|
Fanuankuwel
Fanuankuwel is a "place of a whale with two tails" location in Pacific and Polynesian mythology, recorded in the traditional celestial navigation techniques of the Caroline Islands. Part of the '' Trigger fishes tied together'' mnemonic-navigational system, it is sometimes grouped with Kafeŕoor as a 'ghost island'. See also * celestial navigation *Kafeŕoor *Polynesian mythology *Polynesian navigation *Micronesian navigation *Wa (watercraft) ''Wa'' are traditional sailing outrigger canoes of the Caroline Islands, Palau, and Yap. They have a single outrigger. They are similar to the '' sakman'' of the Northern Marianas. Design and construction ''Wa'' are proa — vessels with ide ... References {{Oceania-myth-stub Polynesian mythology Celestial navigation Mythological islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kafeŕoor
Kafeŕoor is a "mythical vanishing island" location in Pacific and Polynesian mythology, recorded in the traditional celestial navigation techniques of the Caroline Islands. Part of the '' Trigger fishes tied together'' mnemonic-navigational system, it is sometimes grouped with Fanuankuwel as a 'ghost island'. See also * Celestial navigation * Fanuankuwel *Polynesian mythology *Polynesian navigation *Micronesian navigation *Wa (watercraft) ''Wa'' are traditional sailing outrigger canoes of the Caroline Islands, Palau, and Yap. They have a single outrigger. They are similar to the '' sakman'' of the Northern Marianas. Design and construction ''Wa'' are proa — vessels with ide ... * Phantom island References Polynesian mythology {{sailing-stub Mythological islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wa (watercraft)
''Wa'' are traditional sailing outrigger canoes of the Caroline Islands, Palau, and Yap. They have a single outrigger. They are similar to the ''sakman'' of the Northern Marianas. Design and construction ''Wa'' are proa — vessels with identical bow and stern, allowing the craft to reverse without turning. They are made from hewn-out hulls, typically breadfruit trunks, with single wide top-strakes, and carved head and stern pieces. Sails are lateen rigged and were traditionally made of pandanus mat sailcloth. Benjamin Morrell recorded in the 1830s that sails were "made in small pieces of about three feet square, sewed together. In cutting the sail to its proper shape, the pieces which come off one side answer to go on the other; this gives it the proper form, and causes the halliards to be bent on in the middle of the yard." After World War II sails switched to canvas, and after 1973 the use of dacron began to increase. Early accounts agreed upon "a lee-platform on the side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Polynesian Mythology
The Polynesian narrative or Polynesian mythology encompasses the oral traditions of the people of Polynesia (a grouping of Central and South Pacific Ocean island archipelagos in the Polynesian Triangle) together with those of the scattered cultures known as the Polynesian outliers. Polynesians speak languages that descend from a language reconstructed as Proto-Polynesian - probably spoken in the Tonga - Samoa area around 1000 BC. Description Prior to the 15th century AD, Polynesian peoples fanned out to the east, to the Cook Islands, and from there to other groups such as Tahiti and the Marquesas. Their descendants later discovered the islands from Tahiti to Rapa Nui, and later Hawai‘i and New Zealand. The latest research puts the settlement of New Zealand at about 1300 AD. The various Polynesian languages are all part of the Austronesian language family. Many are close enough in terms of vocabulary and grammar to permit communication between some other language speakers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface of the Earth) without having to rely solely on estimated positional calculations, commonly known as "dead reckoning", made in the absence of satellite navigation or other similar modern electronic or digital positioning means. Celestial navigation uses "sights", or timed angular measurements, taken typically between a celestial body (e.g. the Sun, the Moon, a planet, or a star) and the visible horizon. Celestial navigation can also take advantage of measurements between celestial bodies without reference to the Earth horizon, such as when the Moon and other selected bodies are used in the practice called "lunars" or lunar distance method, used for determining precise time when time is unknown. Celestial navigation by taking sights of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
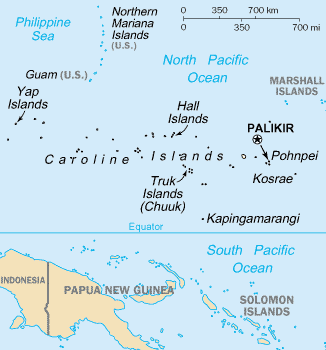
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the central and eastern parts of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end. Historically, this area was also called ''Nuevas Filipinas'' or New Philippines, because they were part of the Spanish East Indies and were governed from Manila in the Philippines. The Carolines are scattered across a distance of approximately 3,540 kilometers (2,200 miles), from the westernmost island, Tobi (island), Tobi, in Palau, to the easternmost island, Kosrae, a Administrative divisions of the Federated States of Micronesia, state of the FSM. Description The group consists of about 500 small coral islands, east of the Philippines, in the Pacific Ocean. The distance from Yap (one of the larger Caroline islands) to Manila is . Most of the islands are made up of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigger Fishes Tied Together
Trigger may refer to: Notable animals and people ;Mononym * Trigger (horse), owned by cowboy star Roy Rogers ;Nickname * Trigger Alpert (1916–2013), American jazz bassist * "Trigger Mike" Coppola (1900–1966), American gangster ;Surname * Bruce Trigger (1937–2006), Canadian archaeologist * Damon Trigger (born 1972), New Zealand born former English cricketer * Hannah Trigger (born 1987), Australian snowboarder * Ian Trigger (1938–2010), British actor Technology * Trigger (firearms), a mechanism that actuates the firing of firearms * Database trigger, procedural code that is automatically executed in response to certain events * Dead man's trigger, a safety device that activates safeguards if the operator is incapacitated * Flip-flop (electronics), called a trigger circuit by IBM * Image trigger, a device used in high speed cameras * Schmitt trigger, an electronic circuit Art, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Trigger (''Only Fools and Horses''), a BBC sitc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The Polynesian Society
The Polynesian Society is a non-profit organisation based at the University of Auckland, New Zealand, dedicated to the scholarly study of the history, ethnography, and mythology of Oceania. History The society was co-founded in 1892 by Percy Smith and Edward Tregear, largely in response to a conviction, widely held at the time, that the Māori and other Polynesian peoples were a dying race. Smith and his friends hoped that it would help to preserve the traditional lore of the Māori before it disappeared and provide scholars with a forum for learned discussion of their ethnographic research (Byrnes 2006). The initial membership of the society was 112, which had grown to 1,300 by 1965. Presidents have included bishops H. W. and W. L. Williams; James Pope, Edward Tregear, Percy Smith, Elsdon Best, William Skinner, Sir Āpirana Ngata, Harry Skinner, J. M. McEwen, Professor Sir Hugh Kawharu and Dame Joan Metge. The present president is Dr Richard Benton. Until her death in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auckland University
The University of Auckland is a public university, public research university based in Auckland, New Zealand. It is the largest, most comprehensive and highest-ranked university in New Zealand and consistently places among the top 100 universities in the QS World University Rankings. The institution was established in 1883 as a constituent college of the University of New Zealand. Originally it was housed in a disused courthouse. Today, the University of Auckland is List of universities in New Zealand, New Zealand's largest university by enrolment, hosting about 40,000 students on five Auckland campuses. The City Campus, in the Auckland CBD, has the bulk of the students and faculty (division), faculties. There are eight faculties, including a University of Auckland Law School, law school, as well as three associated research institutes. History Origins The University of Auckland began as a constituent college of the University of New Zealand, founded on 23 May 1883 as ''Auckla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesian Navigation
Polynesian navigation or Polynesian wayfinding was used for thousands of years to enable long voyages across thousands of kilometers of the Pelagic zone, open Pacific Ocean. Polynesians made contact with nearly every island within the vast Polynesian Triangle, using outrigger canoes or double-hulled canoes. The double-hulled canoes were two large hulls, equal in length, and lashed side by side. The space between the paralleled canoes allowed for storage of food, hunting materials, and nets when embarking on long voyages. Polynesian navigators used wayfinding techniques such as the navigation by the stars, and observations of birds, ocean swells, and wind patterns, and relied on a large body of knowledge from oral tradition. Navigators travelled to small inhabited islands using wayfinding techniques and knowledge passed by oral tradition from master to apprentice, often in the form of song. Generally, each island maintained a guild of navigators who had very high status; in times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micronesian Navigation
Micronesian navigation techniques are those navigation skills used for thousands of years by the navigators who voyaged between the thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean in the subregion of Oceania, that is commonly known as Micronesia. These voyagers used wayfinding techniques such as the navigation by the stars, and observations of birds, ocean swells, and wind patterns, and relied on a large body of knowledge from oral tradition. These navigation techniques continued to be held by Polynesian navigation, Polynesian navigators and navigators from the Santa Cruz Islands. The Polynesian Voyaging Society, re-creations of Polynesian voyaging in the late 20th century used traditional stellar navigational methods that had remained in everyday use in the Caroline Islands. Early voyaging Based on the current scientific consensus, the Micronesians are considered, by linguistic, archaeological, and human genetic evidence, to be a subset of the sea-migrating Austronesian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface of the Earth) without having to rely solely on estimated positional calculations, commonly known as "dead reckoning", made in the absence of satellite navigation or other similar modern electronic or digital positioning means. Celestial navigation uses "sights", or timed angular measurements, taken typically between a celestial body (e.g. the Sun, the Moon, a planet, or a star) and the visible horizon. Celestial navigation can also take advantage of measurements between celestial bodies without reference to the Earth horizon, such as when the Moon and other selected bodies are used in the practice called "lunars" or lunar distance method, used for determining precise time when time is unknown. Celestial navigation by taking sights of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)