|
Ficus Platypoda
''Ficus platypoda'', commonly known as the desert fig or rock fig, is a fig that is endemic to central and northern Australia. It is a lithophytic plant that grows on rocky outcrops, reaching 10 m in height. Taxonomy Dutch botanist Friedrich Anton Wilhelm Miquel described the desert fig in 1847 as ''Urostigma platypodum'', from material collected on both the east and west coast of Australia. The material collected by Allan Cunningham from York Sound in Western Australia became the type material. E.J.H. Corner synonymised ''F. platypoda'' with ''Ficus leucotricha'', which was described by Miquel in 1861, however as the former name is older, it has become the accepted name instead. The various populations and subspecies of ''Ficus platypoda'' were examined genetically in 2001 and found to contain a number of distinct species. Hence '' Ficus brachypoda'', '' Ficus atricha'' and '' Ficus cerasicarpa'' were described as separate species. With over 750 species, ''Ficus'' is one of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Anton Wilhelm Miquel
Friedrich Anton Wilhelm Miquel (24 October 1811 – 23 January 1871) was a Dutch botanist, whose main focus of study was on the flora of the Dutch East Indies. Early life Miquel was born in Neuenhaus and studied medicine at the University of Groningen, where, in 1833, he received his doctorate. After starting work as a doctor at the Buitengasthuis Hospital in Amsterdam, in 1835, he taught medicine at the clinical school in Rotterdam. In 1838 he became correspondent of the Royal Institute, which later became the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, and in 1846 he became member. He was professor of botany at the University of Amsterdam (1846–1859) and Utrecht University (1859–1871). He directed the Rijksherbarium (National Herbarium) at Leiden from 1862. In 1866, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Research Miquel did research on the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy of plants. He was interested in the flora of the Dutch Empire, speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Series (botany)
In botany and plant taxonomy, a series is a subdivision of a genus, a taxonomic rank below that of section (and subsection) but above that of species. Sections and/or series are typically used to help organize very large genera, which may have hundreds of species. Cultivar marketing The term "series" is also used (in seed marketing) for groupings of cultivars, but this term has no formal status with that meaning in the ''ICNCP The ''International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants'' (ICNCP), is a guide to the rules and regulations for naming cultigens, plants whose origin or selection is primarily due to intentional human activity. It is also known as Cultivate ...''.Glossary in References Botanical nomenclature Plant taxonomy {{Botany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Top End
The Top End of Australia's Northern Territory is a geographical region encompassing the northernmost section of the Northern Territory, which aside from the Cape York Peninsula is the northernmost part of the Australian continent. It covers a rather vaguely defined area of about 245,000 km² (95,000 sq mi) behind the northern coast from the Northern Territory capital of Darwin across to Arnhem Land with the Indian Ocean on the west, the Arafura Sea to the north, and the Gulf of Carpentaria to the east, and with the almost waterless semi-arid interior of Australia to the south, beyond the huge Kakadu National Park. The Top End contains both of the Territory's cities and one of its major towns, Darwin, Palmerston and Katherine. The well-known town of Alice Springs is located further south, in the arid southern part of the Northern Territory, sometimes referred to by Australians as the Red Centre. The landscape is relatively flat with river floodplains and grasslands with eucaly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus Platypoda Fruit
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (''F. carica'') is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region (from Afghanistan to Portugal), which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses. Description ''Ficus'' is a pantropical genus of trees, shrubs, and vines occupying a wide variety of ecological niches; most are evergreen, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus Obliqua
''Ficus obliqua'', commonly known as the small-leaved fig, is a tree in the family Moraceae, native to eastern Australia, New Guinea, eastern Indonesia to Sulawesi and islands in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. Previously known for many years as ''Ficus eugenioides'', it is a banyan of the genus ''Ficus'', which contains around 750 species worldwide in warm climates, including the edible fig (''Ficus carica''). Beginning life as a seedling, which grows on other plants (epiphyte) or on rocks (lithophyte), ''F. obliqua'' can grow to high and nearly as wide with a pale grey buttressed trunk, and glossy green leaves. The small round yellow fruit ripen and turn red at any time of year, although ripening peaks in autumn and winter (April to July). Known as a syconium, the fruit is an inverted inflorescence with the flowers lining an internal cavity. ''Ficus obliqua'' is pollinated by two species of fig wasp—'' Pleistodontes greenwoodi'' and '' P. xanthocephalus''. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus Lilliputiana
''Ficus lilliputiana'' is a fig that is endemic to the Kimberleys and Kununurra in northwestern Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma .... It was first described in 2001 by Australian botanist Dale J. Dixon. References lilliputiana Desert fruits Drought-tolerant plants Rosids of Western Australia Rosales of Australia Trees of Australia {{Australia-rosid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus Subpuberula
''Ficus subpuberula'' is a lithophytic fig that is endemic to Australia. It ranges from extreme western Queensland, through the Northern Territory, into Western Australia Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th .... Description ''Ficus subpuberula'' is a monoecious tree which grows up to tall. Its leaves are long and wide. Its syconia are yellow, orange or red in colour, long and in diameter. References Trees of Australia Flora of Queensland Flora of the Northern Territory Rosids of Western Australia subpuberula Rosales of Australia Taxa named by E. J. H. Corner {{Australia-rosid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an states and territories of Australia, Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory shares its borders with Western Australia to the west (129th meridian east), South Australia to the south (26th parallel south), and Queensland to the east (138th meridian east). To the north, the territory looks out to the Timor Sea, the Arafura Sea and the Gulf of Carpentaria, including Western New Guinea and other islands of the Indonesian archipelago. The NT covers , making it the third-largest Australian federal division, and List of country subdivisions by area, the 11th-largest country subdivision in the world. It is sparsely populated, with a population of only 249,000 – fewer than half as many people as in Tasmania. The largest population center is the capital city of Darwin, Northern Territory, Darwin. The archaeological hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (abbreviated GAPDH) () is an enzyme of about 37kDa that catalyzes the sixth step of glycolysis and thus serves to break down glucose for energy and carbon molecules. In addition to this long established metabolic function, GAPDH has recently been implicated in several non-metabolic processes, including transcription activation, initiation of apoptosis, ER to Golgi vesicle shuttling, and fast axonal, or axoplasmic transport. In sperm, a testis-specific isoenzyme GAPDHS is expressed. Structure Under normal cellular conditions, cytoplasmic GAPDH exists primarily as a tetramer. This form is composed of four identical 37-kDa subunits containing a single catalytic thiol group each and critical to the enzyme's catalytic function. Nuclear GAPDH has increased isoelectric point (pI) of pH 8.3–8.7. Of note, the cysteine residue C152 in the enzyme's active site is required for the induction of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Notably, post-tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
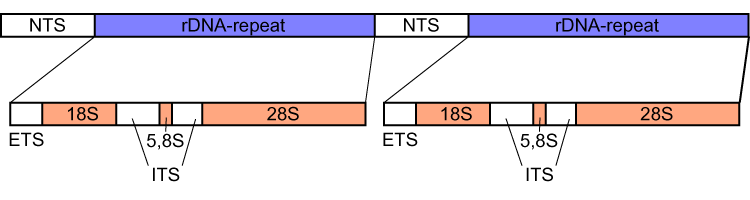
External Transcribed Spacer
External transcribed spacer (ETS) refers to a piece of non-functional RNA, closely related to the internal transcribed spacer, which is situated outside structural ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) on a common precursor transcript. ETS sequences characteristic to an organism can be used to trace its phylogeny A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec .... References {{genetics-stub DNA Phylogenetics de:Spacer (Biologie) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Transcribed Spacer
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. ITS across life domains In bacteria and archaea, there is a single ITS, located between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Conversely, there are two ITSs in eukaryotes: ITS1 is located between 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes, while ITS2 is between 5.8S and 28S (in opisthokonts, or 25S in plants) rRNA genes. ITS1 corresponds to the ITS in bacteria and archaea, while ITS2 originated as an insertion that interrupted the ancestral 23S rRNA gene. Organization In bacteria and archaea, the ITS occurs in one to several copies, as do the flanking 16S and 23S genes. When there are multiple copies, these do not occur adjacent to one another. Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid Sequence
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of Nucleobase, bases signified by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. By convention, sequences are usually presented from the Directionality (molecular biology), 5' end to the 3' end. For DNA, the Sense (molecular biology), sense strand is used. Because nucleic acids are normally linear (unbranched) polymers, specifying the sequence is equivalent to defining the covalent structure of the entire molecule. For this reason, the nucleic acid sequence is also termed the Biomolecular structure#Primary structure, primary structure. The sequence has capacity to represent information. Biological deoxyribonucleic acid represents the information which directs the functions of an organism. Nucleic acids also have a Nucleic acid secondary structure, secondary structure and Nucleic acid tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Primary structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |