|
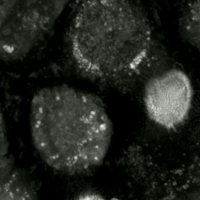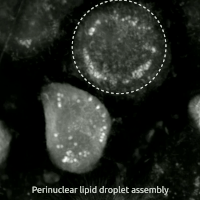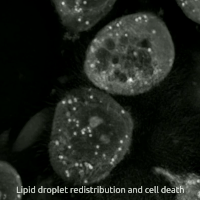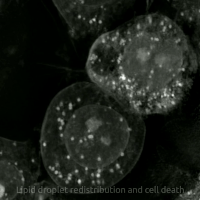
Ferroptosis Human Prostate Cancer Model
Ferroptosis is a type of programmed cell death dependent on iron and characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxides, and is genetically and biochemically distinct from other forms of regulated cell death such as apoptosis. Ferroptosis is initiated by the failure of the glutathione-dependent antioxidant defenses, resulting in unchecked lipid peroxidation and eventual cell death. Lipophilic antioxidants and iron chelators can prevent ferroptotic cell death. Although the connection between iron and lipid peroxidation has been appreciated for years, it was not until 2012 that Brent Stockwell and Scott J. Dixon coined the term ferroptosis and described several of its key features. Researchers have identified roles in which ferroptosis can contribute to the medical field, such as the development of cancer therapies. Ferroptosis activation plays a regulatory role on growth of tumor cells in the human body. However, the positive effects of ferroptosis could be potentially neutralize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmed Cell Death
Programmed cell death (PCD; sometimes referred to as cellular suicide) is the death of a cell as a result of events inside of a cell, such as apoptosis or autophagy. PCD is carried out in a biological process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's lifecycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and animal tissue development. Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death. Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Necrosis was long seen as a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury, but in the 2000s, a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, was recognized as an alternative form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorafenib
Sorafenib, sold under the brand name Nexavar, is a kinase inhibitor drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer (advanced renal cell carcinoma), advanced primary liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma), FLT3-ITD positive AML and radioactive iodine resistant advanced thyroid carcinoma. Mechanism of action Sorafenib is a protein kinase inhibitor with activity against many protein kinases, including VEGFR, PDGFR and RAF kinases. Of the RAF kinases, sorafenib is more selective for c-Raf than B-RAF. (See BRAF (gene)#Sorafenib for details the drug's interaction with B-Raf.) Sorafenib treatment induces autophagy, which may suppress tumor growth. Based on its 1,3-disubstituted urea structure, sorafenib is also a potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor and this activity likely reduces the severity of its adverse effects. Medical uses Sorafenib is indicated as a treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), unresectable hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) and thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an intracellular signaling pathway important in regulating the cell cycle. Therefore, it is directly related to cellular quiescence, proliferation, cancer, and longevity. PI3K activation phosphorylates and activates AKT, localizing it in the plasma membrane. AKT can have a number of downstream effects such as activating CREB, inhibiting p27, localizing FOXO in the cytoplasm, activating PtdIns-3ps, and activating mTOR which can affect transcription of p70 or 4EBP1. There are many known factors that enhance the PI3K/AKT pathway including EGF, shh, IGF-1, insulin, and CaM. Both leptin and insulin recruit PI3K signalling for metabolic regulation. The pathway is antagonized by various factors including PTEN, GSK3B, and HB9. In many cancers, this pathway is overactive, thus reducing apoptosis and allowing proliferation. This pathway is necessary, however, to promote growth and proliferation over differentiation of adult stem cells, neural stem cells sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase A
Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA), also known as high affinity nerve growth factor receptor, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1, or TRK1-transforming tyrosine kinase protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NTRK1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor (NTKR) family. This kinase is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon neurotrophin binding, phosphorylates itself (autophosphorylation) and members of the MAPK pathway. The presence of this kinase leads to cell differentiation and may play a role in specifying sensory neuron subtypes. Mutations in this gene have been associated with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis, self-mutilating behaviors, intellectual disability and/or cognitive impairment and certain cancers. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been found, but only three have been characterized to date. Function and Interaction with NGF TrkA is the high affinity cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Growth Factor
Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide primarily involved in the regulation of growth, maintenance, proliferation, and survival of certain target neurons. It is perhaps the prototypical growth factor, in that it was one of the first to be described. Since it was first isolated by Nobel Laureates Rita Levi-Montalcini and Stanley Cohen in 1956, numerous biological processes involving NGF have been identified, two of them being the survival of pancreatic beta cells and the regulation of the immune system. Structure NGF is initially in a 7S, 130-kDa complex of 3 proteins – Alpha-NGF, Beta-NGF, and Gamma-NGF (2:1:2 ratio) when expressed. This form of NGF is also referred to as proNGF (NGF precursor). The gamma subunit of this complex acts as a serine protease, and cleaves the N-terminal of the beta subunit, thereby activating the protein into functional NGF. The term ''nerve growth factor'' usually refers to the 2.5S, 26-kDa beta subunit of the protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Cervical Ganglion
The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS); more specifically, it is part of the sympathetic nervous system, a division of the ANS most commonly associated with the fight or flight response. The ANS is composed of pathways that lead to and from ganglia, groups of nerve cells. A ganglion allows a large amount of divergence in a neuronal pathway and also enables a more localized circuitry for control of the innervated targets. The SCG is the only ganglion in the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. It is the largest and most rostral (superior) of the three cervical ganglia. The SCG innervates many organs, glands and parts of the carotid system in the head. Structure Location The SCG is located opposite the second and third cervical vertebrae. It lies deep to the sheath of the internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein, and anterior to the Longus capitis muscle. The SCG contains neurons that supply sympathetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurodegeneration
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, and prion diseases. Neurodegeneration can be found in the brain at many different levels of neuronal circuitry, ranging from molecular to systemic. Because there is no known way to reverse the progressive degeneration of neurons, these diseases are considered to be incurable; however research has shown that the two major contributing factors to neurodegeneration are oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomedical research has revealed many similarities between these diseases at the subcellular level, including atypical protein assemblies (like proteinopathy) and induced cell death. These similarities suggest that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroglia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin in the peripheral nervous system, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells and satellite cells. Function They have four main functions: *to surround neurons and hold them in place *to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons *to insulate one neuron from another *to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. They also play a role in neurotransmission and synaptic connections, and in physiological processes such as breathing. While glia were thought to outnumber neurons by a ratio of 10:1, recent studies using newer methods and reappraisal of historical qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initiating branches of an adaptive immune response. Although mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live-cell Imaging
Live-cell imaging is the study of living cells using time-lapse microscopy. It is used by scientists to obtain a better understanding of biological function through the study of cellular dynamics. Live-cell imaging was pioneered in the first decade of the 21st century. One of the first time-lapse microcinematographic films of cells ever made was made by Julius Ries, showing the fertilization and development of the sea urchin egg. Since then, several microscopy methods have been developed to study living cells in greater detail with less effort. A newer type of imaging using quantum dots have been used, as they are shown to be more stable. The development of holotomographic microscopy has disregarded phototoxicity and other staining-derived disadvantages by implementing digital staining based on cells’ refractive index. Overview Biological systems exist as a complex interplay of countless cellular components interacting across four dimensions to produce the phenomenon calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystine/glutamate Transporter
Cystine/glutamate transporter is an antiporter that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC7A11'' gene. The SLC7A11 gene codes for a sodium-independent cystine- glutamate antiporter that is chloride dependent, known as system Xc- or xCT. It regulates synaptic activity by stimulating extrasynaptic receptors and performs nonvesicular glutamate release. This gene is highly expressed by astrocytes and couples the uptake of one molecule of cystine with the release of one molecule of glutamate. The dimer cystine gets taken up by glial cells and the monomer of cystine, cysteine, is taken up by neurons. The expression of Xc- was detected throughout the brain with higher expression found in the basolateral amygdala, the Retina and the prefrontal cortex. The inhibition of system Xc- has been found to alter a number of behaviors, which suggests that it plays a key role in excitatory signaling. Structure SLC7A11 is a member of a heterodimeric Na+-independent anionic amino acid transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelation
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a Denticity, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast medium, contrast agents in MRI, MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |