|
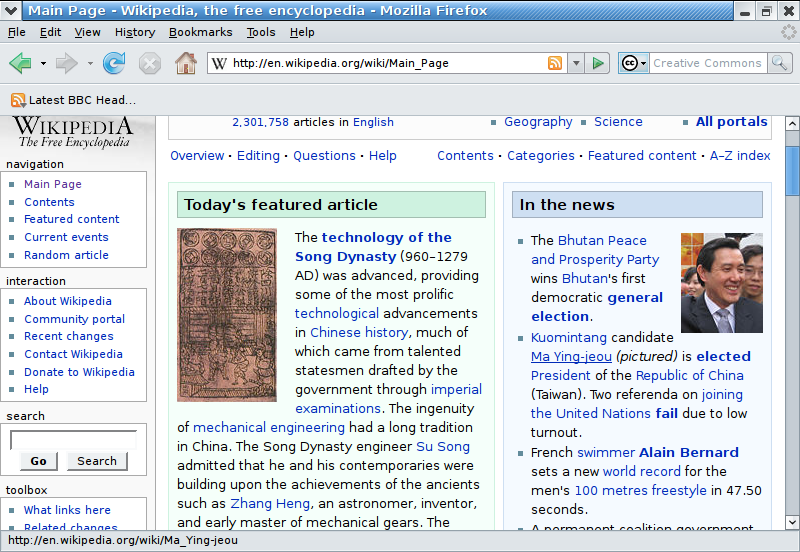
Firefox 3
Mozilla Firefox 3.0 is a version of the Firefox web browser released on June 17, 2008, by the Mozilla Corporation. Firefox 3.0 uses version 1.9 of the Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages. This version fixes many bugs, improves standards compliance, and implements many new web APIs compared to Firefox 2.0. Other new features include a redesigned download manager, a new "Places" system for storing bookmarks and history, and separate themes for different operating systems. Firefox 3.0 had over 8 million unique downloads the day it was released, and by July 2008 held over 5.6% of the recorded usage share of web browsers. Estimates of Firefox 3.0's global market share were generally in the range of 4–5%, and then dropped as users migrated to Firefox 3.5 and later Firefox 3.6. Partially as a result of this, between mid-December 2009 and the end of January 2010, Firefox 3.5 was the most popular browser (when counting individual browser versions), passing Internet Explor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefox 3
Mozilla Firefox 3.0 is a version of the Firefox web browser released on June 17, 2008, by the Mozilla Corporation. Firefox 3.0 uses version 1.9 of the Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages. This version fixes many bugs, improves standards compliance, and implements many new web APIs compared to Firefox 2.0. Other new features include a redesigned download manager, a new "Places" system for storing bookmarks and history, and separate themes for different operating systems. Firefox 3.0 had over 8 million unique downloads the day it was released, and by July 2008 held over 5.6% of the recorded usage share of web browsers. Estimates of Firefox 3.0's global market share were generally in the range of 4–5%, and then dropped as users migrated to Firefox 3.5 and later Firefox 3.6. Partially as a result of this, between mid-December 2009 and the end of January 2010, Firefox 3.5 was the most popular browser (when counting individual browser versions), passing Internet Explor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozilla Firefox Wordmark
Mozilla (stylized as moz://a) is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, spreads and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting exclusively free software and open standards, with only minor exceptions. The community is supported institutionally by the non-profit Mozilla Foundation and its tax-paying subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. Mozilla's current products include the Firefox web browser, Thunderbird e-mail client (now through a subsidiary), Bugzilla bug tracking system, Gecko layout engine, Pocket "read-it-later-online" service, and others. History On January 23, 1998, Netscape made two announcements. First, that Netscape Communicator would be free; second, that the source code would also be free. One day later, Jamie Zawinski from Netscape registered . The project took its name "Mozilla", after the original code name of the Netscape Navigator browser—a portmanteau of " Mosaic and Godzi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Explorer 7
Windows Internet Explorer 7 (IE7) (codenamed Rincon) is a web browser for Windows. It was released by Microsoft on October 18, 2006, as the seventh version of Internet Explorer and the successor to Internet Explorer 6. Internet Explorer 7 is part of a long line of versions of Internet Explorer and was the first major update to the browser since 2001. It was the default browser in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 (later default was Internet Explorer 9), as well as Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 (later default was Internet Explorer 8), and can replace Internet Explorer 6 on Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, but unlike version 6, this version does not support Windows ME or earlier versions of Windows. It also does not support Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2 or later Windows Versions. Internet Explorer 7 requires Windows XP SP2 or Windows Server 2003 SP1 at the minimum. It is the last version of Internet Explorer to support Windows XP x64 Edition RTM and Windows Server 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usage Share Of Web Browsers
The usage share of web browsers is the portion, often expressed as a percentage, of visitors to a group of web sites that use a particular web browser. Accuracy Measuring browser usage in the number of requests (page hits) made by each user agent can be misleading. Overestimation Not all requests are generated by a user, as a user agent can make requests at regular time intervals without user input. In this case, the user's activity might be overestimated. Some examples: * Certain anti-virus products fake their user agent string to appear to be popular browsers. This is done to trick attack sites that might display clean content to the scanner, but not to the browser.'' The Register'' reported in June 2008 that traffic from AVG Linkscanner, using an IE6 user agent string, outstripped human link clicks by nearly 10 to 1. * A user who revisits a site shortly after changing or upgrading browsers may be double-counted under some methods; overall numbers at the time of a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme (computing)
In computing, a theme is a preset package containing graphical appearance and functionality details. A theme usually comprises a set of shapes and colors for the graphical control elements, the window decoration and the window. Themes are used to customize the look and feel of a piece of computer software or of an operating system. Usage Themes are often used to change the look and feel of a wide range of things at once, which makes them much less granular than allowing the user to set each option individually. For example, users might want the window-borders from a particular theme, but installing it would also alter the desktop background. One method for dealing with this is to allow the user to select which parts of the theme they want to load; for example in Windows 98, users could load the background and screensaver from a theme, but leave the icons and sounds untouched. Themed systems Operating systems ; :Microsoft Windows first supported themes in Windows 95 as a separ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browsing History
Web browsing history refers to the list of web pages a user has visited, as well as associated metadata such as page title and time of visit. It is usually stored locally by web browsers in order to provide the user with a history list to go back to previously visited pages. It can reflect the user's interests, needs, and browsing habits.Du, Weidman, Zhenyu Cheryl Qian, Paul Parsons, Yingjie Victor Chen. 2018. “Personal Web Library: organizing and visualizing Web browsing history”. ''International Journal of Web Information Systems'' 14(2): 212-232. All major browsers have a private browsing mode in which browsing history is not recorded. This is to protect against browsing history being collected by third parties for targeted advertising or other purposes. Applications Local history Locally stored browsing history can facilitate rediscovering lost previously visited web pages of which one only has a vague memory in mind, or pages difficult to find due to being located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bookmark (World Wide Web)
In the context of the World Wide Web, a bookmark is a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) that is stored for later retrieval in any of various storage formats. All modern web browsers include bookmark features. Bookmarks are called favorites or Internet shortcuts in Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge, and by virtue of that browser's large market share, these terms have been synonymous with ''bookmark'' since the First Browser War. Bookmarks are normally accessed through a menu in the user's web browser, and folders are commonly used for organization. In addition to bookmarking methods within most browsers, many external applications offer bookmark management. Bookmarks have been incorporated in browsers since the ViolaWWW browser in 1992, and Mosaic browser in 1993. Bookmark lists were called ''Hotlists'' in Mosaic and in previous versions of Opera; this term has faded from common use. Cello, another early browser, also had bookmarking features. With the advent of social book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Download Manager
A download manager is a software tool that manages the download, downloading of computer file, files from the Internet, which may be built: into a Web browser, or as a, usually more sophisticated Application software, program. Data transmission Download managers, {{Software-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefox 2
Mozilla Firefox 2 is a version of Firefox, a web browser released on October 24, 2006 by the Mozilla Corporation. Firefox 2 uses version 1.8 of the Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages. The release contained many new features not found in Firefox 1.5, including improved support for Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) and JavaScript 1.7, as well as user interface changes. On March 22, 2006, the first alpha version of Firefox 2 (Bon Echo Alpha 1) was released. It featured Gecko 1.8.1 for the first time. Mozilla Firefox 2.0.0.20 is the final version to support Windows NT 4.0, Windows 98 and Windows Me, although it can run on Windows 95 and Windows NT 3.51 using tweaks. Mac OS X 10.5 support was added October 18, 2007 with version 2.0.0.8. Firefox 2.0 featured updates to tabbed browsing environment, the extensions manager, the GUI, and the find, search, and software update engines; a new session restore feature; inline spell checking; and an anti-phishing feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build or use such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into the software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |