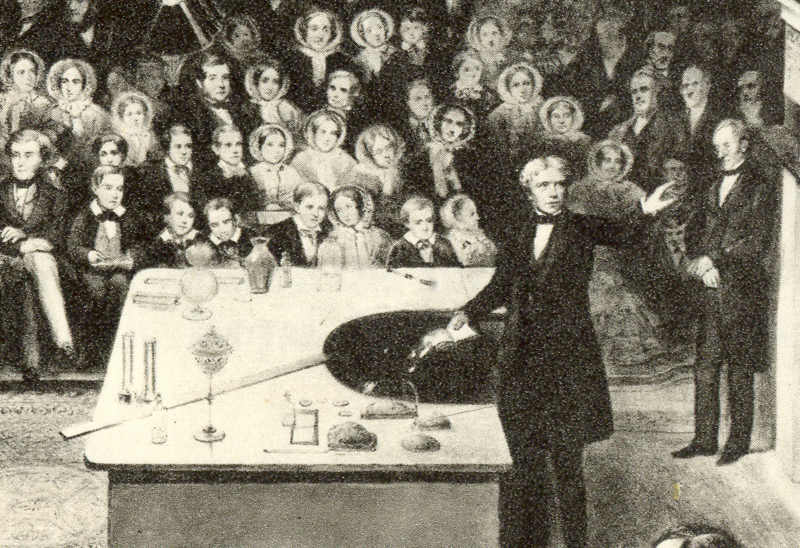|
First World Alliance
The First World Alliance was founded in 1977 by Kefa Nephthys (Lucille Jones) and Bill Jones. They met with Dr. Yosef Ben-Jochannan, aka “Dr. Ben,” after seeing him on Gil Noble's '' Like It Is'', which was televised on ABC in New York City. They are quoted as saying that Dr. Ben gave them some books to read. After reading the books they started meeting with Dr. Ben for a Saturday study group. After studying with Dr. Ben they started the First World Alliance as a community education forum. They would invite various guest scholars and speakers to the forum, which became a weekly forum on Saturdays, as a service to the community known as the First World Alliance at Mt Zion Lutheran Church at 421 West 145th Street in New York City. Kefa Nephthys Jones, in an interview with the Amsterdam News, is quoted as saying, “When people have knowledge-of-self, they gain power-of-self … then they realize who they are, what they can do and what they have done in the past". The First World A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yosef Ben-Jochannan
Yosef Alfredo Antonio Ben-Jochannan (; December 31, 1918 – March 19, 2015), referred to by his admirers as "Dr. Ben", was an American writer and historian. He was considered to be one of the more prominent Afrocentricism, Afrocentric scholars by some Black Nationalism, Black Nationalists, while most mainstream scholars, such as Mary Lefkowitz,''History Lesson'', pp. 67–69. dismissed him because of the basic historical inaccuracies in his work, as well as disputes about the authenticity of his educational degrees and academic credentials.Gabriel Haslip-Viera, ''TaĂno revival: critical perspectives on Puerto Rican identity and cultural politics'', (Markus Wiener Publishers: 2001), p. 14. Early life and education Ben-Jochannan stated that he was born in Ethiopia to a History of the Jews in Puerto Rico, Puerto Rican Jewish mother and an Beta Israel, Ethiopian Jewish father. Other sources say that he "was probably Puerto Rican but claimed to be of Ethiopian Jewish extraction." A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frances Cress Welsing
Frances Luella Welsing (née Cress; March 18, 1935 – January 2, 2016) was an American psychiatrist and well-known proponent of the Black supremacist melanin theory. Her 1970 essay, ''The Cress Theory of Color-Confrontation and Racism (White Supremacy)'', offered her interpretation of what she described as the origins of white supremacy culture. She was the author of ''The Isis Papers: The Keys to the Colors'' (1991). Early life Welsing was born Frances Luella Cress in Chicago on March 18, 1935. Her father, Henry N. Cress, was a physician, and her mother, Ida Mae Griffen, was a teacher. In 1957, she earned a B.S. degree at Antioch College and in 1962 received an M.D. at Howard University. In the 1960s, Welsing moved to Washington, D.C. and worked at many hospitals, especially children's hospitals. While Welsing was an assistant professor at Howard University she formulated her first body of work in 1969, ''The Cress Theory of Color-Confrontation'' and self-published it in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1977 Establishments In New York City
Events January * January 8 – Three bombs explode in Moscow within 37 minutes, killing seven. The bombings are attributed to an Armenian separatist group. * January 10 – Mount Nyiragongo erupts in eastern Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo). * January 17 ** 49 marines from the and are killed as a result of a collision in Barcelona harbour, Spain. * January 18 ** Scientists identify a previously unknown bacterium as the cause of the mysterious Legionnaires' disease. ** Australia's worst railway disaster at Granville, a suburb of Sydney, leaves 83 people dead. ** SFR Yugoslavia Prime minister Džemal Bijedić, his wife and 6 others are killed in a plane crash in Bosnia and Herzegovina. * January 19 – An Ejército del Aire CASA C-207C Azor (registration T.7-15) plane crashes into the side of a mountain near Chiva, on approach to Valencia Airport in Spain, killing all 11 people on board. * January 20 – Jimmy Carter is sworn in as the 39th President of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African-American History In New York City
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of enslaved Africans who are from the United States. While some Black immigrants or their children may also come to identify as African-American, the majority of first generation immigrants do not, preferring to identify with their nation of origin. African Americans constitute the second largest racial group in the U.S. after White Americans, as well as the third largest ethnic group after Hispanic and Latino Americans. Most African Americans are descendants of enslaved people within the boundaries of the present United States. On average, African Americans are of West/ Central African with some European descent; some also have Native American and other ancestry. According to U.S. Census Bureau data, African immigrants generally do not self- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post–civil Rights Era In African-American History
In African-American history, the post–civil rights era is defined as the time period in the United States since Congressional passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Voting Rights Act of 1965, and the Fair Housing Act of 1968, major federal legislation that ended legal segregation, gained federal oversight and enforcement of voter registration and electoral practices in states or areas with a history of discriminatory practices, and ended discrimination in renting or buying housing. Politically, African Americans have made substantial strides in the post–civil rights era. Civil rights leader Jesse Jackson ran for the Democratic Party's presidential nomination in 1984 and 1988, attracting more African Americans into politics and unprecedented support and leverage for people of colour in politics. In 2008, Barack Obama was elected as the first President of the United States of African descent. In the same period, African Americans have suffered disproportionate unemployment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Organizations Based In The United States
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided into formal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecture Series
A public lecture (also known as an open lecture) is one means employed for educating the public in the arts and sciences. The Royal Institution has a long history of public lectures and demonstrations given by prominent experts in the field. In the 19th century, the popularity of the public lectures given by Sir Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution was so great that the volume of carriage traffic in Albemarle Street caused it to become the first one-way street in London. The Royal Institution's Christmas Lectures for young people are nowadays also shown on television. Alexander von Humboldt delivered a series of public lectures at the University of Berlin in the winter of 1827–1828, that formed the basis for his later work ''Kosmos''. Besides public lectures, public autopsies have been important in promoting knowledge of medicine. The public autopsy of Dr. Johann Gaspar Spurzheim, advocate of phrenology, was conducted after his death, and his brain, skull, and heart were remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos Wilson
Amos Nelson Wilson (February 23, 1941 (or 1940) — January 14, 1995) was an African-American theoretical psychologist, social theorist, Pan-African thinker, scholar, author and a professor of psychology at the City University of New York.Our Time Press, ''Dr. Amos Wilson: Why We Do The Things We Do'', February 26, 201/ref> Early life and education Born in Hattiesburg, Mississippi, in 1940 or 1941, Wilson completed his undergraduate degree at the Morehouse College in Atlanta, Georgia, master's degree at The New School of Social Research, and attained a PhD degree from Fordham University in New York. Wilson worked as a psychologist, social caseworker, supervising probation officer and as a training administrator in the New York City Department of Juvenile Justice. As an academic, Wilson also taught at City University of New York from 1981 to 1986 and at the College of New Rochelle from 1987 to 1995. Views on power and racism According to AALBC.com, "Wilson believed that the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gil Noble
Gilbert Edward "Gil" Noble (February 22, 1932 – April 5, 2012) was an American television reporter and interviewer. He was the producer and host of New York City television station WABC-TV's weekly show '' Like It Is'', originally co-hosted with Melba Tolliver. The program focused primarily on issues concerning African Americans and those within the African diaspora. He was born in Harlem, New York, and raised by his parents who were Jamaican immigrants Gil and Iris Noble. After graduating from the City College of New York he worked for Union Carbide. Broadcast journalism career In 1962 he got his professional break into broadcast media when he was hired as a part-time announcer at WLIB radio. He began reading and reporting newscasts. Noble joined WABC-TV in July 1967 as a reporter, after reporting on the 1967 Newark riots. Starting in January 1968 he became an anchor of its Saturday and Sunday night newscasts. He became host of ''Like It Is'' a few months prior to the rebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asa Hilliard
Asa G. Hilliard III (August 22, 1933 – August 13, 2007), also known as Nana Baffour Amankwatia II, was an African-American professor of educational psychology who worked on indigenous ancient African history (ancient Egyptian), culture, education and society. He was the Fuller E. Callaway Professor of Urban Education at Georgia State University, with joint appointments in the Department of Education Policy Studies and the Department of Educational Psychology and Special Education. Prior to his position at Georgia State, Hilliard served as the Dean of the School of Education at San Francisco State University in San Francisco, California. Career In 1981, Hilliard introduced the concept of " Baseline Essays" (short stories "of the experience of a particular geo-cultural group within a particular academic area from earliest times to the present to the Portland, Oregon school district. This resulted in a collection of essays advocating Afrocentrism, authored by "six scholarsknown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard D
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", "Rich", "Rick", "Rico", "Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) * Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |