|
Fedora Project
The Fedora Project is an independent project to coordinate the development of Fedora Linux, a Linux-based operating system, operating with the mission of creating "''an innovative platform for hardware, clouds, and containers that enables software developers and community members to build tailored solutions for their users''". The project also oversees Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux, a special interest group which maintains the eponymous packages. The project was founded in 2003 as a result of a merger between the Red Hat Linux (RHL) and Fedora Linux projects. It is sponsored by Red Hat primarily, but its employees make up only 35% of project contributors, and most of the over 2,000 contributors are unaffiliated members of the community. History The Fedora Project was founded in November 2003 when Red Hat decided to split Red Hat Linux into Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and a community-based operating system, FedoraRed Hat Professional Workstationwas created at this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina, with other offices worldwide. Red Hat has become associated to a large extent with its enterprise operating system Red Hat Enterprise Linux. With the acquisition of open-source enterprise middleware vendor JBoss, Red Hat also offers Red Hat Virtualization (RHV), an enterprise virtualization product. Red Hat provides storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, management products, support, training, and consulting services. Red Hat creates, maintains, and contributes to many free software projects. It has acquired the codebases of several proprietary software products through corporate mergers and acquisitions, and has released such software under open source licenses. , Red Hat is the second largest co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Of Things
Internet of things (IoT) describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communication networks. The IoT encompasses Electronic engineering, electronics, Telecommunications engineering, communication, and computer science engineering. "Internet of things" has been considered a misnomer because devices do not need to be connected to the public internet; they only need to be connected to a network and be individually addressable. The field has evolved due to the convergence of multiple technologies, including ubiquitous computing, commodity sensors, and increasingly powerful embedded systems, as well as machine learning.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Fault-tolerant cooperative navigation of networked UAV swarms for forest fire monitoring Aerospace Science and Technology, 2022. . Older fields of embedded systems, wireless sensor netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Derivatives
Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives are Linux distributions that are based on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) Linux distribution. History Red Hat Linux was a popular Linux distribution largely because, while there was a paid-for supported version, a freely downloadable one was also available. Since the only difference between the paid-for option and the free option was support, a great number of people chose to use the free version. In 2003, Red Hat made the decision to change its Red Hat Linux product into Red Hat Enterprise Linux for customers who were willing to pay for it. A community-driven Red Hat based Linux distribution called Fedora was available free of charge. Fedora has its own beta cycle and has some issues fixed by contributors, who occasionally included Red Hat staff. However, its quick and nonconservative release cycle means it might not be suitable for some users. Today, Fedora serves as the primary upstream development branch for CentOS Stream, and in tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hackathon
A hackathon (also known as a hack day, hackfest, datathon or codefest; a portmanteau of '' hacking'' and ''marathon'') is an event where people engage in rapid and collaborative engineering over a relatively short period of time such as 24 or 48 hours. They are often run using agile software development practices, such as sprint-like design wherein computer programmers and others involved in software development, including graphic designers, interface designers, product managers, domain experts, and others collaborate intensively on engineering projects, such as software engineering. The goal of a hackathon is to create functioning software or hardware by the end of the event. Hackathons tend to have a specific focus, which can include the programming language used, the operating system, an application, an API, or the subject and the demographic group of the programmers. In other cases, there is no restriction on the type of software being created or the design of the new syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flock
Flock, flocks or flocking may refer to: * Flock (birds), a gathering of individual birds to forage or travel collectively Arts and entertainment Music * ''Flock'' (Bell X1 album), 2005 * ''Flock'' (Jane Weaver album), 2021 * The Flock (band), an American jazz rock band 1969–1970 ** ''The Flock'' (album), 1969 * ''Flock: The Best of the Mutton Birds'', a 2002 compilation album by The Mutton Birds Gaming * '' Flock!'', a 2009 video game * ''The Flock'' (video game), a 2015 multiplayer-only survival horror video game * ''Flock'' (video game), a 2024 video game published by Annapurna Interactive Other uses in arts and entertainment * Flock (sculpture), by Michael Christian, 2001 * ''The Flock'' (film), a 2007 film starring Richard Gere * ''Flocking'' (film), a 2015 Swedish film * ''The Flock'', a 2006 novel by James Robert Smith * ''Flock'' (literary journal), formerly ''Fiction Fix'' * Flock, a fictional character in '' Doraemon: Nobita's Treasure Island'' People * Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president (government title), president or monarch vetoes a bill (law), bill to stop it from becoming statutory law, law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto powers are also found at other levels of government, such as in state, provincial or local government, and in international bodies. Some vetoes can be overcome, often by a supermajority vote: Veto power in the United States, in the United States, a two-thirds vote of the United States House of Representatives, House and United States Senate, Senate can override a presidential veto.Article One of the United States Constitution#Clause 2: From bills to law, Article I, Section 7, Clause 2 of the United States Constitution Some vetoes, however, are absolute and cannot be overridden. For example, United Nations Security Council veto power, in the United Nations Security Council, the five per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trojan Horse (computing)
In computing, a trojan horse (or simply trojan; often capitalized, but see below) is a kind of malware that misleads users as to its true intent by disguising itself as a normal program. Trojans are generally spread by some form of social engineering (security), social engineering. For example, a user may be duped into executing an email attachment disguised to appear innocuous (e.g., a routine form to be filled in), or into clicking on a fake advertisement on the Internet. Although their payload can be anything, many modern forms act as a backdoor (computing), backdoor, contacting a controller who can then have unauthorized access to the affected device. Ransomware attacks are often carried out using a trojan. Unlike computer viruses and Computer worm, worms, trojans generally do not attempt to inject themselves into other files or otherwise propagate themselves. Origins of the term The term is derived from the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek story of the deceptive Trojan Horse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
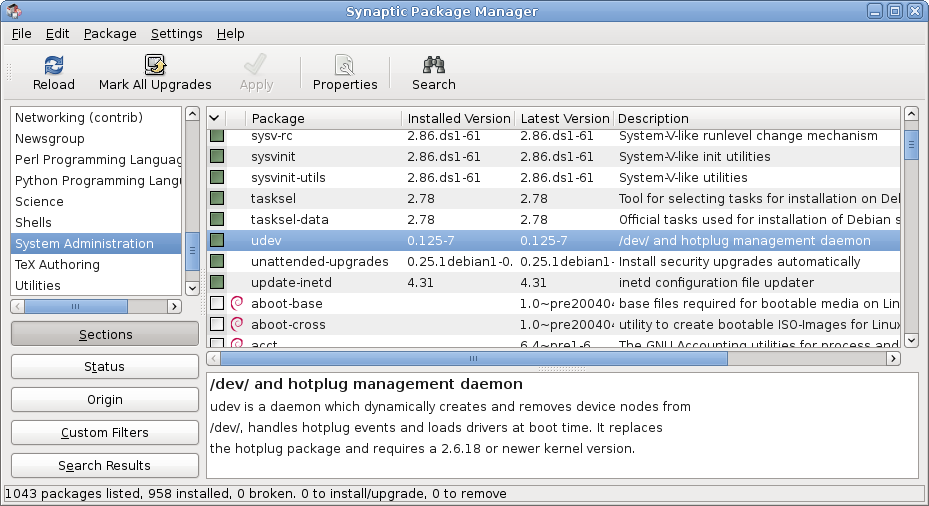
Software Package (installation)
A package manager or package management system is a collection of programming tool, software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with package format, ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of coupling (computer programming), dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repository, software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Containerization (computing)
In software engineering, containerization is operating-system-level virtualization or application-level virtualization over multiple network resources so that software applications can run in isolated user spaces called ''containers'' in any cloud or non-cloud environment, regardless of type or vendor. The term "container" is overloaded, and it is important to ensure that the intended definition aligns with the audience's understanding. Usage Each ''container'' is basically a fully functional and portable cloud or non-cloud computing environment surrounding the application and keeping it independent of other environments running in parallel. Individually, each container simulates a different software application and runs isolated processes by bundling related configuration files, libraries and dependencies. But, collectively, multiple containers share a common operating system kernel (OS). In recent times, containerization technology has been widely adopted by cloud computing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fedora Linux
Fedora Linux is a Linux distribution developed by the Fedora Project. It was originally developed in 2003 as a continuation of the Red Hat Linux project. It contains software distributed under various free and open-source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of open-source technologies. It is now the upstream source for CentOS Stream and Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Since the release of Fedora 21 in December 2014, three editions have been made available: personal computer, server and cloud computing. This was expanded to five editions for containerization and Internet of Things (IoT) as of the release of Fedora 37 in November 2022. A new version of Fedora Linux is released every six months. , Fedora Linux has an estimated 1.2 million users, and is also the distribution used by Linus Torvalds, creator of the Linux kernel (). Features Fedora has a reputation for focusing on innovation, integrating new technologies early on and working closely with upstream Linux commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |