|
Farnetta
Farnetta is a small village in the Terre Arnolfe countryside, 16 miles northwest of the Italian city of Terni, Umbria. It is included in the ''comune'' of Montecastrilli in the province of Terni (central Italy). It has a population of 283. Farnetta derives its name from the old Latin name ''Quercus Frainetto''. It is reputed to be one of Umbria's smallest villages. It has several farms and houses, and a church, dedicated to St Nicolaus, which has its origins in the 16th century but underwent heavy restoration in 1860. The church has been designated by Italian Heritage. On a nearby hill are the remains of a Medieval hill fort known as Palombara, and the 10th- to 11th-century Romanesque Church of San Lorenzo in Nifili. San Lorenzo was built on the remains of a Roman building, and incorporates large stone blocks from that building. The church is located on an important Roman road (Via Amerina) connecting Amelia to Todi and Perugia. History It is likely that the area was also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Lorenzo In Nifili
San Lorenzo in Nifili is a Romanesque-style, Roman Catholic church located in the town of Farnetta, part of the commune of Montecastrilli, in the province of Terni, region of Umbria, Italy. History A church is documented since 1112, when it was donated by the Count Rapizzo degli Arnolfi to the Abbey of Farfa. The church incorporates spolia from an ancient Roman construction. In 1777, it became part of the parish of Farnetta. Beni culturali. References |
Montecastrilli
Montecastrilli is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Terni in the Italian region of Umbria, located about 50 km south of Perugia and about 15 km northwest of Terni Terni ( , ; lat, Interamna (Nahars)) is a city in the southern portion of the region of Umbria in central Italy. It is near the border with Lazio. The city is the capital of the province of Terni, located in the plain of the Nera river. It is .... Main sights Among the churches in the town are: * San Nicolò - 10th or 11th-century church * Santa Maria di Ciciliano- 11th-century church * San Lorenzo in Nifili - 11th-century *Santa Maria Assunta - 11th to 12th-century parish church of Quadrelli *San Bartolomeo - 12th-century parish church of Casteltodino *Monastery of Santa Chiara (1649) *Santa Rosario - 17th-century baroque church in Quadrelli References External links Official website Cities and towns in Umbria {{Umbria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carsulae
Carsulae is an archaeological site in the region of Umbria in central Italy. It is located approximately north of San Gemini, a small comune in the province of Terni. Origins and History Most historians fix the town's foundation about 220-219 BC. with the building of the ancient Roman road, the via Flaminia. Given the pattern of pre-Roman settlements in the area it is possible that some form of earlier Umbrian settlement existed at this site. When the via Flaminia was first built, its western branch proceeded north from Narni (ancient ''Narnia''), sparking the development not only of Carsulae, but also of other locations including Bevagna (ancient ''Mevania''). This branch of the road courses through a gently rolling upland plain at the foot of the Martani mountain range, an area that had been heavily populated since the middle of the Bronze Age. The original course of the via Flaminia, the western branch proceeded from Narni past modern San Gemini, Carsulae, modern Acquas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoleto
Spoleto (, also , , ; la, Spoletum) is an ancient city in the Italian province of Perugia in east-central Umbria on a foothill of the Apennines. It is S. of Trevi, N. of Terni, SE of Perugia; SE of Florence; and N of Rome. History Spoleto was situated on the eastern branch of the Via Flaminia, which forked into two roads at Narni and rejoined at ''Forum Flaminii'', near Foligno. An ancient road also ran hence to Nursia. The ''Ponte Sanguinario'' of the 1st century BC still exists. The Forum lies under today's marketplace. Located at the head of a large, broad valley, surrounded by mountains, Spoleto has long occupied a strategic geographical position. It appears to have been an important town to the original Umbri tribes, who built walls around their settlement in the 5th century BC, some of which are visible today. The first historical mention of ''Spoletium'' is the notice of the foundation of a colony there in 241 BC; and it was still, according to Cicero ''colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangemini
San Gemini is a ''comune'' (municipality) of c. 5,000 inhabitants in the province of Terni in the Italian region Umbria, located about 60 km south of Perugia and about 10 km northwest of Terni. San Gemini borders the municipalities of Montecastrilli, Narni and Terni. The town is a well-preserved medieval burgh with two lines of walls, built over the remains of a small Roman center along the old Via Flaminia. It is especially known for its mineral waters. Main sights * San Gemini Cathedral or Duomo - a 12-century church dedicated to the commune's patron, the locally venerated Saint Gemine, whose relics were recovered in 1775, was rebuilt in 1817. Brother Gemine was a monk of Syrian origins who died in 815. The burial urn and original stone are conserved in the sacristy; the saint has been reburied under the high altar. The saint's day is 9 October. *''Carsulae'' -Archeological site *'' ''San Nicolò'' - Romanesque architecture Romanesque architecture is an architectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trattoria
A ''trattoria'' (plural: ''trattorie'') is an Italian-style eating establishment that is generally much less formal than a '' ristorante'', but more formal than an ''osteria''. A ''trattoria'' rooted in tradition may typically provide no printed menu, casual service, wine sold by the decanter rather than the bottle, and low prices, with an emphasis on a steady clientele rather than on ''haute cuisine''. Food tends to be modest but plentiful, mostly following regional and local recipes, sometimes even served family-style, at common tables. This homely tradition has waned in recent decades. Many ''trattorie'' have taken on some of the trappings of a ''ristorante'', providing relatively few concessions to the old rustic and familial style. The name ''trattoria'' has also been adopted by some high-level restaurants. Optionally, ''trattoria'' food could be bought in containers to be taken home. Etymologically, the word is cognate with the French term ''traiteur'' (a caterer pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farfa Abbey
Farfa Abbey ( it, Abbazia di Farfa) is a territorial abbey in northern Lazio, central Italy. In the Middle Ages it was one of the richest and most famous abbeys in Italy. It belongs to the Benedictine Order and is located about from Rome, in the commune of Fara Sabina, of which it is also a hamlet (''It. frazione''). In 2016 it was added to the "tentative" list to be a UNESCO World Heritage Site, as part of a group of eight Italian medieval Benedictine monasteries, representing "The cultural landscape of the Benedictine settlements in medieval Italy". History A legend in the 12th-century ''Chronicon Farfense'' (Chronicle of Farfa) dates the founding of a monastery at Farfa to the time of the Emperors Julian, or Gratian, and attributes the founding to Laurence of Syria, who had come to Rome with his sister, Susannah, together with other monks, and had been made Bishop of Spoleto. According to the tradition, after being named bishop, he became enamoured of the monastic lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Frainetto
''Quercus frainetto'' (syn. ''Quercus conferta'' Kit., ''Quercus farnetto'' Ten.), commonly known as the Hungarian oak or Italian oak, is a species of oak, native to southeastern Europe (parts of Italy, the Balkans, parts of Hungary, Romania) and Turkey; it is classified in ''Quercus'' sect. ''Mesobalanus''. Description ''Quercus frainetto'' is a large deciduous tree, reaching heights of tall by broad, with a trunk girth of nearly . The bark is light gray in colour and cracks into small square cracking plates. The buds are large, long and pointed, shiny russet or light brown in colour with minute tomentum. The twigs are stout and covered with russet upward pointed hairs. The leaves are large, long, occasionally up to , variable in shape, divided into 6–10 very deep parallel lobes which are usually divided into sublobes. The leaf stalks are usually short, , rarely to 22 mm, long. The leaves are widest close to the apex, which is broad and short pointed. The base of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Flaminia
The Via Flaminia or Flaminian Way was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to ''Ariminum'' (Rimini) on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had for travel between Etruria, Latium, Campania, and the Po Valley. The section running through northern Rome is where Constantine the Great had his famous vision of the Chi Rho, leading to his conversion to Christianity and the Christianization of the Roman Empire. Today the same route, still called by the same name for much of its distance, is paralleled or overlaid by Strada Statale (SS) 3, also called Strada Regionale (SR) 3 in Lazio and Umbria, and Strada Provinciale (SP) 3 in Marche. It leaves Rome, goes up the Val Tevere ("Valley of the Tiber") and into the mountains at Castello delle Formiche, ascends to Gualdo Tadino, continuing over the divide at Scheggia Pass, to Cagli. From there it descends the eastern slope waterways betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
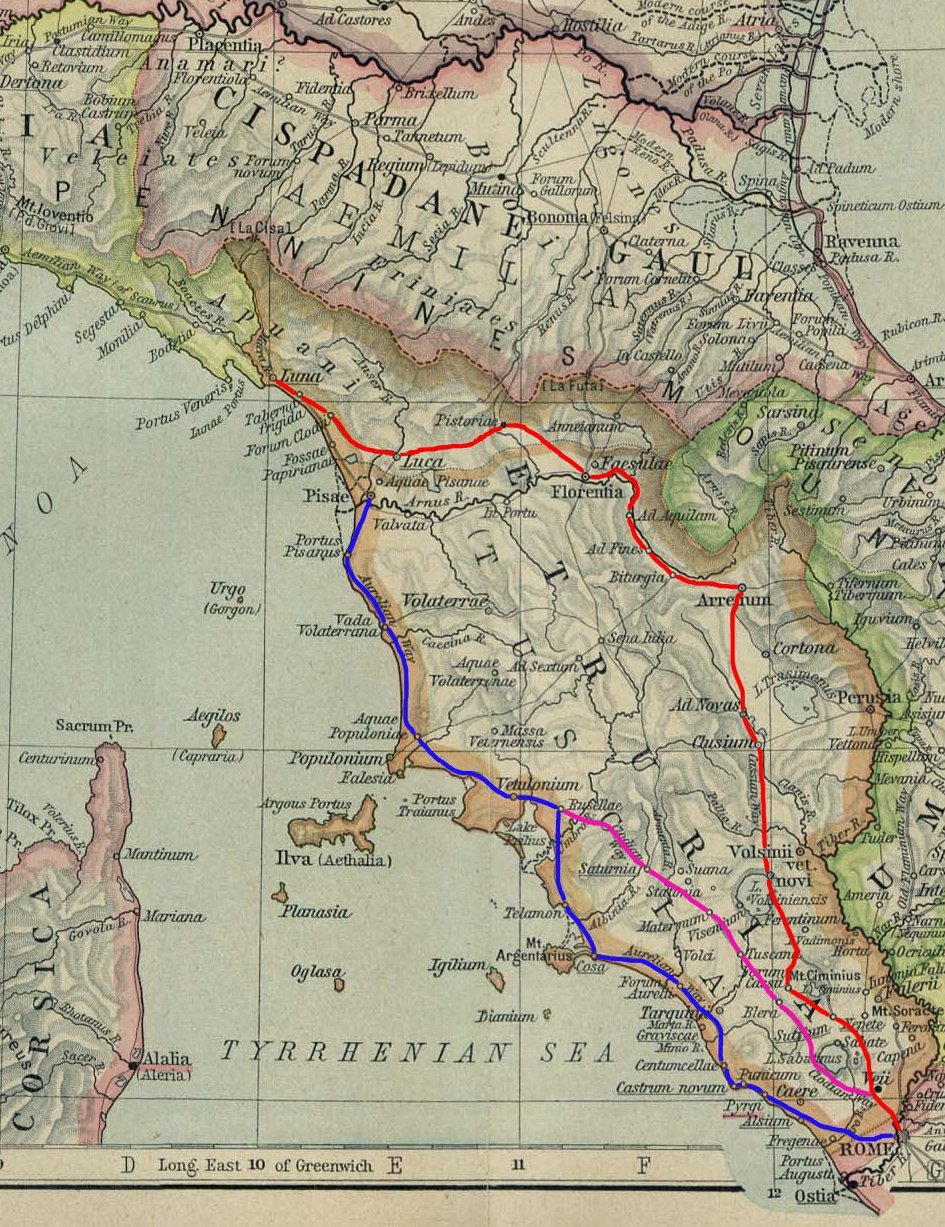
Via Cassia
The ''Via Cassia'' ("way of Cassius") was an important Roman road striking out of the ''Via Flaminia'' near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii, traversed Etruria. The ''Via Cassia'' passed through Baccanae, Sutrium, Volsinii, Clusium, Arretium, Florentia, Pistoria, and Luca, joining the ''Via Aurelia'' at Luna. The ''Via Cassia'' intersected other important roads. At mile 11 the ''Via Clodia'' diverged north-north-west. At Sette Vene, another road, probably the ''Via Annia'', branched off to Falerii. In Sutrium, the ''Via Ciminia'' split off and later rejoined. The date of its construction is uncertain: it cannot have been earlier than 187 BC, when the consul Gaius Flaminius constructed a road from Bononia to Arretium, which must have coincided with a portion of the later Via Cassia. It is not mentioned by any ancient authorities before the time of Cicero, who in 45 BC speaks of the existence of three roads from Rome to Muti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Todi
Todi () is a town and ''comune'' (municipality) of the province of Perugia (region of Umbria) in central Italy. It is perched on a tall two-crested hill overlooking the east bank of the river Tiber, commanding distant views in every direction. In the 1990s, Richard S. Levine, a professor of Architecture at the University of Kentucky, included Todi in academic design exercises aimed at conceiving hypothetical improvements to the city and presented its results in a conference titled "The Sustainable City of the Past and the Sustainable City of the Future". As a result, the Italian press incorrectly reported on Todi as ''the world's most livable city''. History According to the legend, said to have been recorded around 1330 BC by a mythological Quirinus Colonus, Todi was built by Hercules, who here killed Cacus, and gave the city the name of ''Eclis''. Historical Todi was founded by the ancient Italic people of the Umbri, in the 8th-7th century BC, with the name of ''Tutere'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |