|
Fas Languages
The Fas languages are a small language family of Papua New Guinea. Classification Despite the fact that the family consists of just two closely related languages, Baibai and Fas (40% cognate), there has been considerable confusion over its membership, apparently due to a misalignment in the publication (Loving & Bass 1964) of the data used for the initial classification. (See Baron 1983.) The initial name of the family was Fas, but Laycock (1975) changed it to Baibai when he mistakenly moved the Fas language to the Kwomtari family, an error perpetuated in much of the literature. Baibai (Baibai and Biaka) is therefore not a synonym for the Fas family (Baibai and Fas). See Kwomtari–Fas languages for details. A few regular sound correspondences are apparent (Baron 1983:21 ''ff):'' The odd change from *nd to /k/ (via *hr) has also occurred in the Bewani languages and some of the Vanimo languages. * metathesis still operates in Fas. and metathesis has been reconstructed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Kiparsky
René Paul Victor Kiparsky (born January 28, 1941) is a Finnish professor of linguistics at Stanford University. He is the son of the Russian-born linguist and Slavicist Valentin Kiparsky. Kiparsky is especially known for his contributions to phonology. These include coining the terms elsewhere principle, and phonological opacity (including the types feeding, bleeding, counterfeeding, and counterbleeding), and creating the frameworks of Lexical Phonology and Morphology (LPM) and its successor, Stratal Optimality Theory. A noted Pāṇini scholar, he has also made fundamental contributions to historical linguistics and generative metrics, as well as working in morphosyntax, especially on his native Finnish. Academic life Kiparsky was born in Helsinki. He studied at Alabama College (now the University of Montevallo), the University of Helsinki and the University of Minnesota. Kiparsky was a student of Morris Halle at MIT, where he received his PhD in 1965. For two decades, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fas Languages
The Fas languages are a small language family of Papua New Guinea. Classification Despite the fact that the family consists of just two closely related languages, Baibai and Fas (40% cognate), there has been considerable confusion over its membership, apparently due to a misalignment in the publication (Loving & Bass 1964) of the data used for the initial classification. (See Baron 1983.) The initial name of the family was Fas, but Laycock (1975) changed it to Baibai when he mistakenly moved the Fas language to the Kwomtari family, an error perpetuated in much of the literature. Baibai (Baibai and Biaka) is therefore not a synonym for the Fas family (Baibai and Fas). See Kwomtari–Fas languages for details. A few regular sound correspondences are apparent (Baron 1983:21 ''ff):'' The odd change from *nd to /k/ (via *hr) has also occurred in the Bewani languages and some of the Vanimo languages. * metathesis still operates in Fas. and metathesis has been reconstructed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Areca Nut
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of palms in the family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines, Malaysia and India, across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ''Areca'' is derived from a name used locally on the Malabar Coast of India. Usage The best-known member of the genus is '' A. catechu'', the areca nut palm. Several species of areca nuts, known for their bitter and tangy taste, raw or dried, are routinely used for chewing, especially in combination with the leaves of betel and dried leaves of tobacco. Areca nut is also popularly referred to as betel nut because of its usage for chewing with betel leaves. In Assam, areca nut is also known as ''tamul'' in the local dialect. Species (51 species) *'' Areca abdulrahmanii'' J.Dransf. *'' Areca ahmadii'' J.Dransf. *''Areca andersonii'' J.Dransf. *'' Areca gandamatu'' Sultan Mardan Plantation *'' Areca arundinacea'' Becc. *'' Areca brachypoda'' J.Dransf. *'' Areca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird-of-paradise
The birds-of-paradise are members of the family Paradisaeidae of the order Passeriformes. The majority of species are found in eastern Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and eastern Australia. The family has 44 species in 17 genera. The members of this family are perhaps best known for the plumage of the males of the species, the majority of which are sexually dimorphic. The males of these species tend to have very long, elaborate feathers extending from the beak, wings, tail or head. For the most part they are confined to dense rainforest habitat. The diet of all species is dominated by fruit and to a lesser extent arthropods. The birds-of-paradise have a variety of breeding systems, ranging from monogamy to lek-type polygamy. A number of species are threatened by hunting and habitat loss. Taxonomy The family Paradisaeidae was introduced (as Paradiseidae) in 1825 with ''Paradisaea'' as the type genus by the English naturalist William John Swainson. For many years the birds-of-par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
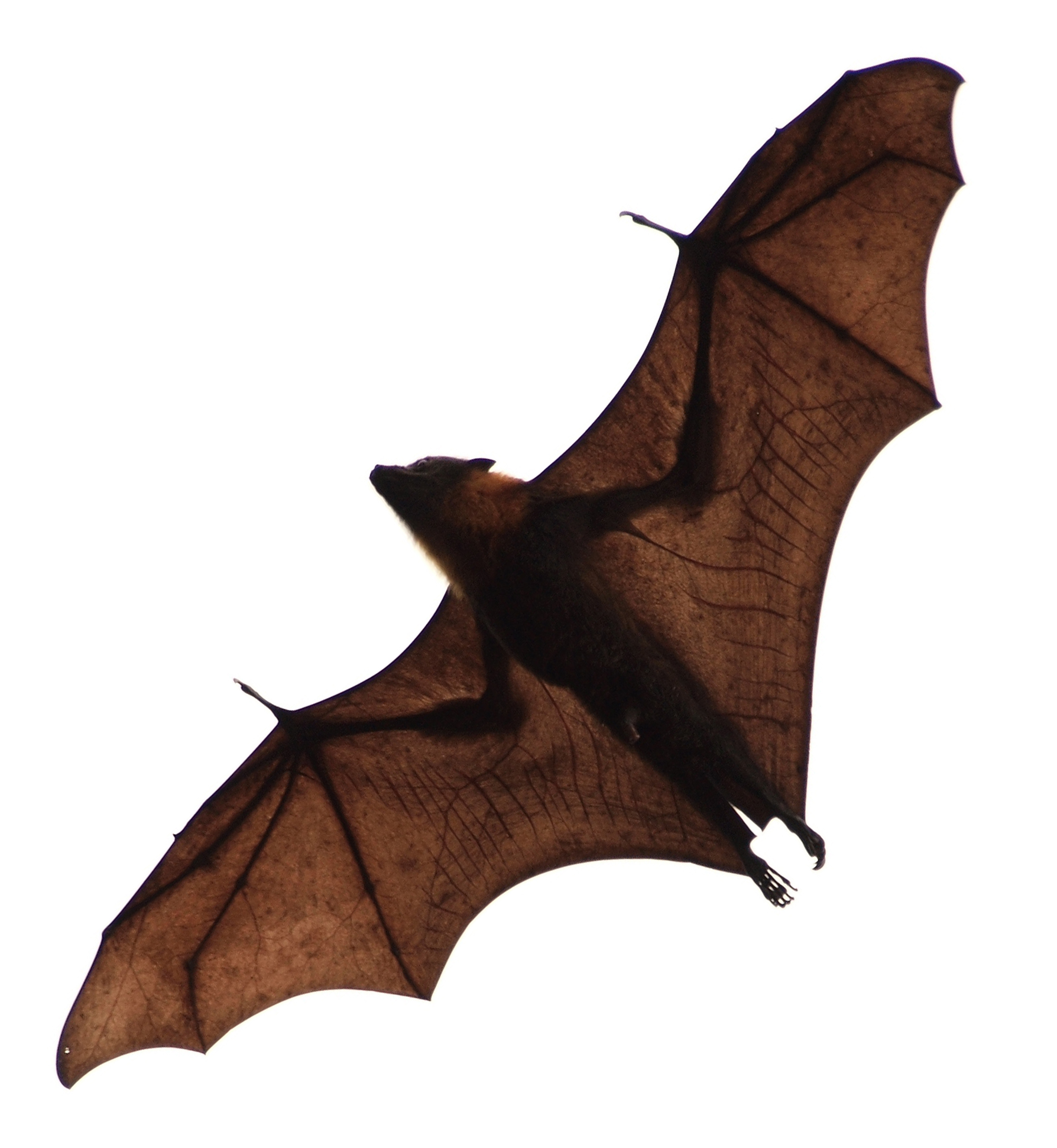
Flying Fox
''Pteropus'' (suborder Yinpterochiroptera) is a genus of megabats which are among the largest bats in the world. They are commonly known as fruit bats or flying foxes, among other colloquial names. They live in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia, East Africa, and some oceanic islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. There are at least 60 extant species in the genus. Flying foxes eat fruit and other plant matter, and occasionally consume insects as well. They locate resources with their keen sense of smell. Most, but not all, are nocturnal. They navigate with keen eyesight, as they cannot echolocate. They have long life spans and low reproductive outputs, with females of most species producing only one offspring per year. Their slow life history makes their populations vulnerable to threats such as overhunting, culling, and natural disasters. Six flying fox species have been made extinct in modern times by overhunting. Flying foxes are often persecuted for their real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilabial Trill
The voiced bilabial trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is B\. Features Features of the voiced bilabial trill: In most instances, it is only found as the trilled release of a prenasalized stop. Varieties Occurrences The Knorkator song " uchstabe (the actual title is a glyph) on the 1999 album '' Hasenchartbreaker'' uses a similar sound (though linguolabial instead of bilabial) to replace "br" in a number of German words (e.g. for ). Prenasalized Prestopped trills and stops with trill release Phonology In many of the languages in which the bilabial trill occurs, it occurs only as part of a prenasalized bilabial stop with trilled release, . That developed historically from a prenasalized stop before a relatively high back vowel like . In such instances, the sounds are usually still limited to the environment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Sydney
The University of Sydney (USYD), also known as Sydney University, or informally Sydney Uni, is a public university, public research university located in Sydney, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in Australia and is one of the country's six sandstone universities. The university comprises eight academic faculties and university schools, through which it offers bachelor, master and doctoral degrees. The university consistently ranks highly both nationally and internationally. QS World University Rankings ranked the university top 40 in the world. The university is also ranked first in Australia and fourth in the world for QS graduate employability. It is one of the first universities in the world to admit students solely on academic merit, and opened their doors to women on the same basis as men. Five Nobel Prize, Nobel and two Crafoord Prize, Crafoord laureates have been affiliated with the university as graduates and faculty. The university has educated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimality Theory
In linguistics, Optimality Theory (frequently abbreviated OT) is a linguistic model proposing that the observed forms of language arise from the optimal satisfaction of conflicting constraints. OT differs from other approaches to phonological analysis, such as autosegmental phonology and linear phonology (SPE), which typically use rules rather than constraints. OT models grammars as systems that provide mappings from inputs to outputs; typically, the inputs are conceived of as underlying representations, and the outputs as their surface realizations. It is an approach within the larger framework of generative grammar. In linguistics, Optimality Theory has its origin in a talk given by Alan Prince and Paul Smolensky in 1991 which was later developed in a book manuscript by the same authors in 1993. Overview There are three basic components of the theory: * Generator () takes an input, and generates the list of possible outputs, or candidates, * Constraint component () provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but may now relate to any linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The building blocks of signs are specifications for movement, location, and handshape. At first, a separate terminology was used for the study of sign phonology ('chereme' instead of 'phoneme', etc.), but the concepts are now considered to apply universally to all human languages. Terminology The word 'phonology' (as in 'phonology of English') can refer either to the field of study or to the phonological system of a given language. This is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwomtari–Fas Languages
The Kwomtari–Fas languages, often referred to ambiguously as Kwomtari, are an apparently spurious language family proposal of six languages spoken by some 4,000 people in the north of Papua New Guinea, near the border with Indonesia. The term "Kwomtari languages" can also refer to one of the established families that makes up this proposal. Classification history Loving and Bass (1964) A "Kwomtari" (= Kwomtari–Fas) phylum was first proposed by Loving and Bass (1964). The following classification is based on their proposal, with the addition of the Pyu and language, added by Laycock (1975): Kwomtari–Fas phylum * Kwomtari–Nas family: Kwomtari, Nai (Biaka) * Fas family: Fas, Baibai Laycock (1975) Laycock (1973; 1975) grouped the languages differently, placing Kwomtari and Fas together in the "Kwomtari family", and Baibai and Nai (Biaka) together in a "Baibai family", and calling the overall grouping "Kwomtari–Baibai". Laycock also added the Pyu isolate, though he admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanimo Languages
The Sko or Skou languages are a small language family spoken by about 7000 people, mainly along the Vanimo coast of Sandaun Province in Papua New Guinea, with a few being inland from this area and at least one just across the border in the Indonesian province of Papua (formerly known as Irian Jaya). Typology Tone Skou languages are unusual among Papuan languages for being tonal; all Skou languages possess contrastive tone. Vanimo, for example, has three tones, ''high, mid, low.'' Example minimal sets illustrating tonal contrasts in various Skou languages: * I’saka: ''ẽy''H ‘louse’, ''wey''L ‘butterfly’, ''wey''LH ‘house’, ''wey''HL ‘language’ * Barupu: ''e''H ‘tooth’, ''e''L ‘garden’, ''e''HL ‘mosquito’, ''e''HLH ‘write’ *Wutung: ''ho''H ‘roof thatch made from sago palm fronds’, ''ho''L ‘star’, ''ho''HL ‘grease’ * Skou: ''ta''H ‘grass’, ''ta''L ‘hair’, ''ta''HL ‘arrow’ Lakes Plain languages, spoken in a discontiguou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)