|
Firebox (steam Engine)
In a steam engine, the firebox is the area where the fuel is burned, producing heat to boil the water in the boiler. Most are somewhat box-shaped, hence the name. The hot gases generated in the firebox are pulled through a rack of tubes running through the boiler. Steam locomotive fire tube firebox In the standard steam locomotive fire-tube boiler, the firebox is surrounded by water space on five sides. The bottom of the firebox is open to atmospheric pressure, but covered by fire grates (solid fuel) or a firing pan (liquid fuel). If the engine burns solid fuel, like wood or coal, there is a grate covering most of the bottom of the firebox to hold the fire. An ashpan, mounted underneath the firebox and below the grates, catches and collects hot embers, ashes, and other solid combustion waste as it falls through the grates. In a coal-burning locomotive, the grates may be shaken to clean dead ash from the bottom of the fire. They are shaken either manually or (in larger locomoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firebox On A Steam Train
Firebox may refer to: *Firebox (steam engine), the area where the fuel is burned in a steam engine *Firebox (architecture), the part of a fireplace where fuel is combusted *Firebox Records, a Finnish record label *Firebox.com, an electronic commerce company based in the UK. *Fire alarm box, an outdoor device used for notifying a fire department of a fire *Firebox (song), a song by Europe from the album ''Bag of Bones'' *Firebox, a miniaturized Linux PC for encrypted text and voice messaging, developed by the CryptoRights Foundation in 2004 as part of its HighFire communications security project {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loading Gauge
A loading gauge is a diagram or physical structure that defines the maximum height and width dimensions in railway vehicles and their loads. Their purpose is to ensure that rail vehicles can pass safely through tunnels and under bridges, and keep clear of platforms, trackside buildings and structures. Classification systems vary between different countries, and loading gauges may vary across a network, even if the track gauge is uniform. The term loading gauge can also be applied to the maximum size of road vehicles in relation to tunnels, overpasses and bridges, and doors into automobile repair shops, bus garages, filling stations, residential garages, multi-storey car parks and warehouses. A related but separate gauge is the structure gauge, which sets limits to the extent that bridges, tunnels and other infrastructure can encroach on rail vehicles. The difference between these two gauges is called the clearance. The specified amount of clearance makes allowance for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive
A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pull train, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for longer and heavier freight trains, companies are increasingly using distributed power: single or multiple locomotives placed at the front and rear and at intermediate points throughout the train under the control of the leading locomotive. Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing motion', and is a shortened form of the term ''locomotive engine'', which was first used in 1814 to distinguish between self-propelled and stationary steam engines. Classifications Prior to locomotives, the motive force for railways had been generated by various lower-technology methods such as human power, horse power, Gravity railroad, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the Federal government of the United States#branches, three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. The Smithsonian Institution has historical holdings of over 157 million items, 21 museums, 21 libraries, 14 education and research centers, a zoo, and historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in Washington, D.C. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York (state), New York, and Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler Explosion
A boiler explosion is a catastrophic failure of a boiler. There are two types of boiler explosions. One type is a failure of the pressure parts of the steam and water sides. There can be many different causes, such as failure of the safety valve, corrosion of critical parts of the boiler, or low water level. Corrosion along the edges of lap joints was a common cause of early boiler explosions. In steam locomotive boilers, as knowledge was gained by trial and error in early days, the explosive situations and consequent damage due to explosions were inevitable. However, improved design and maintenance markedly reduced the number of boiler explosions by the end of the 19th century. Further improvements continued in the 20th century. On land-based boilers, explosions of the pressure systems happened regularly in stationary steam boilers in the Victorian era, but are now very rare because of the various protections provided, and because of regular inspections compelled by governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad Engineer
A train driver is a person who operates a train, railcar, or other rail transport vehicle. The driver is in charge of and is responsible for the mechanical operation of the train, train speed, and all of the train handling (also known as brake handling). Train drivers must follow certain guidelines for driving a train safely. Naming British English terms for a train driver include engine driver, engineman, and locomotive driver. The term in North American English is railroad engineer, but the simpler term engineer is more commonly used. Terms for a train driver in other English dialects include locomotive handler, locomotive engineer, locomotive operator, train operator, and motorman. In American English, a hostler (also known as a switcher) moves engines around rail yards, but does not take them out on the main line tracks; the British English equivalent is a shunter. Career progression For many American railroads, the following career progression is typical: assistant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fireman (steam Engine)
A fireman, stoker or boilerman is a person who tends the fire for the running of a boiler, heating a building, or powering a steam engine. Much of the job is hard physical labor, such as shoveling fuel, typically coal, into the boiler's firebox. On steam locomotives, the title ''fireman'' is usually used, while on steamships and stationary steam engines, such as those driving saw mills, the title is usually ''stoker'' (although the British Merchant Navy did use ''fireman''). The German word ''Heizer'' is equivalent and in Dutch the word ''stoker'' is mostly used too. The United States Navy referred to them as ''watertenders''. Nautical Royal Navy The Royal Navy used the rank structure Ordinary Seaman (rating), stoker 2nd class, Able Seaman (rank), stoker 1st Class, Leading Seaman, leading stoker, Petty Officer, stoker petty officer and Chief Petty Officer, chief stoker. The non-substantive (trade) badge for stokers was a ship's propeller. "Stoker" remains the colloquial ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livio Dante Porta
Livio Dante Porta (21 March 1922 – 10 June 2003) was an Argentine steam locomotive engineer. He is particularly remembered for his innovative modifications to existing locomotive systems in order to obtain better performance and energy efficiency, and reduced pollution. He developed the Kylpor and Lempor exhaust systems. The Lemprex was under development at the time of his death. Early years Porta was born in Paraná, Entre Ríos, and studied civil engineering, concluding his studies in 1946, at a time when steam was already giving way to diesel and electric locomotives in Europe and North America. Career Naturally, Porta's first projects were in Argentina. Taking the work of Andre Chapelon in France as his starting point, he set out to demonstrate that the steam locomotive was far from reaching its maximum potential. His first locomotive project in 1948 took the remains of a 4-6-2 converting it into a 4-cylinder compound 4-8-0 named 'Presidente Peron'/'Argentina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler Feedwater
Boiler feedwater is the water which is supplied to a boiler. The feed water is put into the steam drum from a feed pump. In the steam drum the feed water is then turned into steam from the heat. After the steam is used, it is then dumped to the main condenser. From the condenser, it is then pumped to the deaerated feed tank. From this tank it then goes back to the steam drum to complete its cycle. The feedwater is never open to the atmosphere. This cycle is known as a closed system or Rankine cycle. History of feedwater treatment During the early development of boilers, water treatment was not so much of an issue, as temperatures and pressures were so low that high amounts of scale and rust would not form to such a significant extent, especially if the boiler was “boiler blowdown, blown down”. It was general practice to install zinc plates and/or alkaline chemicals to reduce corrosion within the boiler. Many tests had been performed to determine the cause (and possible protec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment. Water treatment removes contaminants and undesirable components, or reduces their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its desired end-use. This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use. Types Drinking water treatment Water contamination is primarily caused by the discharge of untreated wastewater from enterprises. The effluent from various enterprises, which contains varying levels of contaminants, is dumped into rivers or other water resources. The wastewater may have a high proportion of organic and inorganic contaminants at the initial discharge. Industries generate wastewater as a result of fabrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
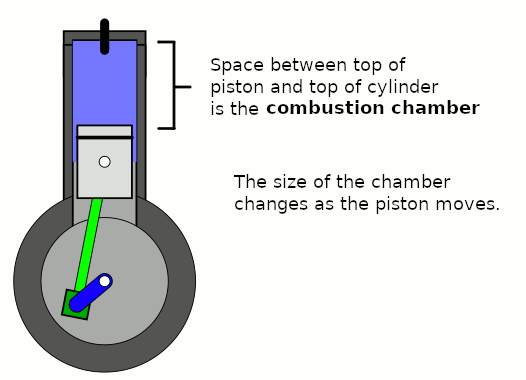
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the air–fuel ratio, fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the Firebox (steam engine), firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol engine, petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |