|
Finite-state Entropy
Asymmetric numeral systems (ANS)J. Duda, K. Tahboub, N. J. Gadil, E. J. Delp''The use of asymmetric numeral systems as an accurate replacement for Huffman coding'' Picture Coding Symposium, 2015.J. Duda''Asymmetric numeral systems: entropy coding combining speed of Huffman coding with compression rate of arithmetic coding'' arXiv:1311.2540, 2013. is a family of entropy encoding methods introduced by Jarosław (Jarek) Duda from Jagiellonian University, used in data compression since 2014 due to improved performance compared to previous methods. ANS combines the compression ratio of arithmetic coding (which uses a nearly accurate probability distribution), with a processing cost similar to that of Huffman coding. In the tabled ANS (tANS) variant, this is achieved by constructing a finite-state machine to operate on a large alphabet without using multiplication. Among others, ANS is used in the Facebook Zstandard compressor [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy Encoding
In information theory, an entropy coding (or entropy encoding) is any lossless data compression method that attempts to approach the lower bound declared by Shannon's source coding theorem, which states that any lossless data compression method must have expected code length greater or equal to the entropy of the source. More precisely, the source coding theorem states that for any source distribution, the expected code length satisfies \mathbb E_(d(x))\geq \mathbb E_ \log_b(P(x))/math>, where l is the number of symbols in a code word, d is the coding function, b is the number of symbols used to make output codes and P is the probability of the source symbol. An entropy coding attempts to approach this lower bound. Two of the most common entropy coding techniques are Huffman coding and arithmetic coding. If the approximate entropy characteristics of a data stream are known in advance (especially for signal compression), a simpler static code may be useful. These static codes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixar
Pixar Animation Studios (commonly known as Pixar () and stylized as P I X A R) is an American computer animation studio known for its critically and commercially successful computer animated feature films. It is based in Emeryville, California, United States. Since 2006, Pixar has been a subsidiary of Walt Disney Studios, which is another studio owned by The Walt Disney Company. Pixar started in 1979 as part of the Lucasfilm computer division, known as the Graphics Group, before its spin-off as a corporation in 1986, with funding from Apple co-founder Steve Jobs, who became its majority shareholder. Disney purchased Pixar in January 2006 at a valuation of $7.4+ billion by converting each share of Pixar stock to 2.3 shares of Disney stock. Pixar is best known for its feature films, technologically powered by RenderMan, the company's own implementation of the industry-standard RenderMan Interface Specification image-rendering API. The studio's mascot is Luxo Jr., a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulative Distribution Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Every probability distribution supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as continuous, is uniquely identified by an ''upwards continuous'' ''monotonic increasing'' cumulative distribution function F : \mathbb R \rightarrow ,1/math> satisfying \lim_F(x)=0 and \lim_F(x)=1. In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from minus infinity to x. Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables. Definition The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable X is the function given by where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable X takes on a value less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANS General Picture
Ans or ANS or ''variation'', may refer to: Places * Ans, Belgium, a municipality in Belgium * Ans, Denmark, a village in Denmark * Angus, Scotland, UK; a council area by its Chapman code * Ainsdale railway station, England, UK (by station code ANS) * Andahuaylas Airport, Peru (by IATA airport code ANS) People * Ans (given name), a Dutch feminine given name * Anna Nicole Smith, American model and actress Organizations * Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States * Astronomical Netherlands Satellite, a Dutch X-ray satellite * American Name Society * American Nuclear Society * American Numismatic Society, formerly the American Numismatic and Archaeological Society * Artificial neural system, or Artificial neural network * ANS Group of Companies, a news organization in Azerbaijan * , a Cambodian resistance group; see Coalition Government of Democratic Kampuchea * Audubon Naturalist Society, an environmental organization based in the Washington, DC ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy Encoding
In information theory, an entropy coding (or entropy encoding) is any lossless data compression method that attempts to approach the lower bound declared by Shannon's source coding theorem, which states that any lossless data compression method must have expected code length greater or equal to the entropy of the source. More precisely, the source coding theorem states that for any source distribution, the expected code length satisfies \mathbb E_(d(x))\geq \mathbb E_ \log_b(P(x))/math>, where l is the number of symbols in a code word, d is the coding function, b is the number of symbols used to make output codes and P is the probability of the source symbol. An entropy coding attempts to approach this lower bound. Two of the most common entropy coding techniques are Huffman coding and arithmetic coding. If the approximate entropy characteristics of a data stream are known in advance (especially for signal compression), a simpler static code may be useful. These static codes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (information Theory)
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable is the average level of "information", "surprise", or "uncertainty" inherent to the variable's possible outcomes. Given a discrete random variable X, which takes values in the alphabet \mathcal and is distributed according to p: \mathcal\to , 1/math>: \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x) = \mathbb \log p(X), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or " shannons"), while base ''e'' gives "natural units" nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or " hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a variable. The concept of information entropy was introduced by Claude Shannon in his 1948 paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication",PDF archived froherePDF archived frohere and is also referred to as Shannon entropy. Shannon's theory def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stirling's Approximation
In mathematics, Stirling's approximation (or Stirling's formula) is an approximation for factorials. It is a good approximation, leading to accurate results even for small values of n. It is named after James Stirling, though a related but less precise result was first stated by Abraham de Moivre. One way of stating the approximation involves the logarithm of the factorial: \ln(n!) = n\ln n - n +O(\ln n), where the big O notation means that, for all sufficiently large values of n, the difference between \ln(n!) and n\ln n-n will be at most proportional to the logarithm. In computer science applications such as the worst-case lower bound for comparison sorting, it is convenient to use instead the binary logarithm, giving the equivalent form \log_2 (n!) = n\log_2 n - n\log_2 e +O(\log_2 n). The error term in either base can be expressed more precisely as \tfrac12\log(2\pi n)+O(\tfrac1n), corresponding to an approximate formula for the factorial itself, n! \sim \sqrt\left(\frac\r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinations
In mathematics, a combination is a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations). For example, given three fruits, say an apple, an orange and a pear, there are three combinations of two that can be drawn from this set: an apple and a pear; an apple and an orange; or a pear and an orange. More formally, a ''k''-combination of a set ''S'' is a subset of ''k'' distinct elements of ''S''. So, two combinations are identical if and only if each combination has the same members. (The arrangement of the members in each set does not matter.) If the set has ''n'' elements, the number of ''k''-combinations, denoted as C^n_k, is equal to the binomial coefficient \binom nk = \frac, which can be written using factorials as \textstyle\frac whenever k\leq n, and which is zero when k>n. This formula can be derived from the fact that each ''k''-combination of a set ''S'' of ''n'' members has k! permutations so P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JPEG XL
JPEG XL is a royalty-free raster-graphics file format that supports both lossy and lossless compression. It is designed to outperform existing raster formats and thus become their universal replacement. Name The name consists of ''JPEG'' (for the ''Joint Photographic Experts Group'', which is the committee which designed the format), ''X'' (part of the name of several JPEG standards since 2000: JPEG XT, JPEG XR, JPEG XS), and ''L'' (for long-term). The L was included because the authors' intention is for the format to replace the legacy JPEG and last as long too. Authors The main authors of the specification are Jyrki Alakuijala, Jon Sneyers, and Luca Versari. Other collaborators are Sami Boukortt, Alex Deymo, Moritz Firsching, Thomas Fischbacher, Eugene Kliuchnikov, Robert Obryk, Alexander Rhatushnyak, Zoltan Szabadka, Lode Vandevenne, and Jan Wassenberg. History In August 2017, JTC1 / SC29 / WG1 (JPEG) published a call for proposals for JPEG XL, the next generation image en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DirectStorage
The Xbox Series X/S are home video game consoles developed by Microsoft. They were both released on November 10, 2020, as the fourth generation Xbox, succeeding the Xbox One. Along with Sony's PlayStation 5, also released in November 2020, the Xbox Series X/S consoles are part of the ninth generation of video game consoles. Rumors regarding the consoles first emerged in early 2019, with the line as a whole codenamed "Scarlett" and consisting of high-end and lower-end models codenamed "Anaconda" and "Lockhart" respectively; "Anaconda" was teased by Microsoft during E3 2019 under the codename "Project Scarlett", and unveiled during The Game Awards in December as Xbox Series X. On September 8, 2020, Microsoft unveiled the lower-end model, Xbox Series S. As with the Xbox One line, the consoles utilize an Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) CPU and GPU. Both models feature a new storage architecture based around solid-state drives to reduce loading times, support for hardware-accelerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology company, technology corporation producing Software, computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Microsoft Windows, Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office Productivity software#Office suite, suite, and the Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge, Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's List of the largest software companies, largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Tech, Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dropbox (service)
Dropbox is a file hosting service operated by the American company Dropbox, Inc., headquartered in San Francisco, California, U.S. that offers cloud storage, file synchronization, personal cloud, and client software. Dropbox was founded in 2007 by MIT students Drew Houston and Arash Ferdowsi as a startup company, with initial funding from seed accelerator Y Combinator. Dropbox has experienced criticism and generated controversy for issues including security breaches and privacy concerns. Dropbox has been blocked in China since 2014. Concept Dropbox brings files together in one central place by creating a special folder on the user's computer. The contents of these folders are synchronized to Dropbox's servers and to other computers and devices where the user has installed Dropbox, keeping the same files up-to-date on all devices. Dropbox uses a freemium business model, where users are offered a free account with set storage size, with paid subscriptions available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

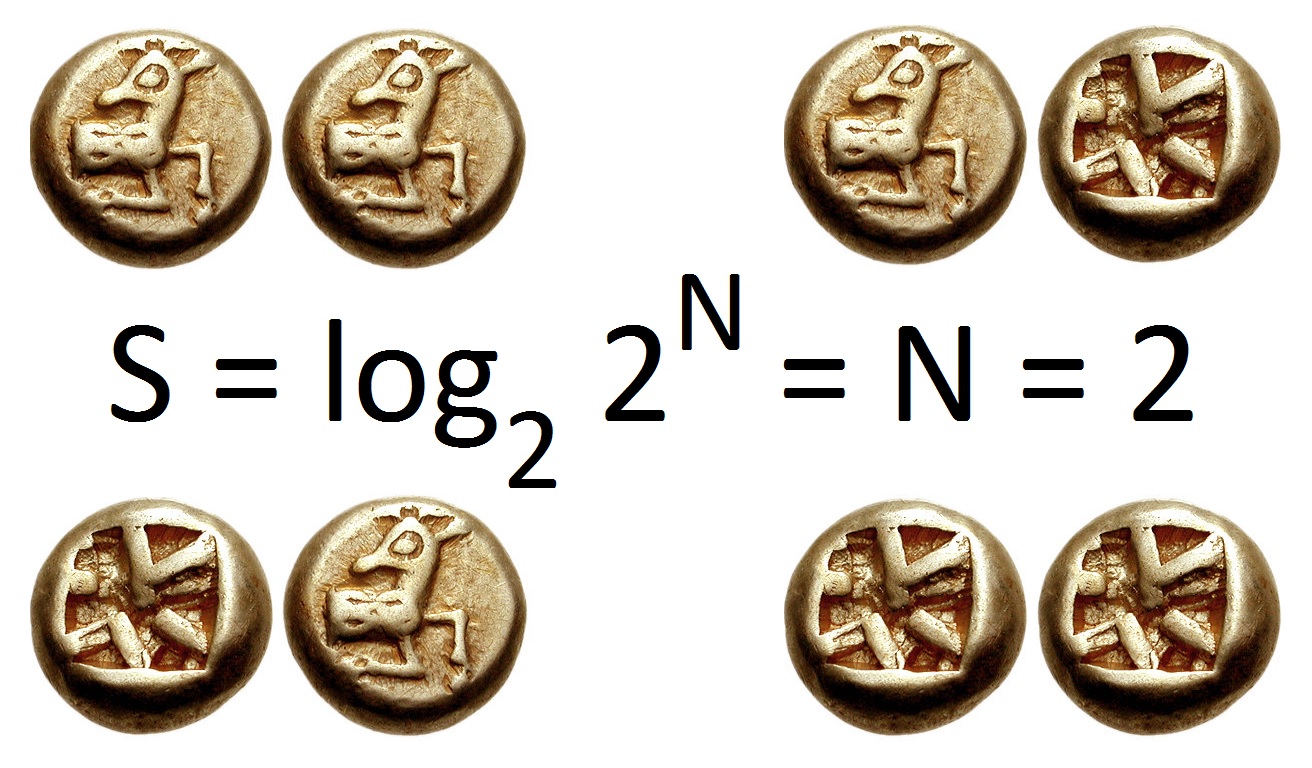
.jpg)

.jpg)