|
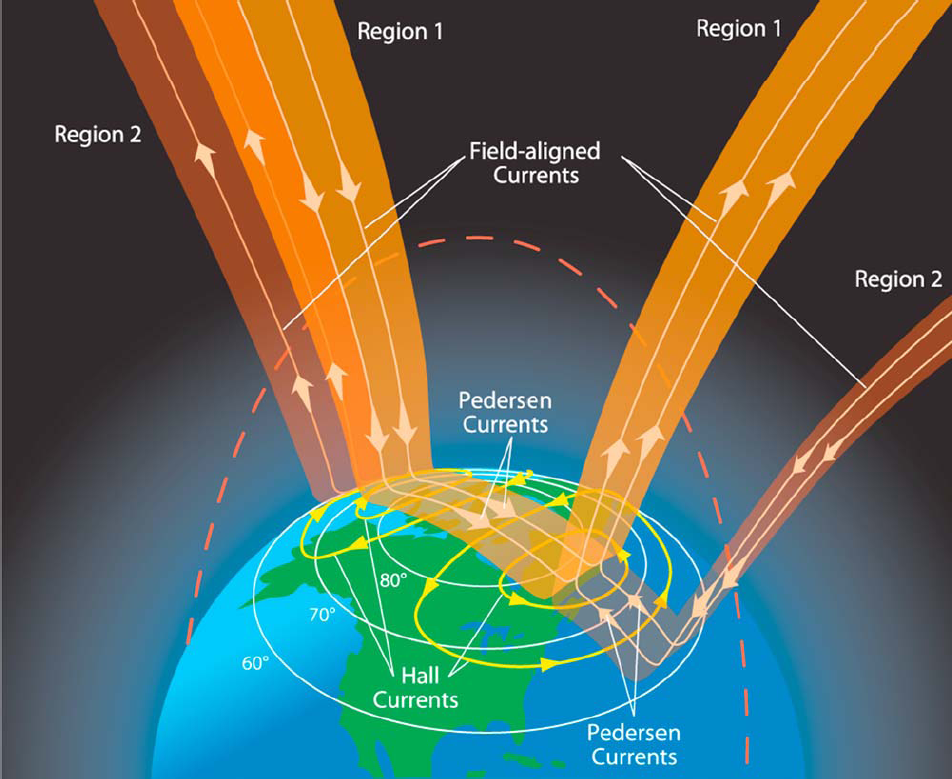
Field-aligned Current
A Birkeland current (also known as field-aligned current) is a set of electrical currents that flow along geomagnetic field lines connecting the Earth's magnetosphere to the Earth's high latitude ionosphere. In the Earth's magnetosphere, the currents are driven by the solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field and by bulk motions of plasma through the magnetosphere (convection indirectly driven by the interplanetary environment). The strength of the Birkeland currents changes with activity in the magnetosphere (e.g. during substorms). Small scale variations in the upward current sheets (downward flowing electrons) accelerate magnetospheric electrons which, when they reach the upper atmosphere, create the Auroras Borealis and Australis. In the high latitude ionosphere (or auroral zones), the Birkeland currents close through the region of the auroral electrojet, which flows perpendicular to the local magnetic field in the ionosphere. The Birkeland currents occur in two pairs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Acceleration
Plasma acceleration is a technique for accelerating charged particles, such as electrons, positrons, and ions, using the electric field associated with electron plasma wave or other high-gradient plasma structures (like shock and sheath fields). The plasma acceleration structures are created either using ultra-short laser pulses or energetic particle beams that are matched to the plasma parameters. These techniques offer a way to build high performance particle accelerators of much smaller size than conventional devices. The basic concepts of plasma acceleration and its possibilities were originally conceived by Toshiki Tajima and John M. Dawson of UCLA in 1979. The initial experimental designs for a "wakefield" accelerator were conceived at UCLA by Chandrashekhar J. Joshi et al. Current experimental devices show accelerating gradients several orders of magnitude better than current particle accelerators over very short distances, and about one order of magnitude better (1 GeV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
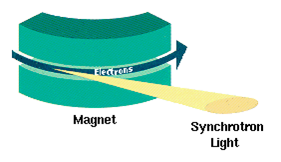
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bennett Pinch
A pinch (or: Bennett pinch (after Willard Harrison Bennett), electromagnetic pinch, magnetic pinch, pinch effect, or plasma pinch.) is the compression of an electrically conducting Electrical filament, filament by magnetic forces, or a device that does such. The conductor is usually a Plasma (physics), plasma, but could also be a solid or liquid metal. Pinches were the first type of device used for experiments in controlled nuclear fusion power. Pinches occur naturally in electrical discharges such as lightning, lightning bolts, planetary Aurora (astronomy), auroras, current sheets, and solar flares. Basic mechanism Types Pinches exist in nature and in laboratories. Pinches differ in their geometry and operating forces. These include: * ''Uncontrolled'' – Any time an electric current moves in large amounts (e.g., lightning, arcs, sparks, discharges) a magnetic force can pull together plasma. This can be insufficient for fusion. * ''Current sheet, Sheet pinch'' – An astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Layer (plasma)
A double layer is a structure in a plasma consisting of two parallel layers of opposite electrical charge. The sheets of charge, which are not necessarily planar, produce localised excursions of electric potential, resulting in a relatively strong electric field between the layers and weaker but more extensive compensating fields outside, which restore the global potential. Ions and electrons within the double layer are accelerated, decelerated, or deflected by the electric field, depending on their direction of motion. Double layers can be created in discharge tubes, where sustained energy is provided within the layer for electron acceleration by an external power source. Double layers are claimed to have been observed in the aurora and are invoked in astrophysical applications. Similarly, a double layer in the auroral region requires some external driver to produce electron acceleration. Electrostatic double layers are especially common in current-carrying plasmas, and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampère's Force Law
In magnetostatics, the force of attraction or repulsion between two current-carrying wires (see first figure below) is often called Ampère's force law. The physical origin of this force is that each wire generates a magnetic field, following the Biot–Savart law, and the other wire experiences a magnetic force as a consequence, following the Lorentz force law. Equation Special case: Two straight parallel wires The best-known and simplest example of Ampère's force law, which underlaid (before 20 May 2019) the definition of the ampere, the SI unit of current, states that the magnetic force per unit length between two straight parallel conductors is \frac = 2 k_ \frac , where k_ is the magnetic force constant from the Biot–Savart law, F_m / L is the total force on either wire per unit length of the shorter (the longer is approximated as infinitely long relative to the shorter), r is the distance between the two wires, and I_1, I_2 are the direct currents carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z-pinch
In fusion power research, the Z-pinch (zeta pinch) is a type of plasma confinement system that uses an electric current in the plasma to generate a magnetic field that compresses it (see pinch). These systems were originally referred to simply as pinch or Bennett pinch (after Willard Harrison Bennett), but the introduction of the θ-pinch (theta pinch) concept led to the need for clearer, more precise terminology. The name refers to the direction of the current in the devices, the Z-axis on a normal three-dimensional graph. Any machine that causes a pinch effect due to current running in that direction is correctly referred to as a Z-pinch system, and this encompasses a wide variety of devices used for an equally wide variety of purposes. Early uses focused on fusion research in donut-shaped tubes with the Z-axis running down the inside the tube, while modern devices are generally cylindrical and used to generate high-intensity x-ray sources for the study of nuclear weapon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin–Helmholtz Instability
The Kelvin–Helmholtz instability (after Lord Kelvin and Hermann von Helmholtz) is a fluid instability that occurs when there is velocity shear in a single continuous fluid or a velocity difference across the interface between two fluids. Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities are visible in the atmospheres of planets and moons, such as in cloud formations on Earth or the Red Spot on Jupiter, and the atmospheres of the Sun and other stars. Theory overview and mathematical concepts Fluid dynamics predicts the onset of instability and transition to turbulent flow within fluids of different densities moving at different speeds. If surface tension is ignored, two fluids in parallel motion with different velocities and densities yield an interface that is unstable to short-wavelength perturbations for all speeds. However, surface tension is able to stabilize the short wavelength instability up to a threshold velocity. If the density and velocity vary continuously in space ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocotron Instability
A diocotron instability is a plasma instability created by two sheets of charge slipping past each other. Energy is dissipated in the form of two surface waves which propagate Propagation can refer to: *Chain propagation in a chemical reaction mechanism *Crack propagation, the growth of a crack during the fracture of materials *Propaganda, non-objective information used to further an agenda *Reproduction, and other forms ... in opposite directions, one flowing over the other. This instability is the plasma analog of the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in fluid mechanics. References * Plasma instabilities Articles containing video clips {{plasma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
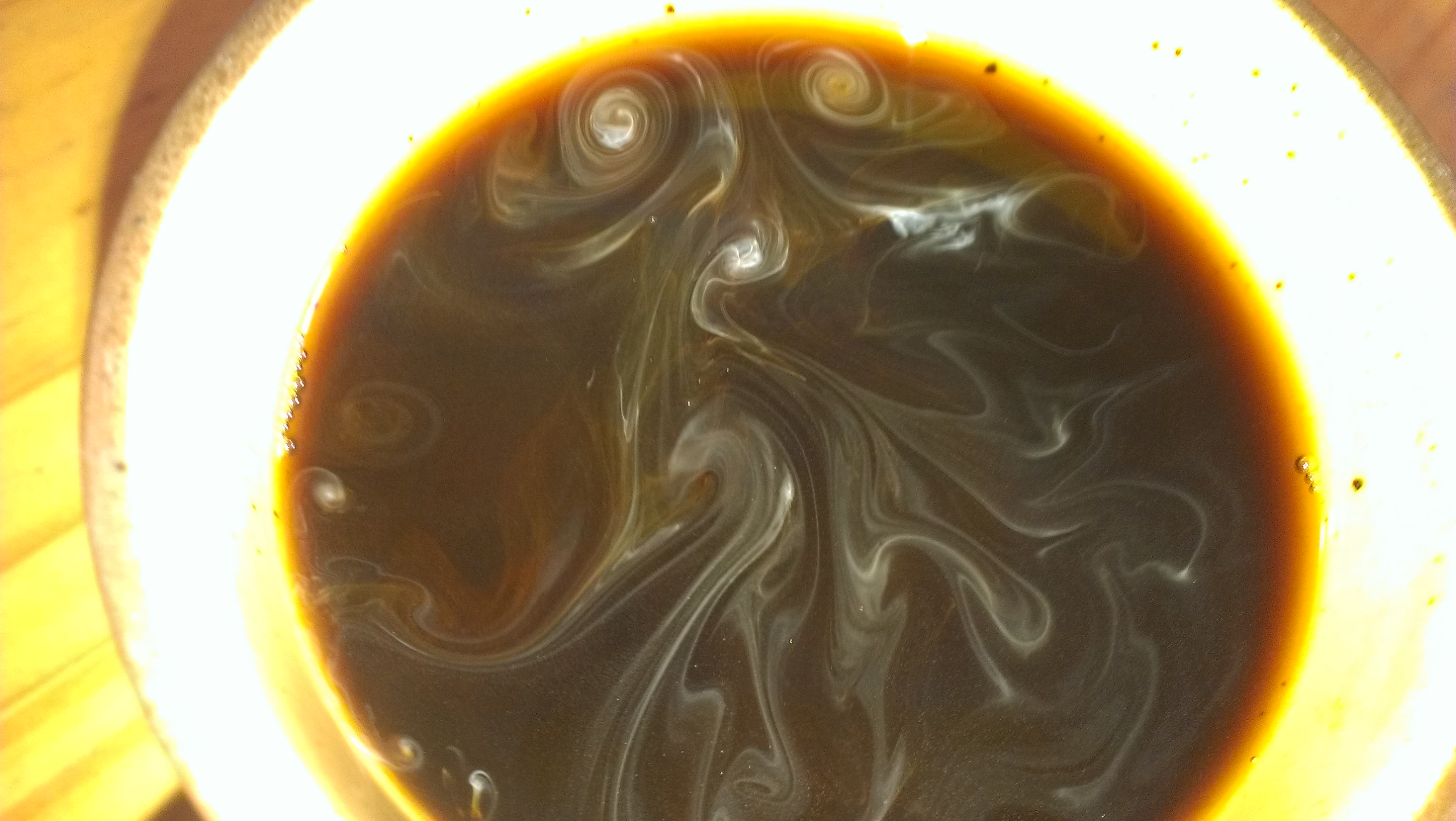
Vortices
In fluid dynamics, a vortex ( : vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsed Power
Pulsed power is the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it instantly, thus increasing the instantaneous power. They can be used in some applications such as food processing, water treatment, weapon, and medical applications. Overview Energy is typically stored within electrostatic fields (capacitors), magnetic fields (inductors), as mechanical energy (using large flywheels connected to special-purpose high-current alternators), or as chemical energy (high-current lead-acid batteries, or explosives). By releasing the stored energy over a very short interval (a process that is called energy compression), a huge amount of peak power can be delivered to a load. For example, if one joule of energy is stored within a capacitor and then evenly released to a load over one second, the average power delivered to the load would only be 1 watt. However, if all of the stored energy were released within one microsecond, the average p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circuit). : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |