|
Federally Recognized Native American Tribes
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.Federal Acknowledgment of the Pamunkey Indian Tribe Of these, 228 are located in Alaska. Description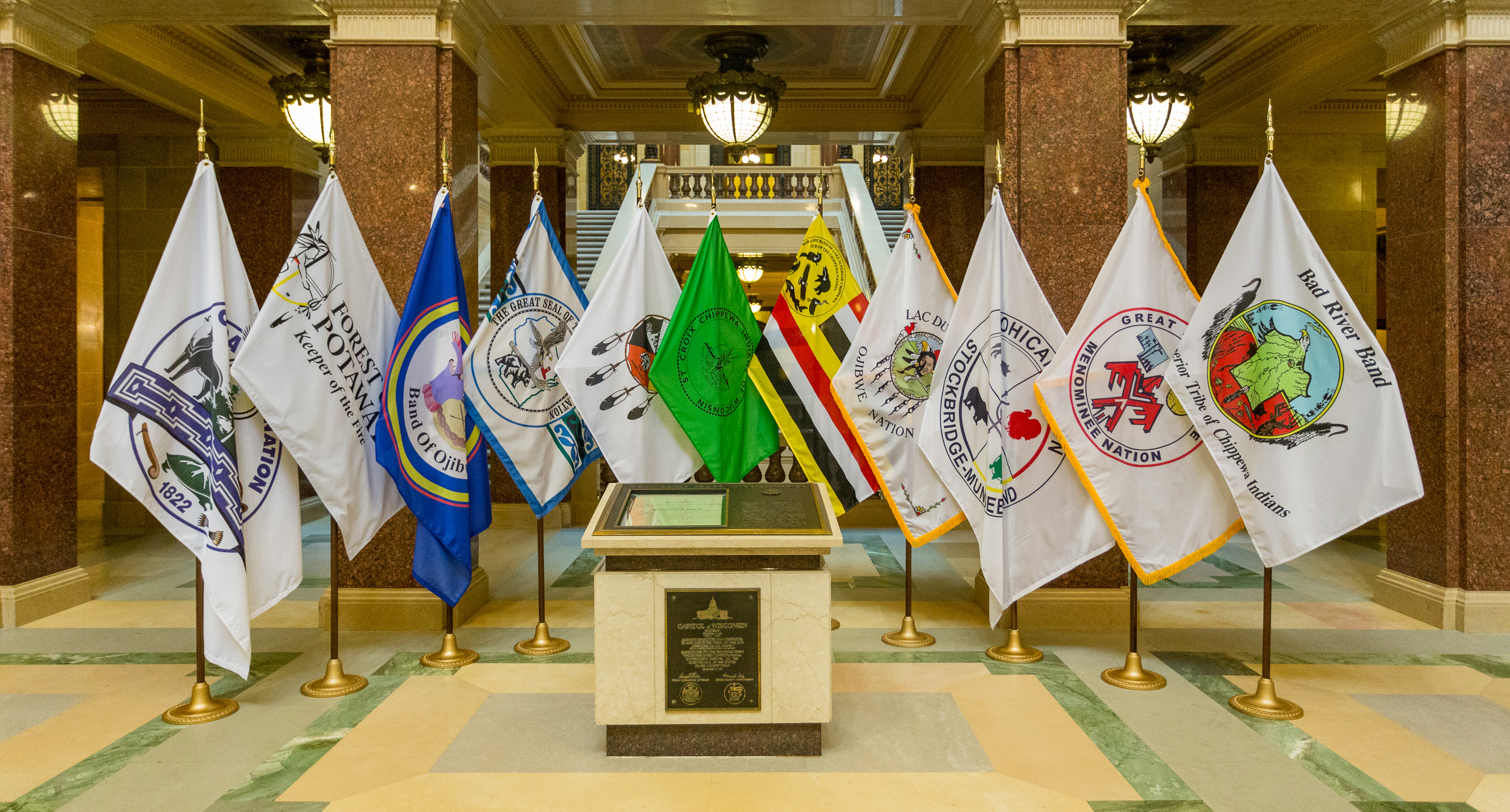  Federally recognized tribes are those Native American tribes recogn ...
Federally recognized tribes are those Native American tribes recogn ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Federally Recognized Tribes By State
Federally recognized tribes are those Native American tribes recognized by the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs for certain federal government purposes. For an alphabetical listing, see list of federally recognized tribes and federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.Federal Acknowledgment of the Pamunkey Indian Tribe Of these, 231 are located in Alaska. Description In the , the Native American tribe is a fundamental unit of sovereign tribal government, and the constitution grants to the |
Washington (state)
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George Washington—the first U.S. president—the state was formed from the western part of the Washington Territory, which was ceded by the British Empire in 1846, by the Oregon Treaty in the settlement of the Oregon boundary dispute. The state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and the Canadian province of British Columbia to the north. It was admitted to the Union as the 42nd state in 1889. Olympia is the state capital; the state's largest city is Seattle. Washington is often referred to as Washington state to distinguish it from the nation's capital, Washington, D.C. Washington is the 18th-largest state, with an area of , and the 13th-most populous state, with more than 7.7 million people. The majority of Washington's residents live in the Seattle metropolitan area, the center of trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Shell Tribe Of Chippewa Indians Of Montana
Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana is a federally-recognized tribe of Ojibwe people in Montana. Due to conflicts with federal authorities in the 19th century, the Little Shell Chippewa Tribe went without an Indian reservation for most of its history. The tribe now owns three acres of land near Great Falls, Montana. Members live in various parts of Montana and elect a government of a chairman and Tribal Council according to their constitution. Others live in Great Falls, Havre, Lewistown, Helena, Butte, Chinook, Hays, Wolf Point, Hamilton, Billings, and elsewhere in Montana. The tribe has been state recognized in Montana. The National Defense Authorization Act, which was signed into law on December 20, 2019, granted the Tribe Federal recognition. This law was led through Congress by Senators Jon Tester and Steve Daines and Representative Greg Gianforte and signed by then-President Donald Trump. Background From likely both northern Ontario and northern Minnes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Register
The ''Federal Register'' (FR or sometimes Fed. Reg.) is the official journal of the federal government of the United States that contains government agency rules, proposed rules, and public notices. It is published every weekday, except on federal holidays. The final rules promulgated by a federal agency and published in the ''Federal Register'' are ultimately reorganized by topic or subject matter and codified in the '' Code of Federal Regulations'' (CFR), which is updated annually. The ''Federal Register'' is compiled by the Office of the Federal Register (within the National Archives and Records Administration) and is printed by the Government Publishing Office. There are no copyright restrictions on the ''Federal Register''; as a work of the U.S. government, it is in the public domain. Contents The ''Federal Register'' provides a means for the government to announce to the public changes to government requirements, policies, and guidance. * Proposed new rules and regulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomasina Jordan
Thomasina Elizabeth Jordan (Red Hawk Woman) (? – 1999) was an American Indian activist who became the first American Indian to serve in the United States Electoral College in 1988. Jordan received bachelor's and master's degrees in fine arts at Bishop Lee College in Boston. She studied at Harvard University, received an educational doctorate from The Catholic University of America, and attended the American Academy of Fine Arts in New York City. She later resided in Alexandria, Virginia, where she was a member of the Alexandria Republican City Committee. Jordan was appointed Chairperson of the Virginia Council on Indians by Governors George Allen and Jim Gilmore. She also founded the American Indian Cultural Exchange, served on the Board of Directors of Save the Children and the National Rehabilitation Hospital, was president of Chapter I of the Capital Speakers Club, and was a recipient of the Medal of Honor of the National Society of the Daughters of the American Revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamunkey
The Pamunkey Indian Tribe is one of 11 Virginia Indian tribal governments recognized by the Commonwealth of Virginia, and the state's first federally recognized tribe, receiving its status in January 2016. Six other Virginia tribal governments, the Chickahominy, the Eastern Chickahominy, the Upper Mattaponi, the Rappahannock, the Monacan, and the Nansemond, were similarly recognized through the passage of the Thomasina E. Jordan Indian Tribes of Virginia Federal Recognition Act of 2017 on January 12, 2018. The historical people were part of the Powhatan paramountcy, made up of Algonquian-speaking nations. The Powhatan paramount chiefdom was made up of over 30 nations, estimated to total about 10,000–15,000 people at the time the English arrived in 1607.Rountree, Helen C. and E. Randolph Turner III. ''Before and After Jamestown: Virginia's Powhatans and Their Predecessors''. Gainesville: University Press of Florida, 2002. The Pamunkey nation made up about one-tenth to one- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Committee On Indian Affairs
The Senate Committee on Indian Affairs is a committee of the United States Senate charged with oversight in matters related to the American Indian, Native Hawaiian, and Alaska Native peoples. A Committee on Indian Affairs existed from 1820 to 1947, after which it was folded into the Committee on Interior and Insular Affairs. A new Native Affairs Committee was created in 1977, initially as a select committee, as a result of the detachment of indigenous affairs from the new Committee on Energy and National Resources, which had succeeded the old Committee on Interior and Insular Affairs. The committee was initially intended to be temporary, but was made permanent in 1984. The committee tends to include senators from Western and Plains states, who have more Native American constituents. History Summary In 1977, the Senate approved which re-established the Committee on Indian Affairs as a temporary select committee. The Select Committee was to disband at the close of the 95th Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinnecock Indian Nation
The Shinnecock Indian Nation is a federally recognized tribe of historically Algonquian-speaking Native Americans based at the eastern end of Long Island, New York. This tribe is headquartered in Suffolk County, on the southeastern shore. Since the mid-19th century, the tribe's landbase is the Shinnecock Reservation within the geographic boundaries of the Town of Southampton. Their name roughly translates into English as "people of the stony shore". History The Shinnecock were among the thirteen Indian bands loosely based on kinship on Long Island, which were named by their geographic locations, but the people were highly decentralized. The most common pattern of indigenous life on Long Island prior to their economic and cultural destruction - and, on occasion, actual enslavement - by the Europeans was the autonomous village linked by kinship to its neighbors. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Claims Commission
The Indian Claims Commission was a judicial relations arbiter between the United States federal government and Native American tribes. It was established under the Indian Claims Act of 1946 by the United States Congress to hear any longstanding claims of Indian tribes against the United States. It took until the late 1970s to complete most of them, with the last case finished in the early 21st century. The commission was conceived as way to thank Native Americans for their unprecedented service in World War II and as a way to relieve the anxiety and resentment caused by the United States' history of colonization of indigenous peoples. Together with the law, the Commission created a process for tribes to address their grievances against the United States, and offered monetary compensation for territory lost as a result of broken federal treaties. However, by accepting the government's monetary offer, the aggrieved tribe abdicated any right to raise their claim again in the future. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
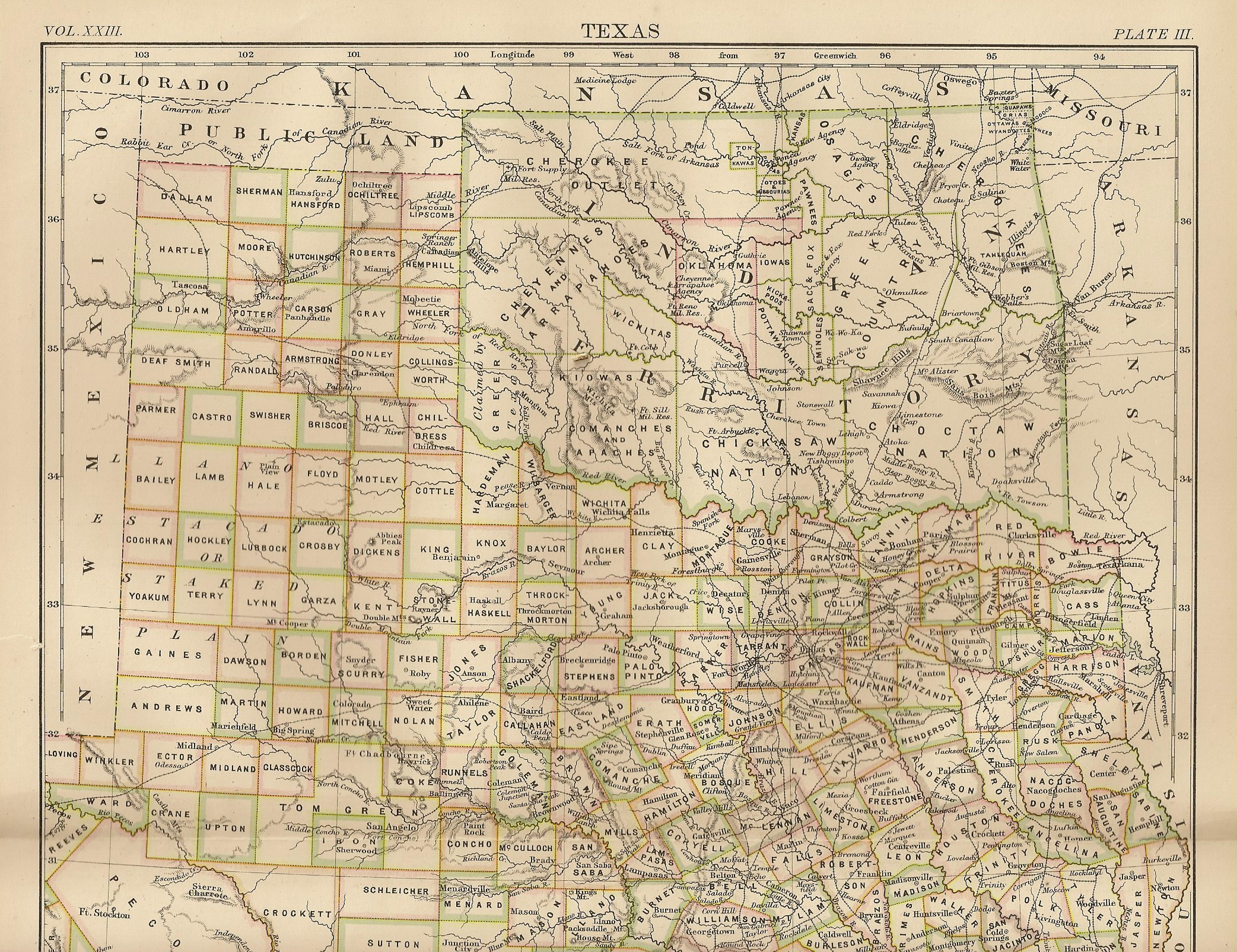
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "Sooners, The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign independent state. In general, the tribes ceded land they occupied in exchange for Land grant#United States, land grants in 1803. The concept of an Indian Territory was an outcome of the US federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the Indian Territory in the American Civil War, American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the US government was one of Cultural assimilation of Native Americans#Americanization and assimilation (1857–1920), assimilation. The term ''Indian Reserve (1763), Indian Reserve'' describes lands the Kingdom of Great Britain, British set aside for Indigenous tribes between the Appalachian Mountains and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a designated Indian Territory (roughly, present-day Oklahoma). The Indian Removal Act, the key law which authorized the removal of Native tribes, was signed by Andrew Jackson in 1830. Although Jackson took a hard line on Indian removal, the law was enforced primarily during the Martin Van Buren administration. After the passage of the Indian Removal Act in 1830, approximately 60,000 members of the Cherokee, Muscogee (Creek), Seminole, Chickasaw, and Choctaw nations (including thousands of their black slaves) were forcibly removed from their ancestral homelands, with thousands dying during the Trail of Tears. Indian removal, a popular policy among incoming settlers, was a consequence of actions by European settlers in North America during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |