|
Finnish-Swedish Ice Class
Finnish-Swedish ice class is an ice class assigned to a vessel operating in first-year ice in the Baltic Sea and calling at Finnish or Swedish ports. Ships are divided into six ice classes based on requirements for hull structural design, engine output and performance in ice according to the regulations issued by the Finnish Transport and Communications Agency (Traficom) and the Swedish Maritime Administration. Purpose During the winter months, Finnish and Swedish authorities may declare traffic restrictions in the Northern Baltic Sea in order to ensure that ships operating in the region are capable of navigating in ice-covered waters safely and efficiently. These restrictions, for example "ice class 1A, 2000 DWT", declare the minimum ice class and other requirements for ships that may be provided with icebreaker assistance. The Finnish fairway dues, a system of fees charged for the use of sea lanes to cover the costs of management and icebreaker assistance, also depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Essberger In Ice
Georg may refer to: * ''Georg'' (film), 1997 * Georg (musical), Estonian musical * Georg (given name) * Georg (surname) George is a surname of Irish, English, Welsh, South Indian Christian, Middle Eastern Christian (usually Lebanese), French, or Native American origin. The German form is Georg. Notable people with the surname include: *Allan George (born 1999), Amer ... * , a Kriegsmarine coastal tanker See also * George (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Numeral
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, each letter with a fixed integer value, modern style uses only these seven: The use of Roman numerals continued long after the decline of the Roman Empire. From the 14th century on, Roman numerals began to be replaced by Arabic numerals; however, this process was gradual, and the use of Roman numerals persists in some applications to this day. One place they are often seen is on clock faces. For instance, on the clock of Big Ben (designed in 1852), the hours from 1 to 12 are written as: The notations and can be read as "one less than five" (4) and "one less than ten" (9), although there is a tradition favouring representation of "4" as "" on Roman numeral clocks. Other common uses include year numbers on monuments and buildings and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to before recorded history. Shipbuilding and ship repairs, both commercial and military, are referred to as "naval engineering". The construction of boats is a similar activity called boat building. The dismantling of ships is called ship breaking. History Pre-history The earliest known depictions (including paintings and models) of shallow-water sailing boats is from the 6th to 5th millennium BC of the Ubaid period of Mesopotamia. They were made from bundled reeds coated in bitumen and had bipod masts. They sailed in shallow coastal waters of the Persian Gulf. 4th millennium BC Ancient Egypt Evidence from Ancient Egypt shows that the early Egyptians knew how to assemble planks of wood into a ship hull as early as 3100 BC. Egyptian potte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Association Of Classification Societies
The International Association of Classification Societies (IACS) is a technically based non-governmental organization that currently consists of eleven member marine classification societies. More than 90% of the world's cargo-carrying ships’ tonnage is covered by the classification standards set by member societies of IACS. Marine classification is a system for promoting the safety of life, property and the environment primarily through the establishment and verification of compliance with technical and engineering standards for the design, construction and life-cycle maintenance of ships, offshore units and other marine-related facilities. These standards are contained in rules established by each Society. IACS provides a forum within which the member societies can discuss, research, and adopt technical criteria that enhance maritime safety. History IACS traces its origins to the recommendations of the International Load Line Convention of 1930. The convention recommended col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel Laying
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship. Keel laying is one of the four specially celebrated events in the life of a ship; the others are launching, commissioning and decommissioning. In earlier times, the event recognized as the keel laying was the initial placement of the central timber making up the backbone of a vessel, called the keel. As steel ships replaced wooden ones, the central timber gave way to a central steel beam. Modern ships are most commonly built in a series of pre-fabricated, complete hull sections rather than around a single keel. The event recognized as the keel laying is the first joining of modular components, or the lowering of the first module into place in the building dock. It is now often called "keel authentication", and is the ceremonial beginning of the ship's life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hietalahti Shipyard
Hietalahti shipyard (also known as Helsinki New Shipyard, fi, Helsingin uusi telakka) is a shipyard in Hietalahti, in downtown Helsinki, Finland. Since 2019, it has been operated by a company named Helsinki Shipyard. History The shipyard, first known as Helsingfors Skeppsdocka ( fi, Hietalahden Laivatelakka) and later as Sandvikens Skeppsdocka och Mekaniska Verkstad ( fi, Hietalahden Sulkutelakka ja Konepaja), was founded in 1865 and delivered its first ship in 1868. It also constructed horse-drawn trams and railroad cars. Wärtsilä bought the parent company Kone ja Silta in the 1930s; it included also the Crichton-Vulcan shipyard in Turku. In 1965 the yard was renamed ''Wärtsilä Helsingin Telakka'' (Wärtsilä Helsinki Shipyard). After the bankruptcy of Wärtsilä Marine in 1989 the yards were operated by the newly formed Masa Yards, bought by the Norwegian Kværner group in the mid 1990s and known as Kvaerner Masa Yards. In 2005 the company merged with the Aker Finnyar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wärtsilä
Wärtsilä Oyj Abp (), trading internationally as Wärtsilä Corporation, is a Finnish company which manufactures and services power sources and other equipment in the marine and energy markets. The core products of Wärtsilä include technologies for the energy sector, including gas, multi-fuel, liquid fuel and biofuel power plants and energy storage systems; and technologies for the marine sector, including cruise ships, ferries, fishing vessels, merchant ships, navy ships, special vessels, tugs, yachts and offshore vessels. Ship design capabilities include ferries, tugs, and vessels for the fishing, merchant, offshore and special segments. Services offerings include online services, underwater services, turbocharger services, and also services for the marine, energy, and oil and gas markets. At the end of June 2018, the company employed more than 19,000 workers. Wärtsilä has two main businesses; Energy Business focusing on the energy market, and Marine Business focusing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Bothnia
The Gulf of Bothnia (; fi, Pohjanlahti; sv, Bottniska viken) is divided into the Bothnian Bay and Bothnian Sea, and it is the northernmost arm of the Baltic Sea, between Finland's west coast ( East Bothnia) and the Sweden's east coast (West Bothnia and North Bothnia). In the south of the gulf lies Åland, between the Sea of Åland and the Archipelago Sea. Name Bothnia is a latinization. The Swedish name was originally just , with being Old Norse for "gulf" or "bay", which is also the meaning of the second element . The name was applied to the Gulf of Bothnia as in Old Norse, after , which at the time referred to the coastland west of the gulf. Later, was applied to the regions on the western side and the eastern side ('East Bottom' and 'West Bottom'). The Finnish name of Österbotten, (, meaning 'land'), gives a hint as to the meaning in both languages: the meaning of includes both 'bottom' and 'north'. is the base word for north, , with an adjectival suffix adde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
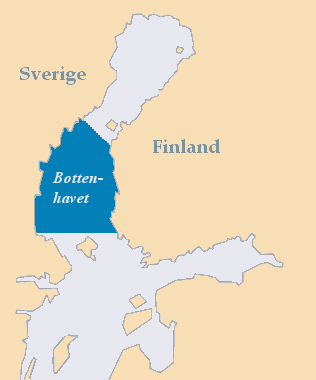
Bothnian Sea
The Bothnian Sea ( sv, Bottenhavet; fi, Selkämeri) links the Bothnian Bay (also called the Bay of Bothnia) with the Baltic proper. Kvarken is situated between the two. Together, the Bothnian Sea and Bay make up a larger geographical entity, the Gulf of Bothnia, where the Bothnian Sea is the southern part. The whole Gulf of Bothnia is situated between Sweden, to the west, Finland, to the east, and the Sea of Åland and Archipelago Sea to the south. The surface area of the Bothnian Sea is approximately 79,000 km². The largest coastal towns, from south to north, are Rauma and Pori in Finland, and Gävle and Sundsvall in Sweden. Umeå (Sweden) and Vaasa (Finland) lie in the extreme north, near Bothnian Bay. See also * Bothnian Sea National Park References External links * {{Marginal seas of the Atlantic Ocean Baltic Sea Gulfs of Sweden Bodies of water of Finland Bothnia The Gulf of Bothnia (; fi, Pohjanlahti; sv, Bottniska viken) is divided into the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg in Russia to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn. The eastern parts of the Gulf of Finland belong to Russia, and some of Russia's most important oil harbors are located farthest in, near Saint Petersburg (including Primorsk). As the seaway to Saint Petersburg, the Gulf of Finland has been and continues to be of considerable strategic importance to Russia. Some of the environmental problems affecting the Baltic Sea are at their most pronounced in the shallow gulf. Proposals for a tunnel through the gulf have been made. Geography The gulf has an area of . The length (from the Hanko Peninsula to Saint Petersburg) is and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Veritas
Bureau Veritas is a French company specialized in testing, inspection and certification founded in 1828. It operates in a variety of sectors, including building and infrastructure (27% of revenue), agri-food and commodities (23% of revenue), marine and offshore (7% of revenue), industry (22% of revenue), certification (7% of revenue) and consumer products (14% of revenue). Bureau Veritas is present in 140 countries through a network of over 1,500 offices and laboratories, and 82,000 employees. Bureau Veritas generated €4.8 billion in revenue in 2021. Didier Michaud-Daniel has been the CEO of Bureau Veritas since March 2012. On 24 February 2022, Bureau Veritas announced the appointment of Hinda Gharbi as COO, with plans to appoint her as the company's next CEO. History Bureau Veritas was founded in Antwerp, Belgium, in 1828. Originally called the ''Bureau de renseignements pour les assurances maritimes'' (Information Office for Maritime Insurance), its mission was to "est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lloyd's Register
Lloyd's Register Group Limited (LR) is a technical and professional services organisation and a maritime classification society, wholly owned by the Lloyd’s Register Foundation, a UK charity dedicated to research and education in science and engineering. The organisation dates to 1760. Its stated aims are to enhance the safety of life, property, and the environment, by helping its clients (including by validation, certification, and accreditation) to improve the safety and performance of complex projects, supply chains and critical infrastructure. In July 2012, the organisation converted from an industrial and provident society to a company limited by shares, named Lloyd’s Register Group Limited, with the new Lloyd’s Register Foundation as the sole shareholder. At the same time the organisation gave to the Foundation a substantial bond and equity portfolio to assist it with its charitable purposes. It will benefit from continued funding from the group’s operating arm, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)