|
Farenya
Farenya is a settlement in Boffa Prefecture, Boké Region, Guinea. It is situated 69 miles (or 111 km) north of Conakry. It is located on the Pongo River. History Farenya was founded by Stiles Edward Lightbourn, a slave trader from South Carolina and his Luso-African wife Niara Bely Niara Bely (c. 1790 – 1879), also known as Elizabeth Bailey Gomez, was a Luso-African queen who became a prominent businesswoman in nineteenth century Guinea. She was active in the slave trade in Farenya, Guinea. Biography Niara Bely was the da .... They had originally lived in nearby Bangalan and established Farenya in 1809. British raid in 1841 The location was used to warehouse a variety of goods. In 1841 some boats of war from the corvette HMS ''Iris'' part of the British West Africa Squadron, raided Farenya burning the warehouses and the goods located inside them. References {{Boffa Prefecture Populated places in the Boké Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niara Bely
Niara Bely (c. 1790 – 1879), also known as Elizabeth Bailey Gomez, was a Luso-African queen who became a prominent businesswoman in nineteenth century Guinea. She was active in the slave trade in Farenya, Guinea. Biography Niara Bely was the daughter of Emmanuel Gomez, the Luso-African ruler of Bakia, Guinea. She studied in Liverpool. At some point, she also adopted the westernised name of Elizabeth Bailey Gomez. Slave trader In 1809 she married the slave trader Stiles Edward Lightbourn who spent much of his time on voyages across the Atlantic. The couple originally lived in Bangalan. Bely subsequently maintained a trading settlement located in Farenya, Guinea. While there, she became a prominent businesswoman involved in the slave trade. She resided in the fortified settlement, in a two-storey building she described as a "palace". Archaeological evidence suggests that the area became a village only after Bely set up her trading outpost. It was the destination fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
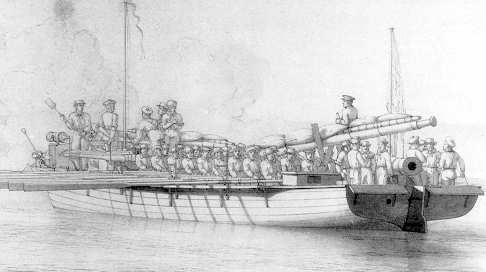
HMS Iris (1840)
HMS ''Iris'' was a 26-gun sixth-rate frigate launched on 14 July 1840 from Devonport Dockyard. She spent some time with the West Africa Squadron suppressing the slave trade and later with the East Indies Station was involved in operations in Borneo. ''Iris'' was the first flagship of the Australia Station between 1859 and 1861 during which time she participated in the First Taranaki War.Bastock, p. 27. In 1864 she was extensively modified to allow her to ferry transatlantic telegraph cable to the cable-laying ship ''Great Eastern''. She was decommissioned and sold off in 1869. Service 1840–1861 Between 1840 and 15 August 1843, she served with the West Africa Squadron. On 28April 1841, her ship's boats were involved in burning the warehouses and other property of Niara Bely in Farenya, on the Pongo River. ''Iris'' was subsequently assigned to the East Indies Station. In 1844 she raced the French ships ''Sirène'', ''Sabine'' and ''Victorieuse'' at Singapore and beat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Guinea
Guinea is divided into 8 administrative regions. 7 regions other than Conakry Region are further subdivided into 33 prefectures. See also * Administrative divisions of Guinea * Prefectures of Guinea * Sub-prefectures of Guinea The sub-prefectures (known in French as ''sous-prefectures'') are the third-level administrative divisions in Guinea. As of 2009 there were 303 rural sub-prefectures of Guinea and 38 urban sub-prefectures, 5 of which compose the Conakry greater urb ... * ISO 3166-2:GN References Subdivisions of Guinea Guinea, Regions Guinea 1 Regions, Guinea Guinea geography-related lists {{Guinea-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Trader
The history of slavery spans many cultures, nationalities, and Slavery and religion, religions from Ancient history, ancient times to the present day. Likewise, its victims have come from many different ethnicities and religious groups. The social, economic, and legal positions of enslaved people have differed vastly in different systems of slavery in different times and places. Slavery has been found in some hunter-gatherer populations, particularly as hereditary slavery, but the conditions of agriculture with increasing social and economic complexity offer greater opportunity for mass chattel slavery. Slavery was already institutionalized by the time the first civilizations emerged (such as Sumer in Mesopotamia, which dates back as far as 3500 BC). Slavery features in the Mesopotamian ''Code of Hammurabi'' (c. 1750 BC), which refers to it as an established institution. Slavery was widespread in the ancient world in Europe, Asia, Middle East, and Africa. It became less common thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shallop
Shallop is a name used for several types of boats and small ships (French ''chaloupe'') used for coastal navigation from the seventeenth century. Originally smaller boats based on the chalupa, the watercraft named this ranged from small boats a little larger than a banks dory to gunboats. The shallops used by English explorers were about long and equipped with oars and a mast with one or two sails. These larger English shallops could take over a dozen people and usually had a shallow draft of about . The larger vessels of this design could carry a substantial load and be armed with cannon. Captain John Smith used shallops to explore Chesapeake Bay in the summer of 1608. The boats were disassembled and stowed aboard the ''Susan Constant'', being reassembled when the colonists arrived in North America. The Danes armed large boats called shallops for use as gunboats, particularly in the Gunboat War (1807–1814) between Denmark–Norway and the British Navy during the Napoleonic W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luso-Africans
Luso-Africans are people of mixed Portuguese and African ancestry who speak Portuguese. The vast majority of Luso-Africans live in former Portuguese Africa, now referred to as ''Lusophone Africa'', comprising the modern countries of Angola, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde, Mozambique, São Tomé and Príncipe, and Equatorial Guinea. A sizable number of Luso-Africans have also settled in Portugal where they form a racial minority. This ethnic identity arose from the sixteenth century as primarily male Portuguese settlers, often ''Lançados'', settled in various parts of Africa, often marrying African women. In the fifteenth and sixteenth century, Portuguese traders settled in the Cape Verde Islands and along the West African coast from Senegal to Sierra Leone. Descendants of these traders and of local African women formed the nucleus of a Luso-African community that soon developed a distinctive culture, joining elements of European and local African culture. These Luso-Africans, or 'Portu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no) , anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind" , Former = Province of South Carolina , seat = Columbia , LargestCity = Charleston , LargestMetro = Greenville (combined and metro) Columbia (urban) , BorderingStates = Georgia, North Carolina , OfficialLang = English , population_demonym = South Carolinian , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = General Assembly , Upperhouse = Senate , Lowerhouse = House of Representatives , Judiciary = South Carolina Supreme Court , Senators = , Representative = 6 Republicans1 Democrat , postal_code = SC , TradAbbreviation = S.C. , area_rank = 40th , area_total_sq_mi = 32,020 , area_total_km2 = 82,932 , area_land_sq_mi = 30,109 , area_land_km2 = 77,982 , area_water_sq_mi = 1,911 , area_water_km2 = 4,949 , area_water_percent = 6 , population_rank = 23rd , population_as_of = 2022 , 2010Pop = 5282634 , population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stiles Edward Lightbourn
Stiles or Styles may refer to: Places * Ezra Stiles College, a residential college of Yale University, U.S. * Stiles, County Antrim, a townland in County Antrim, Northern Ireland, U.K. * Stiles, Texas, U.S. * Stiles, Wisconsin, U.S. ** Stiles (community), Wisconsin, an unincorporated community * Stiles, Pennsylvania, U.S. People Surnames Stiles * Aeriel Stiles, American guitarist and songwriter * B.J. Stiles (born 1933), American retired nonprofit leader * Baxter B. Stiles (1824–1878), American politician * Bert Stiles (1920–1944), American short story writer * Billy Stiles (1871–1908), American outlaw * Charles Wardell Stiles (1867–1941), American zoologist * Chester Stiles (born 1970), American criminal * Cyril Stiles (1904–1985), New Zealand rower (aka Bob Stiles) * Dan Stiles, American artist and designer * Danny Stiles (1923–2011), American radio personality * Darron Stiles (born 1973), American professional golfer * Edward H. Stiles (1836–1921), American p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boké Region
Boké Region is located in western Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Senegal and Guinea-Bissau and the Guinean regions of Kindia and Labé. Its capital is the city of Boké. Administrative divisions Boké Region is divided into five prefectures; which are further sub-divided into 37 sub-prefectures: * Boffa Prefecture (8 sub-prefectures) * Boké Prefecture (10 sub-prefectures) * Fria Prefecture (4 sub-prefectures) * Gaoual Prefecture (8 sub-prefectures) * Koundara Prefecture (7 sub-prefectures) Mining reserves Boké Region is the home to a great part of Guinea's aluminium (or bauxite) reserves. At least two of the country's largest mining facilities are located there: *Compagnie des Bauxites de Guinée, or CBG, which is operated by Halco Mining, an international and intercorporate aluminium mining entity. * Alumina Company of Guinea, or ACG, operating the Friguia bauxite-alumina complex in Fria Prefecture. See also *Aluminium in Africa Aluminium in Africa orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pongo River (Guinea)
The Pongo River or Rio Pongo is a river that flows into the Atlantic Ocean near Boffa, Guinea. Its source is located in Fouta Djallon. The surrounding area has also been known as "Pongoland" or "Bongo Country".SeSamuel Crighton's Baptismal entryin the All Saints, Poplar, parish register of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets referring to the baptism of Samuel Crighton, son of William Fernandez, a local Luso-African King. The estuary has been designated as a Ramsar site since 1992. History Rio Pongo became a significant area for the setting up factories in the transatlantic slave trade. Sir George Collier listed 76 surnames of families involved in the slave trade in 1820. He was commodore of the British West Africa Squadron between 1818 and 1821 and as such organised anti-slaving patrols up the Pongo River and other surrounding areas. In literature Part of the plot of the historical novel ''Anthony Adverse'' – and the film A film also called a movie, motion pic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conakry
Conakry (; ; sus, Kɔnakiri; N’ko: ߞߐߣߊߞߙߌ߫, Fula: ''Konaakiri'' 𞤑𞤮𞤲𞤢𞥄𞤳𞤭𞤪𞤭) is the capital and largest city of Guinea. A port city, it serves as the economic, financial and cultural centre of Guinea. Its population as of the 2014 Guinea census was 1,660,973. The current population of Conakry is difficult to ascertain, although the U.S. Department of State's Bureau of African Affairs has estimated it at two million, accounting for one-sixth of the entire population of the country. History Conakry was originally settled on the small Tombo Island and later spread to the neighboring Kaloum Peninsula, a stretch of land wide. The city was essentially founded after Britain ceded the island to France in 1887. In 1885 the two island villages of Conakry and Boubinet had fewer than 500 inhabitants. Conakry became the capital of French Guinea in 1904 and prospered as an export port, particularly after a railway (now closed) to Kankan opened up t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(14764251532).jpg)