|
Fear Of Medical Procedures
Most people have a fear of medical procedures at some point in their lifetime, which can include the fear of surgery, dental work, doctors, or needles. These fears are seldom diagnosed or treated, as they are often extinguished into adulthood and do not often develop into phobias preventing individuals from seeking medical attention. Formally, medical fear is defined as "any experience that involves medical personnel or procedures involved in the process of evaluating or modifying health status in traditional health care settings." Classification Fear of medical procedures can be classified under a broader category of "blood, injection, and injury phobias". This is one of five subtypes that classify specific phobias. A specific phobia is defined as a "marked and persistent fear that is excessive or unreasonable, cued by the presence (or anticipation) of a specific object or situation." Often these fears begin to appear in childhood, around the age of five to nine. It is normal to bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Movement Desensitization And Reprocessing
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) is a form of psychotherapy developed by Francine Shapiro in the 1980s that was originally designed to alleviate the distress associated with traumatic memories such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). In EMDR, the person being treated recalls distressing experiences whilst doing bilateral stimulation, such as side-to-side eye movement or physical stimulation, such as tapping either side of the body. The 2013 World Health Organization (WHO) practice guideline states that EMDR "is based on the idea that negative thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are the result of unprocessed memories. The treatment involves standardized procedures that include focusing simultaneously on spontaneous associations of traumatic images, thoughts, emotions and bodily sensations and bilateral stimulation that is most commonly in the form of repeated eye movements." EMDR is included in several evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of PTSD, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Fear
Dental fear, or dentophobia, is a normal emotional reaction to one or more specific threatening stimuli in the dental situation. However, dental anxiety is indicative of a state of apprehension that something dreadful is going to happen in relation to dental treatment, and it is usually coupled with a sense of losing control. Similarly, dental phobia denotes a severe type of dental anxiety, and is characterised by marked and persistent anxiety in relation to either clearly discernible situations or objects (e.g. drilling, local anaesthetic injections) or to the dental setting in general. The term ‘dental fear and anxiety’ (DFA) is often used to refer to strong negative feelings associated with dental treatment among children, adolescents and adults, whether or not the criteria for a diagnosis of dental phobia are met. Dental phobia can include fear of dental procedures, dental environment or setting, fear of dental instruments or fear of the dentist as a person. People with dent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
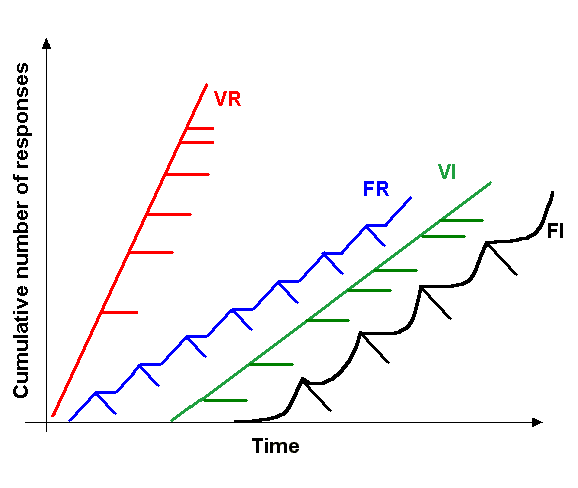
Positive Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Coat Hypertension
White coat hypertension (WHT), more commonly known as white coat syndrome, is a form of labile hypertension in which people exhibit a blood pressure level above the normal range in a clinical setting, although they do not exhibit it in other settings. It is believed that the phenomenon is due to anxiety experienced during a clinic visit. The patient's daytime ambulatory blood pressure is used as a reference as it takes into account ordinary levels of daily stress. Many problems have been incurred in the diagnosis and treatment of white coat hypertension. Masked hypertension (MH) is the contrasting phenomenon, whereby a patient's blood pressure is above the normal range during daily living but not in a clinic setting. Diagnosis In studies, white coat hypertension can be defined as the presence of a defined hypertensive average blood pressure in a clinic setting, although it isn't present when the patient is at home. Diagnosis is made difficult as a result of the unreliable measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fear Of Needles
Fear of needles, known in medical literature as needle phobia, is the extreme fear of medical procedures involving injections or hypodermic needles. This can lead to avoidance of medical care, including vaccine hesitancy. It is occasionally referred to as ''aichmophobia'', although this term may also refer to a more general fear of sharply pointed objects. Overview and incidence The condition was officially recognized in 1994 in the DSM-IV (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition) as a specific phobia of blood-injection-injury type phobia (BII phobia). Phobic level responses to injections cause sufferers to avoid inoculations, blood tests, and in the more severe cases, all medical care. It is estimated that at least 10% of American adults have a fear of needles, and it is likely that the actual number is larger, as the most severe cases are never documented due to the tendency of the sufferer to avoid all medical treatment. The diagnosis criteria for B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |