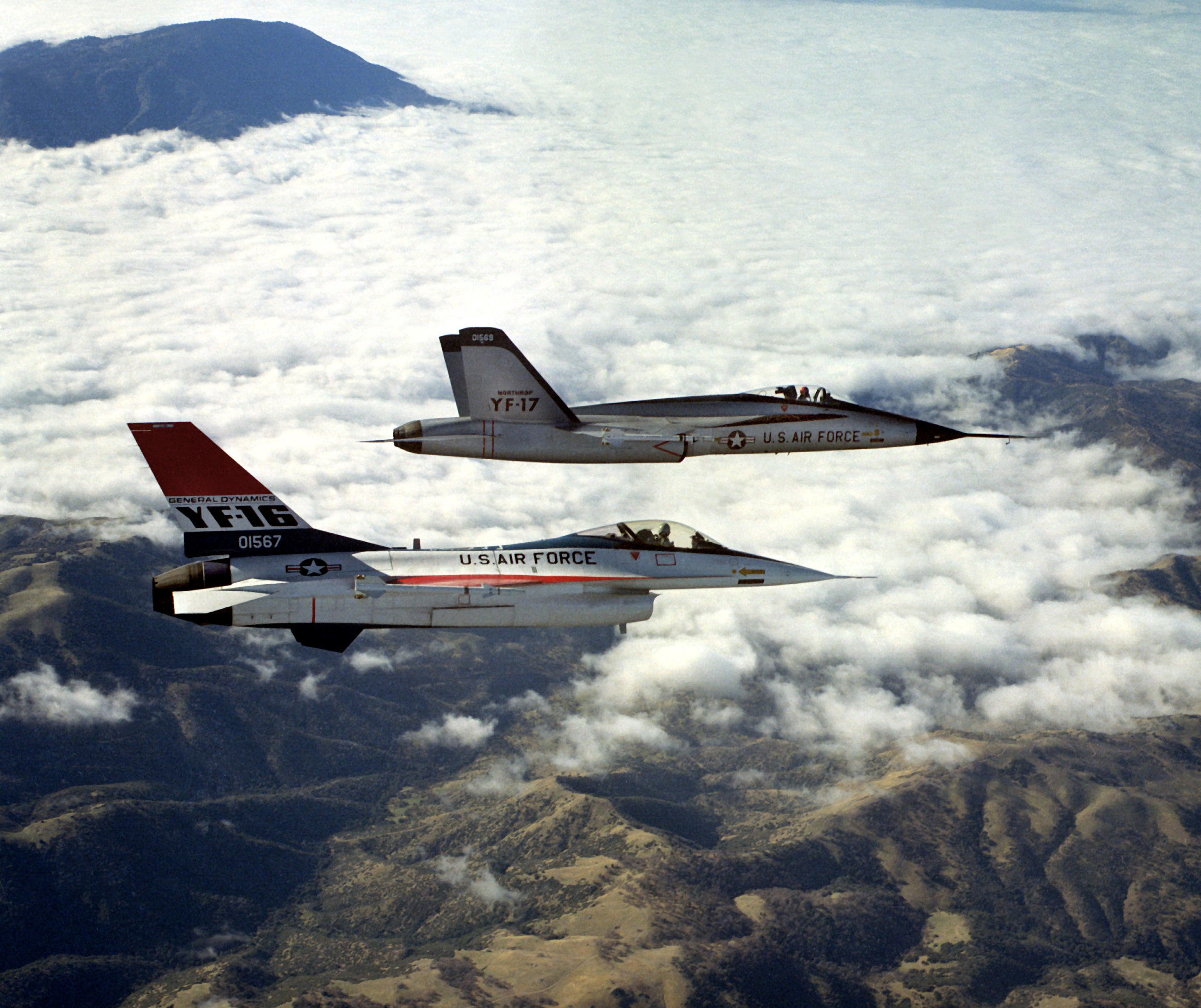
McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet
The McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet is an all-weather, twin-engine, supersonic, carrier-capable, multirole combat aircraft, designed as both a fighter and attack aircraft (hence the F/A designation). Designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing) and Northrop (now part of Northrop Grumman), the F/A-18 was derived from the latter's YF-17 in the 1970s for use by the United States Navy and Marine Corps. The Hornet is also used by the air forces of several other nations, and formerly by the U.S. Navy's Flight Demonstration Squadron, the Blue Angels. The F/A-18 was designed to be a highly versatile aircraft due to its avionics, cockpit displays, and excellent aerodynamic characteristics, with the ability to carry a wide variety of weapons. The aircraft can perform fighter escort, fleet air defense, suppression of enemy air defenses, air interdiction, close air support, and aerial reconnaissance. Its versatility and reliability have proven it to be a valuable carrier ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings (magazine)
''Proceedings'' is a 96-page monthly magazine published by the United States Naval Institute. Launched in 1874, it is one of the oldest continuously published magazines in the United States. ''Proceedings'' covers topics concerning global security and includes articles from military professionals and civilian experts, historical essays, book reviews, full-color photography, and reader commentary. Roughly a third are written by active-duty personnel, a third by retired military, and a third by civilians. ''Proceedings'' also frequently carries feature articles by Secretaries of Defense, Secretaries of the Navy, Chairmen of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and top leaders of the Navy, Marine Corps and Coast Guard. Notable contributors Over the decades many notable names have contributed articles to Proceedings either early in their careers or when they reached the upper echelons of leadership, and in many cases, both. * Tom Clancy, best-selling author of techno-thrillers such as The Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
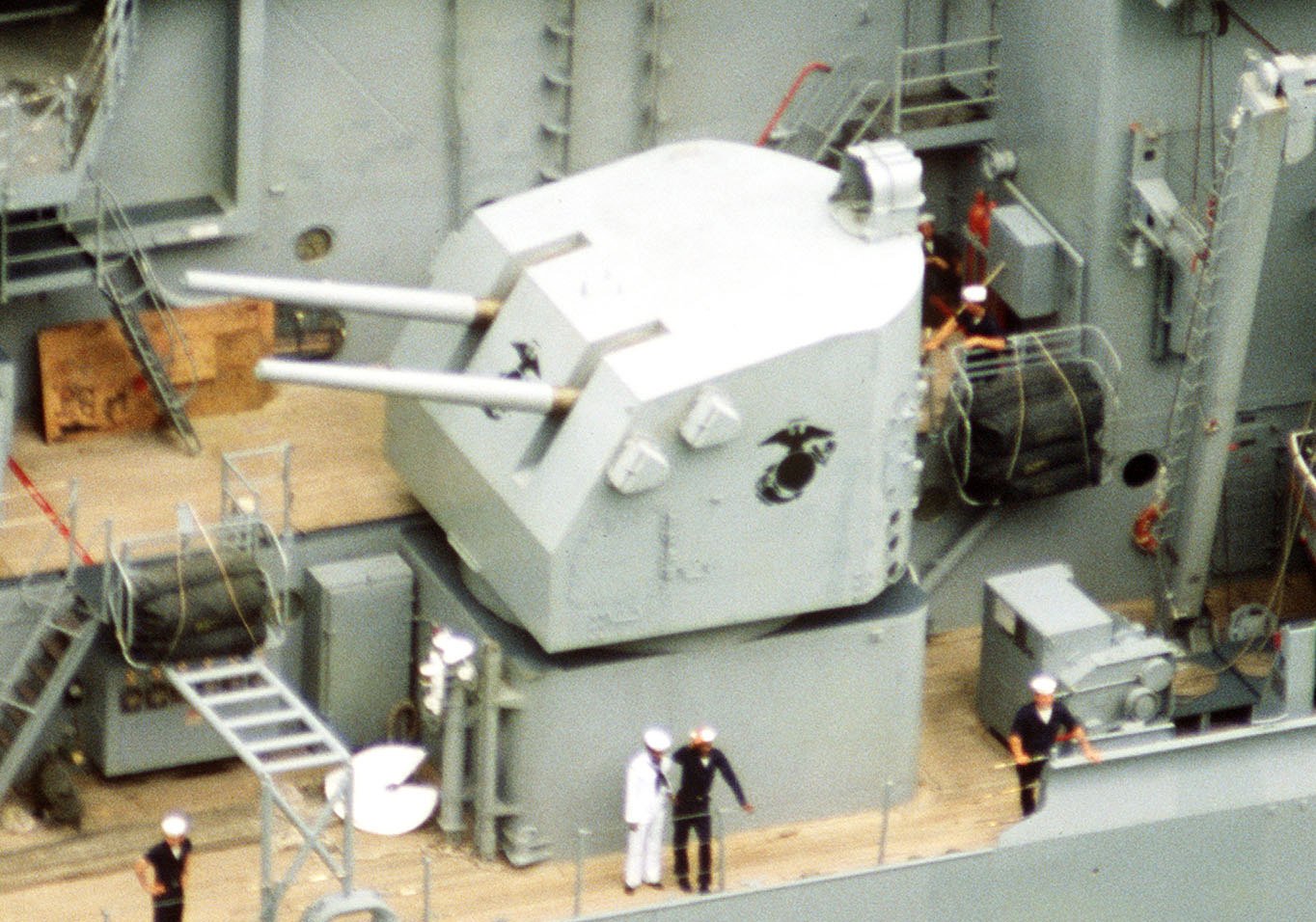
Iowa-class Battleship
The ''Iowa'' class was a class of six fast battleships ordered by the United States Navy in 1939 and 1940. They were initially intended to intercept fast capital ships such as the Japanese while also being capable of serving in a traditional battle line alongside slower battleships and act as its "fast wing". The ''Iowa'' class was designed to meet the Second London Naval Treaty's "escalator clause" limit of standard displacement. Four vessels, , , , and , were completed; two more, and , were laid down but canceled in 1945 and 1958, respectively, before completion, and both hulls were scrapped in 1958–1959. The four ''Iowa''-class ships were the last battleships commissioned in the US Navy. All older US battleships were decommissioned by 1947 and stricken from the ''Naval Vessel Register'' (NVR) by 1963. Between the mid-1940s and the early 1990s, the ''Iowa''-class battleships fought in four major US wars. In the Pacific Theater of World War II, they served primarily as fas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-ship Missile
An anti-ship missile (AShM) is a guided missile that is designed for use against ships and large boats. Most anti-ship missiles are of the sea skimming variety, and many use a combination of inertial guidance and active radar homing. A good number of other anti-ship missiles use infrared homing to follow the heat that is emitted by a ship; it is also possible for anti-ship missiles to be guided by radio command all the way. The first anti-ship missiles, which were developed and built by Nazi Germany, used radio command guidance.https://airandspace.si.edu/collection-objects/bomb-guided-fritz-x-x-1/nasm_A19840794000#:~:text=The%20Fritz%20X%2C%20also%20known,the%20Henschel%20Hs%20293%20missile. These saw some success in the Mediterranean Theatre during 1943–44, sinking or heavily damaging at least 31 ships with the Henschel Hs 293 and more than seven with the ''Fritz X'', including the Italian battleship ''Roma'' and the light cruiser . A variant of the HS 293 had a TV ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Of Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, just before 8:00a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the US-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
