|
Ficus Pleurocarpa
''Ficus pleurocarpa'', commonly known as the banana fig, karpe fig or gabi fig, is a fig that is endemic to the wet tropical rainforests of northeastern Queensland, Australia. It has characteristic ribbed orange and red cylindrical syconia. It begins life as a hemiepiphyte, later becoming a tree up to tall. ''F. pleurocarpa'' is one of the few figs known to be pollinated by more than one species of fig wasp. Taxonomy ''Ficus pleurocarpa'' was described by German-Australian botanist Ferdinand von Mueller in 1874 in ''Fragmenta Phytographiae Australiae''. Retrieved on 2008-07-13 Its specific epithet is derived from Ancient Greek ''pleuro-'', ribbed, and ''-carpus'', fruit, or flesh of the fruit, hence "ribbed fruit". This is derived from the 5–10 ribs that run along the length of the fruit. With over 750 species, ''Ficus'' is one of the largest angiosperm genera. On the basis of morphology, English botanist E. J. H. Corner divided the genus into four subgenera which were l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Von Mueller
Baron Sir Ferdinand Jacob Heinrich von Mueller, (german: Müller; 30 June 1825 – 10 October 1896) was a German-Australian physician, geographer, and most notably, a botanist. He was appointed government botanist for the then colony of Victoria (Australia) by Governor Charles La Trobe in 1853, and later director of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Melbourne. He also founded the National Herbarium of Victoria. He named many Australian plants. Early life Mueller was born at Rostock, in the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. After the early death of his parents, Frederick and Louisa, his grandparents gave him a good education in Tönning, Schleswig. Apprenticed to a chemist at the age of 15, he passed his pharmaceutical examinations and studied botany under Professor Ernst Ferdinand Nolte (1791–1875) at Kiel University. In 1847, he received his degree of Doctor of Philosophy from Kiel for a thesis on the plants of the southern regions of Schleswig. Mueller's sister Bertha had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Section (botany)
In botany, a section ( la, sectio) is a taxonomic rank below the genus, but above the species. The subgenus, if present, is higher than the section, and the rank of series, if present, is below the section. Sections may in turn be divided into subsections.Article 4 in Sections are typically used to help organise very large genera, which may have hundreds of species. A botanist wanting to distinguish groups of species may prefer to create a taxon at the rank of section or series to avoid making new combinations, i.e. many new binomial names for the species involved. Examples: * ''Lilium'' sectio ''Martagon'' Rchb. are the Turks' cap lilies * ''Plagiochila aerea'' Taylor is the type species of ''Plagiochila'' sect. ''Bursatae'' See also * Section (biology) References Section Section, Sectioning or Sectioned may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea * Section (typography), a subdivision, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatorial evergreen rainforest''. True rainforests are typically found between 10 degrees north and south of the equator (see map); they are a sub-set of the tropical forest biome that occurs roughly within the 28-degree latitudes (in the equatorial zone between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn). Within the World Wildlife Fund's biome classification, tropical rainforests are a type of tropical moist broadleaf forest (or tropical wet forest) that also includes the more extensive seasonal tropical forests. Overview Tropical rainforests are characterized by two words: hot and wet. Mean monthly temperatures exceed during all months of the year. Average annual rainfall is no less than and can exceed although it typically lies betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherton Tableland
The Atherton Tableland is a fertile plateau which is part of the Great Dividing Range in Queensland, Australia. The principal river flowing across the plateau is the Barron River. It was dammed to form an irrigation reservoir named Lake Tinaroo. Tinaroo Hydro, a small 1.6 MW hydroelectric power station, is located near the spillway. Physiography This area is a distinct physiographic section of the larger North Queensland Highlands province, which in turn is part of the larger East Australian Cordillera physiographic division. South of the Tablelands is the Bellenden Ker Range. Geological history About 100 million years ago, the eastern edge of the Australian continent extended much further to the east, before tectonic forces fractured the eastern margin, pulling it apart. At the same time, slowly rising mantle material caused a doming up of the continental crust. As the eastern part of the continent broke away, it gradually sank below sea level. Since that time, the up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Tribulation
Cape Tribulation is a headland and coastal locality in the Shire of Douglas in northern Queensland, Australia. In the , Cape Tribulation had a population of 118 people. Geography The locality is north of Cairns. It is within the Daintree National Park and the Wet Tropics World Heritage area. It is within the local government area of Shire of Douglas (between 2008 and 2013, it was within the Cairns Region). The locality contains a small number of bed and breakfast eco lodges, tourism resorts and backpacker hostels. A few very rare plants can be found on Cape Tribulation. History ''Kuku Yalanji'' (also known as ''Gugu Yalanji'', ''Kuku Yalaja'', and ''Kuku Yelandji'') is an Australian Aboriginal language of the Mossman and Daintree areas of North Queensland. The language region includes areas within the local government area of Shire of Douglas and Shire of Cook, particularly the localities of Mossman, Daintree, Bloomfield River, China Camp, Maytown, Palmer, Cape Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptic Species Complex
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each other, further blurring any distinctions. Terms that are sometimes used synonymously but have more precise meanings are cryptic species for two or more species hidden under one species name, sibling species for two (or more) species that are each other's closest relative, and species flock for a group of closely related species that live in the same habitat. As informal taxonomic ranks, species group, species aggregate, macrospecies, and superspecies are also in use. Two or more taxa that were once considered conspecific (of the same species) may later be subdivided into infraspecific taxa (taxa within a species, such as bacterial strains or plant varieties Variety may refer to: Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats * Variety ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistodontes Deuterus
''Pleistodontes deuterus'' is a species of fig wasp which is native to Australia. It has an obligate mutualism with ''Ficus pleurocarpa ''Ficus pleurocarpa'', commonly known as the banana fig, karpe fig or gabi fig, is a fig that is endemic to the wet tropical rainforests of northeastern Queensland, Australia. It has characteristic ribbed orange and red cylindrical syconia. It ...'', the fig species it pollinates. References Agaonidae Hymenoptera of Australia Insects described in 2002 {{Chalcidoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistodontes Regalis
''Pleistodontes regalis'' is a species of fig wasp which is native to Australia. It has an obligate mutualism with ''Ficus pleurocarpa ''Ficus pleurocarpa'', commonly known as the banana fig, karpe fig or gabi fig, is a fig that is endemic to the wet tropical rainforests of northeastern Queensland, Australia. It has characteristic ribbed orange and red cylindrical syconia. It ...'', the fig species it pollinates. References Agaonidae Hymenoptera of Australia Insects described in 1952 {{Chalcidoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutualism (biology)
Mutualism describes the ecological interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of ecological interaction. Prominent examples include most vascular plants engaged in mutualistic interactions with mycorrhizae, flowering plants being pollinated by animals, vascular plants being dispersed by animals, and corals with zooxanthellae, among many others. Mutualism can be contrasted with interspecific competition, in which each species experiences ''reduced'' fitness, and exploitation, or parasitism, in which one species benefits at the expense of the other. The term ''mutualism'' was introduced by Pierre-Joseph van Beneden in his 1876 book ''Animal Parasites and Messmates'' to mean "mutual aid among species". Mutualism is often conflated with two other types of ecological phenomena: cooperation and symbiosis. Cooperation most commonly refers to increases in fitness through within-species (intraspecific) interactions, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoecious
Monoecy (; adj. monoecious ) is a sexual system in seed plants where separate male and female cones or flowers are present on the same plant. It is a monomorphic sexual system alongside gynomonoecy, andromonoecy and trimonoecy. Monoecy is connected to anemophily. It can prevent self-pollination in an individual flower but cannot prevent self-pollination between male and female flowers on the same plant. Monoecy in angiosperms has been of interest for evolutionary biologists since Charles Darwin. Terminology Monoecious comes from the Greek words for one house. History The term monoecy was first introduced in 1735 by Carl Linnaeus. Darwin noted that the flowers of monoecious species sometimes showed traces of the opposite sex function. Monoecious hemp was first reported in 1929. Occurrence Monoecy is most common in temperate climates and is often associated with inefficient pollinators or wind-pollinated plants. It may be beneficial to reducing pollen-stigma interferenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
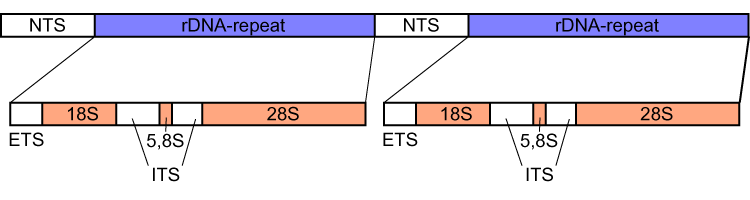
External Transcribed Spacer
External transcribed spacer (ETS) refers to a piece of non-functional RNA, closely related to the internal transcribed spacer, which is situated outside structural ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) on a common precursor transcript. ETS sequences characteristic to an organism can be used to trace its phylogeny A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec .... References {{genetics-stub DNA Phylogenetics de:Spacer (Biologie) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Transcribed Spacer
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. ITS across life domains In bacteria and archaea, there is a single ITS, located between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Conversely, there are two ITSs in eukaryotes: ITS1 is located between 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes, while ITS2 is between 5.8S and 28S (in opisthokonts, or 25S in plants) rRNA genes. ITS1 corresponds to the ITS in bacteria and archaea, while ITS2 originated as an insertion that interrupted the ancestral 23S rRNA gene. Organization In bacteria and archaea, the ITS occurs in one to several copies, as do the flanking 16S and 23S genes. When there are multiple copies, these do not occur adjacent to one another. Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)