|
Ferryhill Railway Station
Ferryhill was a railway station located in Ferryhill in County Durham, Northeast England. It was located on what became the East Coast Main Line between and , close to the junctions with several former branches, including the extant freight-only Stillington Line to and . History The Clarence Railway reached the town of Ferryhill when its main line from Stockton and opened to mineral traffic on 16 January 1834, and was first served by passenger trains on 11 July 1835. The first station was developed by the Clarence on the current site in 1840, serving a town population of 850. The position was chosen as it lay close to both natural deposits of coal and limestone. The 1829 Clarence Railway Act gave the Clarence powers to construct branches to Wingate for the City of Durham, Sherburn and although only the latter of these ever reached its intended destinations. The Sherburn Branch was only opened as far as whilst the City of Durham Branch made it no further than Thrislingt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferryhill
Ferryhill is a town in County Durham, England, with an estimated population in 2018 of 9,362. The town grew in the 1900s around the coal mining industry. The last mine officially closed in 1968. It is located between the towns of Bishop Auckland, Newton Aycliffe, Sedgefield, Shildon, Spennymoor and the cathedral city of Durham. Geography Ferryhill sits on the western edge of the Ferryhill Gap, a natural gateway in limestone escarpment that outcrops on the Eastern Durham Plateau. The main settlement lies along the 'SW-NE' ridge, with later developments made to the south of the ridge. Ferryhill lies on the medieval Great North Road, which used to be the A1. It was bypassed when the Ferryhill Cut was excavated in 1923. The road is now the A167, which leads to Durham and Newcastle-upon-Tyne to the North, and to Darlington in the south. Ferryhill Carrs is a Site of Special Scientific Interest and designated Local Nature Reserve at the Eastern edge of the town. Sections of Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabteilung'' of the Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the ''Luftwaffe''s existence was publicly acknowledged on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a ''Luftwaffe'' detachment sent to aid Nationalist forces in the Spanish Civil War, provided the force with a valuable testing grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Axe
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965), written by Richard Beeching and published by the British Railways Board. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and 67,700 British Rail positions, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes for significant investment. The 1963 report also recommended some less well-publicised changes, including a switch to the now-standard practice of containerisation for rail freight, and the replacement of some services wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockton Railway Station (County Durham)
Stockton is a railway station on the Durham Coast Line, which runs between Newcastle and Middlesbrough via Hartlepool. The station, situated west of Middlesbrough, serves the market town of Stockton-on-Tees in County Durham, England. It is owned by Network Rail and managed by Northern Trains. Thornaby railway station (known as "South Stockton" until 1892), across the River Tees from Stockton-on-Tees provides a wider range of services and acts as the main railway station for most of Stockton-on-Tees. This station originally had a roof but it was removed in 1979 due to being in a bad state of repair and it has not been replaced since (the same work also saw the removal of redundant track & platforms). The other main buildings are also no longer in rail use, having been converted into apartments. Station facilities here have been improved and included new fully lit waiting shelters, digital information screens and the installation of CCTV. The long-line Public Address system (PA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Coal Board
The National Coal Board (NCB) was the statutory corporation created to run the nationalised coal mining industry in the United Kingdom. Set up under the Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946, it took over the United Kingdom's collieries on "vesting day", 1 January 1947. In 1987, the NCB was renamed the British Coal Corporation, and its assets were subsequently privatised. Background Collieries were taken under government control during the First and Second World Wars. The Sankey Commission in 1919 gave R. H. Tawney, Sidney Webb and Sir Leo Chiozza Money the opportunity to advocate nationalisation, but it was rejected. Coal reserves were nationalised during the war in 1942 and placed under the control of the Coal Commission, but the mining industry remained in private hands. At the time, many coal companies were small, although some consolidation had taken place in the years before the war. Formation and organisation The NCB was one of a number of public corporations cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainsforth Colliery
Mainsforth Colliery was situated between Ferryhill and the small hamlet of Mainsforth in County Durham, England, United Kingdom. It was adjacent to the former Ferryhill railway station in the Ferryhill Station area of the town. Mainsforth Colliery operated from 1872 to 1968, mining coal in the UK, deep underground. Name The name ‘Mainsforth’ is thought to mean the ford of someone called Maino (a Germanic name) and the ford probably crossed the boggy land called ‘The Carrs’ to the west. Operating life In 1872 Mainsforth Colliery opened. In 1873 two shafts, the East and the West, were sunk 270 ft to the Five Quarter seam. It was worked until 1876 before being laid in. These workings were abandoned by 1877 and the shafts used as a rubbish dump. 23 years later, in 1900 the Carlton Iron Company re-excavated the abandoned shafts and de-watered the workings. The Colliery reopened in 1904 and the company deepened the shafts to the Harvey seam and to prove the Busty and Bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coking Coal
Metallurgical coal or coking coal is a grade of coal that can be used to produce good-quality coke. Coke is an essential fuel and reactant in the blast furnace process for primary steelmaking. The demand for metallurgical coal is highly coupled to the demand for steel. Primary steelmaking companies often have a division that produces coal for coking, to ensure a stable and low-cost supply. Metallurgical coal comes mainly from Canada, the United States, and Australia, with Australia exporting 58% of seaborne trade, mostly going to China. In the United States, the electric power sector used "93% of total U.S. coal consumption between 2007 and 2018"; only 7% of the total was metallurgical coal and coal for other uses such as heating. Characteristics Metallurgical coal is low in ash, moisture, sulfur and phosphorus content, and its rank is usually bituminous. Some grades of anthracite coal are used for sintering, pulverized coal injection, direct blast furnace charge, pelleti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolckow Vaughan
Bolckow, Vaughan & Co., Ltd was an English steelmaking, ironmaking and mining company founded in 1864, based on the partnership since 1840 of its two founders, Henry Bolckow and John Vaughan (ironmaster), John Vaughan. The firm drove the dramatic growth of Middlesbrough and the production of coal and iron in the north-east of England in the 19th century. The two founding partners had an exceptionally close working relationship which lasted until Vaughan's death. By 1907 Bolckow, Vaughan was possibly the largest producer of pig iron in the world. The firm failed to modernise at the start of the 20th century, and was closed in 1929. History Origins, 1840–51 In 1840, Henry Bolckow (1806–1878) and John Vaughan (Ironmaster), John Vaughan (1799–1868) set up in business in Middlesbrough to make iron. They lived side by side in two town houses, the Cleveland Buildings, about away from their ironworks which were on Vulcan Street, and they married a pair of sisters, which may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London King's Cross Railway Station
King's Cross railway station, also known as London King's Cross, is a passenger railway terminus in the London Borough of Camden, on the edge of Central London. It is in the London station group, one of the List of busiest railway stations in Great Britain, busiest stations in the United Kingdom and the southern terminus of the East Coast Main Line to North East England and Scotland. Adjacent to King's Cross station is St Pancras railway station, St Pancras International, the London terminus for Eurostar services to continental Europe. Beneath both main line stations is King's Cross St Pancras tube station on the London Underground; combined they form one of the country's largest and busiest transport hubs. The station was opened in Kings Cross, London, Kings Cross in 1852 by the Great Northern Railway (Great Britain), Great Northern Railway on the northern edge of Central London to accommodate the East Coast Main Line. It quickly grew to cater for suburban lines and was expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
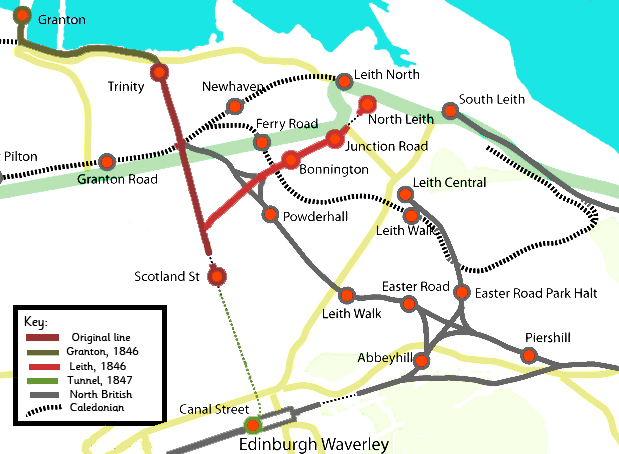
Edinburgh Waverley Railway Station
Edinburgh Waverley railway station (also known simply as Waverley; gd, Waverley Dhùn Èideann) is the principal railway station serving Edinburgh, Scotland. It is the second busiest station in Scotland, after Glasgow Central. It is the northern terminus of the East Coast Main Line, from , although some trains operated by London North Eastern Railway continue to other Scottish destinations beyond Edinburgh. Location Waverley station is situated in a steep, narrow valley between the medieval Old Town and the 18th century New Town. Princes Street, the premier shopping street, runs close to its north side. The valley is bridged by the North Bridge, rebuilt in 1897 as a three-span iron and steel bridge, on huge sandstone piers. This passes high above the station's central section, with the greater half of the station being west of North Bridge. The central booking hall is just west of the northern massive stone pier of the bridge and cleverly hides it within its bulk. Wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle And Darlington Junction Railway
The York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway (YN&BR) was an English railway company formed in 1847 by the amalgamation of the York and Newcastle Railway and the Newcastle and Berwick Railway. Both companies were part of the group of business interests controlled by George Hudson, the so-called ''Railway King''. In collaboration with the York and North Midland Railway and other lines he controlled, he planned that the YN&BR would form the major part of a continuous railway between London and Edinburgh. At this stage the London terminal was Euston Square (nowadays called Euston) and the route was through Normanton. This was the genesis of the East Coast Main Line, but much remained to be done before the present-day route was formed, and the London terminus was altered to King's Cross. The YN&BR completed the plans of its predecessors, including building a central passenger station in Newcastle, the High Level Bridge across the River Tyne, and the viaduct across the River Tweed, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |