|
Ferenc Pfaff
Ferenc Pfaff (born as Franz Pfaff, Mohács, 19 November 1851 – Budapest, 21 August 1913) was a Hungarian architect and academic. Career Pfaff received his degree in 1880 after studying under Imre Steindl at the József Nádor Technical University in Budapest. Early in his career, he designed a number of smaller buildings, among which is the Roman Catholic church at Svábhegy. However, he is best known for his career as an architect with the Hungarian Railways. Joining in 1887, he later became director of building works right across the Hungarian lands within the Austro-Hungarian Empire. In the following two decades he would design some 20 large, and numerous smaller railway stations, mainly in the Renaissance eclectic style. These buildings were often modest but notable for their fine sense of proportion and scale. He also redesigned a number of existing stations, notably in Croatia (Zagreb and Rijeka) and in Hungary (Győr, Kassa and Miskolc). Railway stations * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hungary (1526–1867)
The Kingdom of Hungary between 1526 and 1867 existed as a state outside the Holy Roman Empire, but part of the lands of the Habsburg monarchy that became the Austrian Empire in 1804. After the Battle of Mohács in 1526, the country was ruled by two crowned kings (John Zápolya, John I and Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I). Initially, the exact territory under Habsburg rule was disputed because both rulers claimed the whole kingdom. This unsettled period lasted until 1570 when John Sigismund Zápolya (John II) abdicated as King of Hungary in Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Maximilian II's favor. In the early stages, the lands that were ruled by the Habsburg Hungarian kings were regarded as both the "Kingdom of Hungary" and "Royal Hungary". Royal Hungary was the symbol of the continuity of formal law after the Ottoman occupation, because it could preserve its legal traditions, but in general, it was ''de facto'' a Habsburg province.Raphael PataThe Jews of Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg , image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg , anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland") , image_map = , map_caption = , capital = Zagreb , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Croatian , languages_type = Writing system , languages = Latin , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2021 , religion = , religion_year = 2021 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Zoran Milanović , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Andrej Plenković , leader_title3 = Speaker of Parliament , leader_name3 = Gordan Jandroković , legislature = Sabor , sovereignty_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
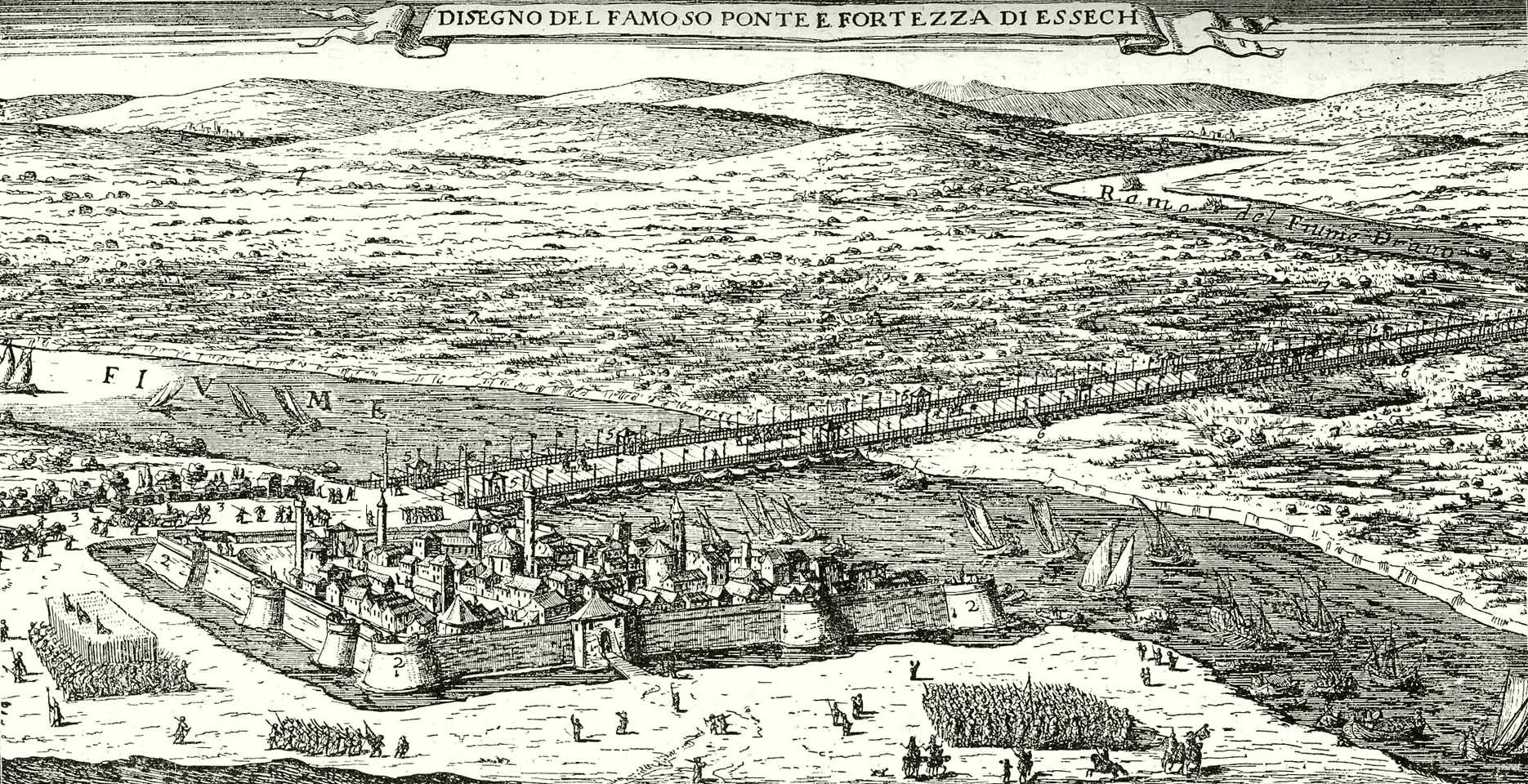
Osijek
Osijek () is the fourth-largest city in Croatia, with a population of 96,848 in 2021. It is the largest city and the economic and cultural centre of the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia, as well as the administrative centre of Osijek-Baranja County. Osijek is located on the right bank of the Drava River, upstream of its confluence with the Danube, at an elevation of . Name The name was given to the city due to its position on elevated ground, which prevented the city being flooded by the local swamp waters. Its name "Osijek" derives from the Croatian word ''oseka'', which means "ebb tide". Due to its history within the Habsburg monarchy and briefly in the Ottoman Empire, as well as the presence of German, Hungarian, and Serbian minorities throughout its history, Osijek has (or had) its names in other languages, Осек/Osek or Осијек/Osijek in Serbian, Hungarian: ''Eszék'', german: link=no, Esseg or Essegg, tr, Ösek, la, Essek. It is also spelled ''Esgek''. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debrecen
Debrecen ( , is Hungary's second-largest city, after Budapest, the regional centre of the Northern Great Plain region and the seat of Hajdú-Bihar County. A city with county rights, it was the largest Hungarian city in the 18th century and it is one of the Hungarian people's most important cultural centres.Antal Papp: Magyarország (Hungary), Panoráma, Budapest, 1982, , p. 860, pp. 463-477 Debrecen was also the capital city of Hungary during the revolution in 1848–1849. During the revolution, the dethronement of the Habsburg dynasty was declared in the Reformed Great Church. The city also served as the capital of Hungary by the end of World War II in 1944–1945. It is home of the University of Debrecen. Etymology The city is first documented in 1235, as ''Debrezun''. The name derives from the Turkic word , which means 'live' or 'move' and is also a male given name. Another theory says the name is of Slavic origin and means 'well-esteemed', from Slavic Dьbricinъ or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chop Railway Station
Chop ( uk, Чоп, hu, Csap) is a railway station that is located in a small city of Chop, Zakarpattia Oblast in Ukraine. It is part of the Uzhhorod administration (Lviv Railways). General description The station is an important transportation hub and gateway to Ukraine. There are two border checkpoints: Strazh for Slovakia and Druzhba for Hungary. The station serves passengers and freight trains. Among the services provided at the station is only embarkment and disembarkment of passengers for commuter and regional lines. Locomotive depot The station also contains a locomotive depot that services locomotives. Currently there are no locomotive units assigned to the depot and all M62, ChME3, and D1 multiple units were transferred either to Mukacheve or Koroleve locomotive depots. Gallery File:Railway station cop ukraine.JPG, Railway station building File:Bogie change station at Chop station Ukraine.jpg, Bogie exchange station for track gauge transition File:Electric locomotive VL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celldömölk
Celldömölk (german: Kleinmariazell) is the fifth largest town in Vas County, Hungary. Parts of the Eragon movie were filmed here. The town with 11,000 inhabitants can be found in the centre of Kemenesalja Hills. History Celldömölk has a history older than 750 years. On the western boundaries of the town, there are the remains of the abbey built in the 12th century in Roman style. Before World War II, there was a large Jewish community. Most of the Jews in the community were deported by the Hungarian Nyilaskeresztes Párt as part of the Hungarian cleansing during The Holocaust. On 7 October 1944 the 2nd BG was seeking a target of opportunity bombed the railroad junction with 5 x 1,000 GP bombs. The B-17's were returning from the primary at Wien-Lobau Shell oil blending plant which was partially obscured. Sights The Virgin Mary Roman Catholic Church was built between 1747 and 1748, while the Way of the Cross was built in 1755, with a small place with a shrine of Virgin Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arad Central Railway Station
Arad Central railway station ( ro, Gara Centrală din Arad) is the largest railway station in the city of Arad, and the largest in the Arad County. It is the second largest railway station in the western region of Romania, immediately after Timișoara Nord railway station. History The main building was designed by Hungarian architect Ferenc Pfaff, when Arad was a major city of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Operators The station is being served by the national operator CFR, which owns the station building and infrastructure, and the private operator Regiotrans. Arad Central services are in majority connected to the CFR 200 Main Line from Brașov/ Bucureṣti Nord to Curtici. The Arad–Curtici line is the main railway link to Western Europe toward Budapest Keleti. ICN/IC services International IR services Lines * Line 200 : Curtici–Arad–Deva–Vințu de Jos–Sibiu–Făgăraș–Brașov (to Bucharest it continues as the 1000 main line) * Line 215 : Arad– Arad Vest� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gara Jimbolia
''Gara'' (Basque: ''We Are'') is a bilingual (Basque/Spanish) newspaper published in the city of Donostia-San Sebastián in the Basque Autonomous Community. The newspaper's target market comprises the area of the Basque Country, but its circulation is largely constrained to the Southern Basque territory (Spain), since Spanish is mainly used. Gara, the third most-read newspaper in the Basque Autonomous Community and Navarre, was first published on 30 January 1999 as successor to the leftist and Basque nationalist newspaper ''Egin'', which had been shut down by the noted prosecuting judge Baltasar Garzón in a highly controversial move on 15 July 1998. The case was dismissed and defendants acquitted, with the final verdict stating that no illicit activity was engaged by Egin (2009). On 12 March 2004, ETA denied in a communique to Gara and the Basque public broadcaster EITB its involvement in the March 11, 2004 Madrid attacks. In July 2008, the newspaper denounced that its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miskolc
Miskolc ( , , ; Czech language, Czech and sk, Miškovec; german: Mischkolz; yi, script=Latn, Mishkoltz; ro, Mișcolț) is a city in northeastern Hungary, known for its heavy industry. With a population of 161,265 (1 Jan 2014) Miskolc is the List of cities and towns in Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, fourth largest city in Hungary (behind Budapest, Debrecen, and Szeged). It is also the county capital of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén and the Regions of Hungary, regional centre of Northern Hungary. Etymology The name derives from ''Miško'', Slavic languages, Slavic form of Michael (given name), Michael. ''Miškovec'' → ''Miskolc'' with the same development as ''Lipovec'' → ''Lipólc'', ''Lipóc''. The name is associated with the Miskolc (genus), Miskolc clan (also Miskóc or Myscouch, Slovak language, Slovak Miškovec, plural Miškovci) named after the settlement or vice versa. Earliest mentions are ''que nunc vocatur Miscoucy'' (around 1200), ''de Myschouch'' (1225), ''Ponyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Košice
Košice ( , ; german: Kaschau ; hu, Kassa ; pl, Коszyce) is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest city in Slovakia, after the capital Bratislava. Being the economic and cultural centre of eastern Slovakia, Košice is the seat of the Košice Region and Košice Self-governing Region, and is home to the Slovak Constitutional Court, three universities, various dioceses, and many museums, galleries, and theatres. In 2013 Košice was the European Capital of Culture, together with Marseille, France. Košice is an important industrial centre of Slovakia, and the U.S. Steel Košice steel mill is the largest employer in the city. The town has extensive railway connections and an international airport. The city has a preserved historical centre which is the largest among Slovak towns. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |