|
Felipe De Neve (Gobernador De Las Californias)
Felipe de Neve y Padilla (1724 – 3 November 1784) was a Spanish soldier who served as the 4th Governor of the Californias, from 1775 to 1782. Neve is one of the founders of Los Angeles and was instrumental in the foundation of San Jose and Santa Barbara. Biography Early life Born in Bailén, Spain, Neve was the son of Mary D. Padilla y Costilla and Felipe de Neve Noguera Castro y Figueroa and was born into one of the well-respected families of Andalucia. Neve entered the military in 1744 at about 16 years of age. Neve served as a soldier in Cantabria, Flanders, Milan, and Portugal before arriving in New Spain. During his time as a major he administered the colleges of Zacatecas, New Spain. Neve was appointed as acting Governor of Las Californias on October 18, 1774 by Viceroy Antonio Maria de Buareli y Ursua. For the first two years of his appointment, Neve was based in Loreto, Baja California and later moved to Monterey. Las Californias It was during Neve's administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles III Of Spain
it, Carlo Sebastiano di Borbone e Farnese , house = Bourbon-Anjou , father = Philip V of Spain , mother = Elisabeth Farnese , birth_date = 20 January 1716 , birth_place = Royal Alcazar of Madrid, Spain , death_date = , death_place = Royal Palace of Madrid, Spain , place of burial= El Escorial , religion = Roman Catholicism , signature = Autograph Charles III of Spain.svg Charles III (born Charles Sebastian; es, Carlos Sebastián; 20 January 1716 – 14 December 1788) was King of Spain (1759–1788). He also was Duke of Parma and Piacenza, as Charles I (1731–1735); King of Naples, as Charles VII, and King of Sicily, as Charles V (1734–1759). He was the fifth son of Philip V of Spain, and the eldest son of Philip's second wife, Elisabeth Farnese. A proponent of enlightened absolutism and regalism, he succeeded to the Spanish throne on 10 August 1759, upon the death of his childless half-brother Ferdinand VI. In 1731, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacatecas
, image_map = Zacatecas in Mexico (location map scheme).svg , map_caption = State of Zacatecas within Mexico , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Mexico , subdivision_type1 = Capital , subdivision_name1 = Zacatecas , subdivision_type2 = Municipalities , subdivision_name2 = 58 , established_title = Admission , established_date = December 23, 1823 , established_title2 = Order , established_date2 = 10th , founder = , seat_type = , seat = , government_footnotes = , leader_party = , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = David Monreal Ávila , leader_title1 = Senators , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = Deputies , leader_name2 = , unit_pref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
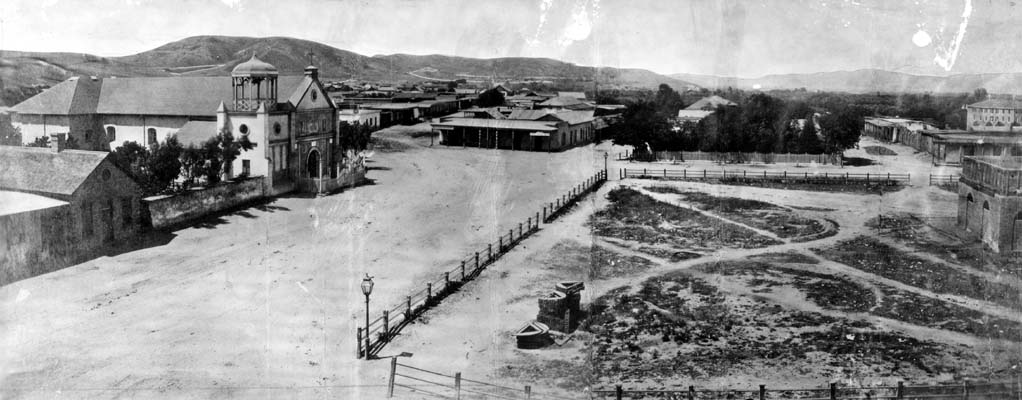
Pueblo De Los Ángeles
El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles (English language, English: ''The town of Our Lady the Queen of the Angels''), shortened to Pueblo de los Ángeles, was the Spanish civilian ''Municipality, pueblo'' settled in 1781, which by the 20th century became the American metropolis of Los Angeles. The pueblo was built using labor from the adjacent village of Yaanga and was totally dependent on local Indigenous peoples of California, Indigenous labor for its survival. Official settlements in Alta California were of three types: ''presidio'' (military), ''Spanish missions in California, mission'' (religious) and ''pueblo'' (civil). The Pueblo de los Ángeles was the second pueblo (town) created during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonization of California (the first was History of San Jose, California#First Spanish pueblo in California San José/, San Jose, in 1777). —'The Town of the Queen of Angels' was founded twelve years after the first '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidio Of Monterey
The Presidio of Monterey (POM), located in Monterey, California, is an active US Army installation with historic ties to the Spanish colonial era. Currently, it is the home of the Defense Language Institute Foreign Language Center (DLI-FLC). It is the last and only Presidio in California to have an active military installation. History The Spanish explorer Sebastián Vizcaíno visited, named and charted Monterey Bay (especially the southern end) in 1602. In his official report, Vizcaíno recommended the natural harbor he found as an appropriate site for a seaport, military fortification and colonization. It would be over 150 years, until news of Pacific Coast moves by Spain's European rivals brought the remote area back to the attention of the leaders of New Spain. José de Gálvez's grand plan In 1768, José de Gálvez, special deputy (''visitador'') of King Carlos III in New Spain (Mexico), received this order: "Occupy and fortify San Diego and Monterey for God and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was split off into a separate province in 1804 (named ). Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed in 1824. The territory included all of the modern U.S. states of California, Nevada, and Utah, and parts of Arizona, Wyoming, Colorado, and New Mexico. In the 1836 Siete Leyes government reorganization, the two Californias were once again combined (as a single ). That change was undone in 1846, but rendered moot by the U.S. military occupation of California in the Mexican-American War. Neither Spain nor Mexico ever colonized the area beyond the southern and central coastal areas of present-day California and small areas of present-day Arizona, so they exerted no effective cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Californias
The Californias (Spanish: ''Las Californias''), occasionally known as The Three Californias or Two Californias, are a region of North America spanning the United States and Mexico, consisting of the U.S. state of California and the Mexican states of Baja California and Baja California Sur. Historically, the term ''Californias'' was used to define the vast northwestern region of Spanish America, as the ''Province of the Californias'' ( es, Provincia de las Californias), and later as a collective term for Alta California and the Baja California Peninsula. Originally a single, vast entity within the Spanish Empire, as the Californias became defined in their geographical limits, their administration was split various times into Baja California (''Lower California'') and Alta California (''Upper California''), especially during the Mexican control of the region, following the Mexican War of Independence. As a part of the Mexican–American War (1846–48), the American Conquest of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of New Spain
The following is a list of Viceroys of New Spain. In addition to viceroys, the following lists the highest Spanish governors of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, before the appointment of the first viceroy or when the office of viceroy was vacant. Most of these individuals exercised most or all of the functions of viceroy, usually on an interim basis. Governor of the West Indies This office covered the territories that were discovered by Christopher Columbus. : 1492–1499 – Christopher Columbus, as governor and viceroy of the West Indies : 1499–1502 – Francisco de Bobadilla, as governor of the West Indies : 1502–1509 – Nicolás de Ovando y Cáceres, as governor of the West Indies : 1509–1518 – Diego Columbus, as governor of the West Indies until 1511, thereafter as viceroy Governor of New Spain This office covered the territories that were claimed by Hernán Cortés. The office covered the territories that were under the control of the Governor of the Indies after 152 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio María De Bucareli Y Ursúa
Antonio is a masculine given name of Etruscan origin deriving from the root name Antonius. It is a common name among Romance language-speaking populations as well as the Balkans and Lusophone Africa. It has been among the top 400 most popular male baby names in the United States since the late 19th century and has been among the top 200 since the mid 20th century. In the English language it is translated as Anthony, and has some female derivatives: Antonia, Antónia, Antonieta, Antonietta, and Antonella'. It also has some male derivatives, such as Anthonio, Antón, Antò, Antonis, Antoñito, Antonino, Antonello, Tonio, Tono, Toño, Toñín, Tonino, Nantonio, Ninni, Totò, Tó, Tonini, Tony, Toni, Toninho, Toñito, and Tõnis. The Portuguese equivalent is António (Portuguese orthography) or Antônio (Brazilian Portuguese). In old Portuguese the form Antão was also used, not just to differentiate between older and younger but also between more and less important. In Galician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of San Jose, California
San Jose, California, is the third largest city in the state, and the largest of all cities in the San Francisco Bay Area and Northern California, with a population of 1,021,795. Site chosen by Anza For thousands of years before the arrival of European settlers, the area now known as San Jose was inhabited by several groups of Ohlone Native Americans. Permanent European presence in the area came with the 1770 founding of the Presidio of Monterey and Mission San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo by Gaspar de Portolà and Junípero Serra, about sixty miles (100 km) to the south. Don Pedro Fages, the military governor at Monterey, passed through the area on his 1770 and 1772 expeditions to explore the East Bay and Sacramento River Delta. Late in 1775, Juan Bautista de Anza led the first overland expedition to bring colonists from New Spain (Mexico) to California and to locate sites for two missions, one presidio, and one pueblo (town). He left the colonists at Monterey in 1776, and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Bautista De Anza
Juan Bautista de Anza Bezerra Nieto (July 6 or 7, 1736 – December 19, 1788) was an expeditionary leader, military officer, and politician primarily in California and New Mexico under the Spanish Empire. He is credited as one of the founding fathers of Spanish California and served as an official within New Spain as Governor of the Province of New Mexico. Early life Juan Bautista de Anza Bezerra Nieto was born in Fronteras, New Navarre, New Spain (today Sonora, Mexico) in 1736 (near Arizpe), most probably at Cuquiarachi, Sonora, but possibly at the Presidio of Fronteras. His family was a part of the military leadership in Nueva España, as his father and maternal grandfather, Captain Antonio Bezerra Nieto, had both served Spain, their families living on the frontier of Nueva Navarre. He was the son of Juan Bautista de Anza I. It is traditionally thought that he may have been educated at the College of San Ildefonso in Mexico City, and later at the military academy there. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
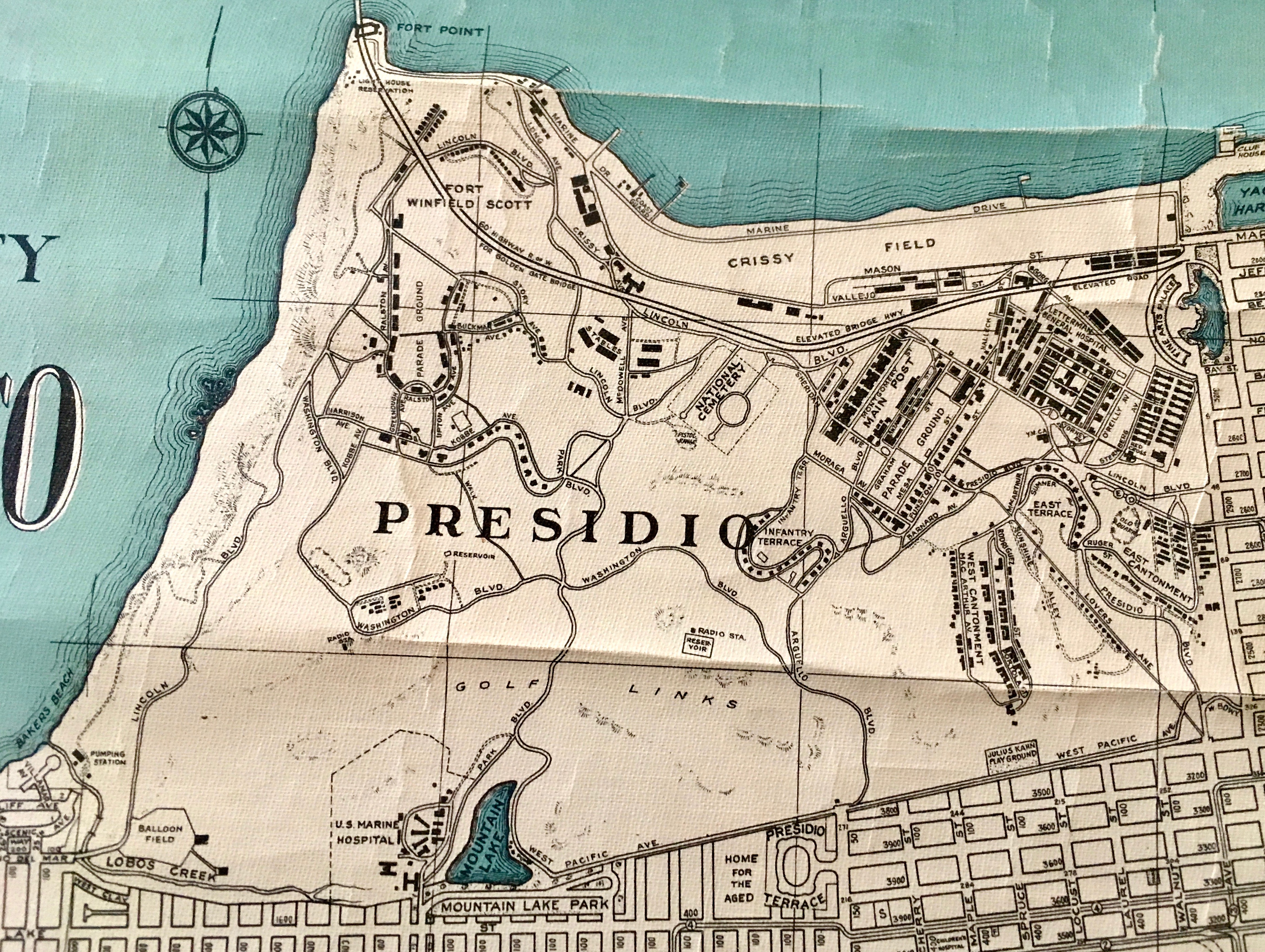
Presidio Of San Francisco
The Presidio of San Francisco (originally, El Presidio Real de San Francisco or The Royal Fortress of Saint Francis) is a park and former U.S. Army post on the northern tip of the San Francisco Peninsula in San Francisco, California, and is part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. It had been a fortified location since September 17, 1776, when New Spain established the presidio to gain a foothold in Alta California and the San Francisco Bay. It passed to Mexico in 1820, which in turn passed it to the United States in 1848. As part of a 1989 military reduction program under the Base Realignment and Closure ( BRAC) process, Congress voted to end the Presidio's status as an active military installation of the U.S. Army. On October 1, 1994, it was transferred to the National Park Service, ending 219 years of military use and beginning its next phase of mixed commercial and public use. In 1996, the United States Congress created the Presidio Trust to oversee and manage the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Joaquín Moraga
José Joaquín de la Santísima Trinidad Moraga (22 August 1745 – 13 July 1785), usually simply known as José Joaquín Moraga, was a Spanish colonial expeditionary and soldier who founded San Jose, California, in 1777. Life José Joaquín Moraga was born on August 22, 1745 at Mission Los Santos Ángeles de Guevavi, New Navarre, Viceroyalty of New Spain (in present-day Santa Cruz County, Arizona). Moraga was second in command to Juan Bautista de Anza in the 1776 overland colonizing expedition from the region of Alta California which would become part of southern Arizona and northern Mexico, to what is now San Francisco, California. When de Anza returned south to the established base in 1777, Moraga was left in charge of efforts to build housing for the colonists and a military headquarters, the Presidio of San Francisco. Moraga founded the Pueblo of San José on orders from Antonio María de Bucareli y Ursúa, Spanish Viceroy of New Spain. The pueblo was founded in honor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
_(cropped).gif)


.jpg)