|
Fertilizer Runoff
Agricultural wastewater treatment is a farm management agenda for controlling pollution from confined animal operations and from surface runoff that may be contaminated by chemicals in fertilizer, pesticides, animal slurry, crop residues or irrigation water. Agricultural wastewater treatment is required for continuous confined animal operations like milk and egg production. It may be performed in plants using mechanized treatment units similar to those used for industrial wastewater. Where land is available for ponds, settling basins and facultative lagoons may have lower operational costs for seasonal use conditions from breeding or harvest cycles. Animal slurries are usually treated by containment in anaerobic lagoons before disposal by spray or trickle application to grassland. Constructed wetlands are sometimes used to facilitate treatment of animal wastes. Nonpoint source pollution includes sediment runoff, nutrient runoff and pesticides. Point source pollution includes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Lagoon At Cal Poly
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to: * Anaerobic adhesive, a bonding agent that does not cure in the presence of air *Anaerobic respiration, respiration in the absence of oxygen, using some other molecule as the final electron acceptor **Anaerobic organism, any organism whose redox metabolism does not depend on free oxygen **Anammox, anaerobic ammonium oxidation, a globally important microbial process of the nitrogen cycle **Anaerobic filter, an anaerobic digester with a tank containing a filter medium where anaerobic microbes can establish themselves **Anaerobic digestion, the use of anaerobic bacteria to break down waste, with biogas as a byproduct ***Anaerobic clarigester, an anaerobic digester that treats dilute biodegradable feedstocks and allows different retention times for solids and liquids ***Anaer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion Control
Erosion control is the practice of preventing or controlling wind or water erosion in agriculture, land development, coast, coastal areas, Bank (geography), river banks and construction. Effective erosion controls handle surface runoff and are important techniques in preventing water pollution, soil erosion, soil loss, wildlife habitat loss and human property loss. Usage Erosion controls are used in natural areas, agricultural settings or urban environments. In urban areas erosion controls are often part of stormwater runoff management programs required by local governments. The controls often involve the creation of a physical barrier, such as vegetation or rock, to absorb some of the energy of the wind or water that is causing the erosion. They also involve building and maintaining storm drains. On construction sites they are often implemented in conjunction with sediment controls such as sediment basins and silt fences. Bank erosion is a natural process: without it, River, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, " watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of the drainage divide line. A drainage basin's boundaries are determined by watershed delineation, a common task in environmental engineering and science. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, rather than flowing to the ocean, water converges toward the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water pollution results when contaminants mix with these water bodies. Contaminants can come from one of four main sources. These are sewage discharges, industrial activities, agricultural activities, and urban runoff including stormwater. Water pollution may affect either surface water or groundwater pollution, groundwater. This form of pollution can lead to many problems. One is the environmental degradation, degradation of aquatic ecosystems. Another is spreading Waterborne diseases, water-borne diseases when people use polluted water for drinking or irrigation. Water pollution also reduces the ecosystem services such as drinking water provided by the Water resources, water resource. Sources of water pollution are either p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonpoint Source Pollution
Nonpoint source (NPS) pollution refers to diffuse contamination (or pollution) of water or air that does not originate from a single discrete source. This type of pollution is often the cumulative effect of small amounts of contaminants gathered from a large area. It is in contrast to point source pollution which results from a single source. Nonpoint source pollution generally results from land runoff, precipitation, atmospheric deposition, drainage, seepage, or hydrological modification (rainfall and snowmelt) where tracing pollution back to a single source is difficult. Nonpoint source water pollution affects a water body from sources such as polluted runoff from agricultural areas draining into a river, or wind-borne debris blowing out to sea. Nonpoint source air pollution affects air quality, from sources such as smokestacks or car tailpipes. Although these pollutants have originated from a point source, the long-range transport ability and multiple sources of the pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
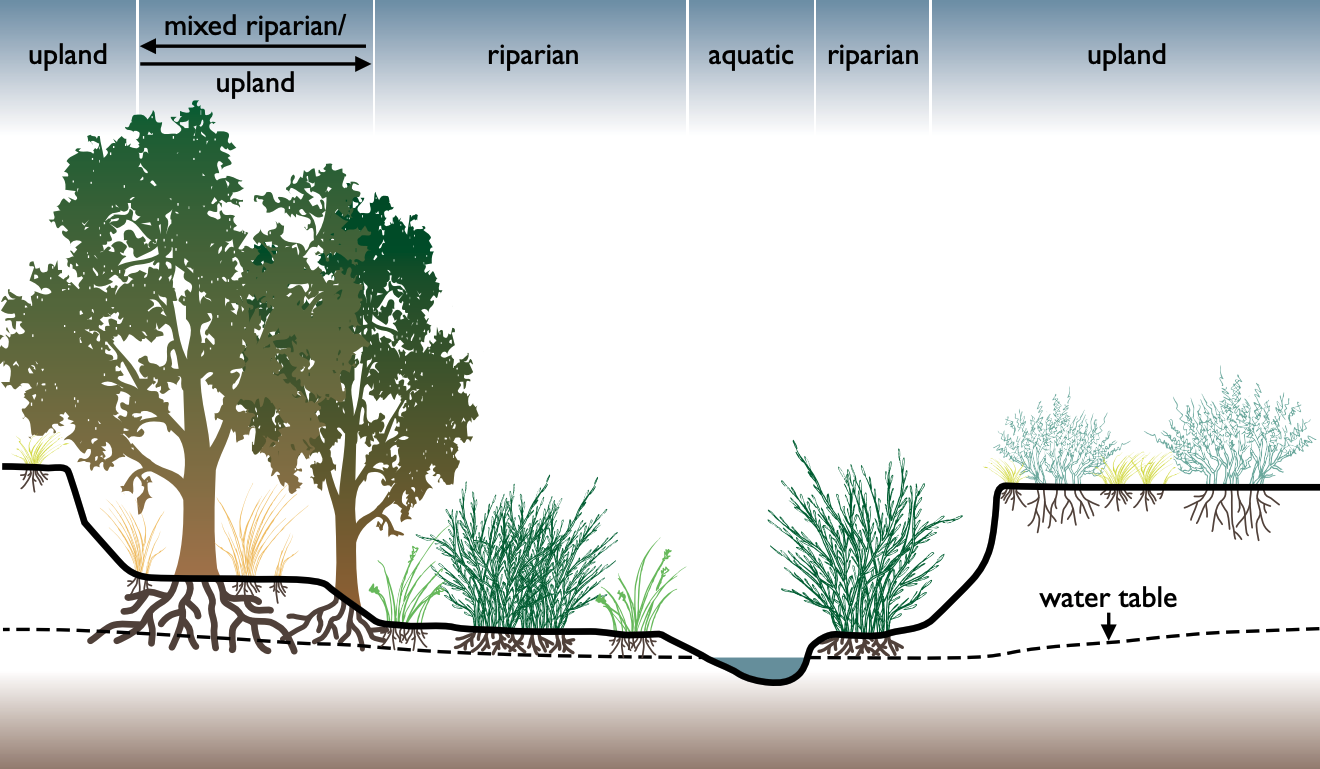
Riparian Buffer On Bear Creek In Story County, Iowa
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning "river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zones a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Pest Control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, whether pest animals such as insects and mites, weeds, or pathogens affecting animals or plants by using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs. There are three basic strategies for biological control: classical (importation), where a natural enemy of a pest is introduced in the hope of achieving control; inductive (augmentation), in which a large population of natural enemies are administered for quick pest control; and inoculative (conservation), in which measures are taken to maintain natural enemies through regular reestablishment. Natural enemies of insects play an important part in limiting the densities of potential pests. Biological control agents such as these include predators, parasitoids, pathogens, and com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM), also known as integrated pest control (IPC) integrates both chemical and non-chemical practices for economic control of pests. The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization defines IPM as "the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures that discourage the development of pest populations and keep pesticides and other interventions to levels that are economically justified and reduce or minimize risks to human health and the environment. IPM emphasizes the growth of a healthy crop with the least possible disruption to agro-ecosystems and encourages natural pest control mechanisms." Entomologists and ecologists have urged the adoption of IPM pest control since the 1970s. IPM is a safer pest control framework than reliance on the use of chemical pesticides, mitigating risks such as: insecticide-induced resurgence, pesticide resistance and (especially food) crop residues.Bateman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrient Pollution
Nutrient pollution is a form of water pollution caused by too many Nutrient, nutrients entering the water. It is a primary cause of eutrophication of surface waters (lakes, rivers and Coast, coastal waters), in which excess nutrients, usually nitrogen or phosphorus, stimulate algae, algal growth. Sources of nutrient pollution include surface runoff from farms, waste from septic tanks and feedlots, and air pollution, emissions from burning fuels. Raw sewage, which is rich in nutrients, also contributes to the issue when dumped in water bodies. Excess Reactive nitrogen, nitrogen causes environmental problems such as harmful algal blooms, Hypoxia (environmental), hypoxia, acid rain, nitrogen saturation in forests, and climate change. Agricultural production relies heavily on the use of natural and synthetic Fertilizer, fertilizers, which often contain high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. When nitrogen and phosphorus are not fully used by the growing plants, they can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrient Management
Nutrient management is the science and practice directed to link soil, crop, weather, and hydrologic factors with cultural, irrigation, and soil and water conservation practices to achieve optimal nutrient use efficiency, crop yields, crop quality, and economic returns, while reducing off-site transport of nutrients (fertilizer) that may impact the environment. It involves matching a specific field soil, climate, and crop management conditions to rate, source, timing, and place (commonly known as the 4R nutrient stewardship) of nutrient application. Important factors that need to be considered when managing nutrients include (a) the application of nutrients considering the achievable optimum yields and, in some cases, crop quality; (b) the management, application, and timing of nutrients using a budget based on all sources and sinks active at the site; and (c) the management of soil, water, and crop to minimize the off-site transport of nutrients from nutrient leaching out of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riparian Buffer
A riparian buffer or stream buffer is a vegetated area (a " buffer strip") near a stream, usually forested, which helps shade and partially protect the stream from the impact of adjacent land uses. It plays a key role in increasing water quality in associated streams, rivers, and lakes, thus providing environmental benefits. With the decline of many aquatic ecosystems due to agriculture, riparian buffers have become a very common conservation practice aimed at increasing water quality and reducing pollution. Benefits Riparian buffers act to intercept sediment, nutrients, pesticides, and other materials in surface runoff and reduce nutrients and other pollutants in shallow subsurface water flow. They also serve to provide habitat and wildlife corridors in primarily agricultural areas. They can also be key in reducing erosion by providing stream bank stabilization. Large scale results have demonstrated that the expansion of riparian buffers through the deployment of plantati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perennial Crop
Perennial crops are a perennial plant species that are cultivated and live longer than two years without the need of being replanted each year. Naturally perennial crops include many fruit and nut crops; some herbs and vegetables also qualify as perennial. Perennial crops have been cultivated for thousands of years; their cultivation differs from the mainstream Annual plants, annual agriculture because regular tilling is not required and this results in decreased soil erosion and increased soil health. Some perennial plants that are not cultivated as perennial crops are tomatoes, whose vines can live for several years but often freeze and die in winters outside of temperate climates, and potatoes which can live for more than two years but are usually harvested yearly. Despite making up 94% of plants on earth, perennials take up only 13% of global cropland. In contrast, grain crops take up about 70% of global cropland and global caloric consumption and are largely annual plants. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |