|
Fall Of Rome
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided among several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading peoples outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climatic changes and both endemic and epidemic disease drove many of these immediate factors. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the historiog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
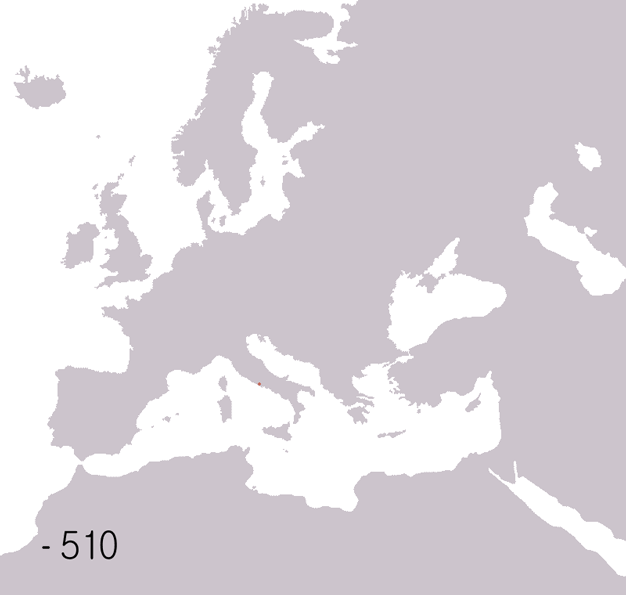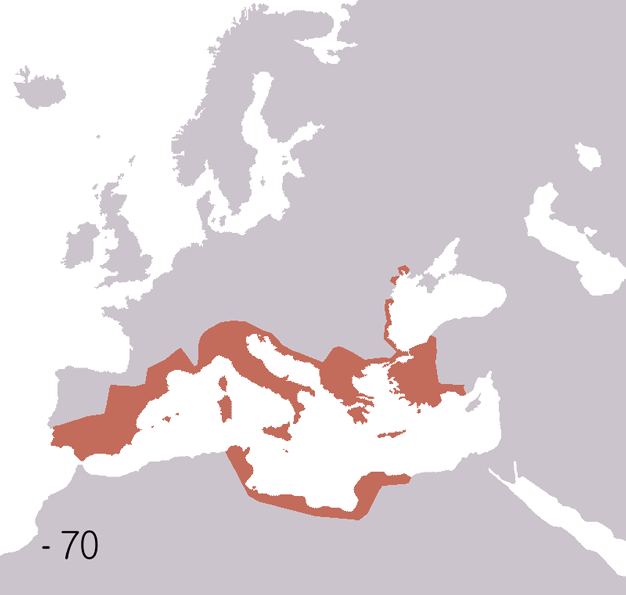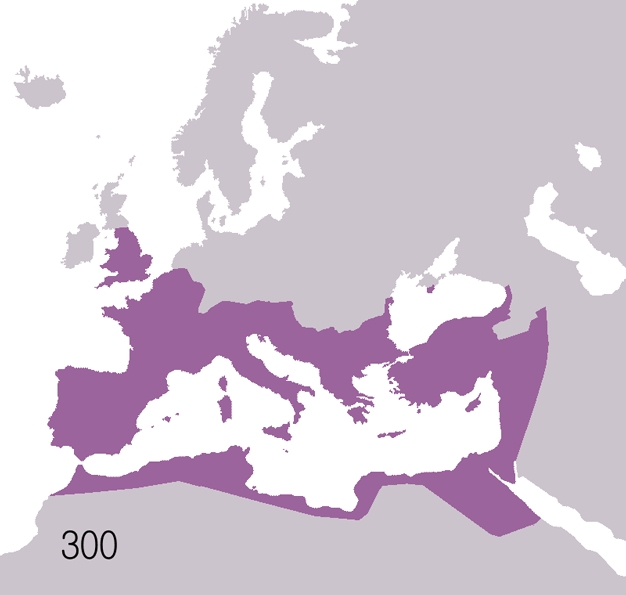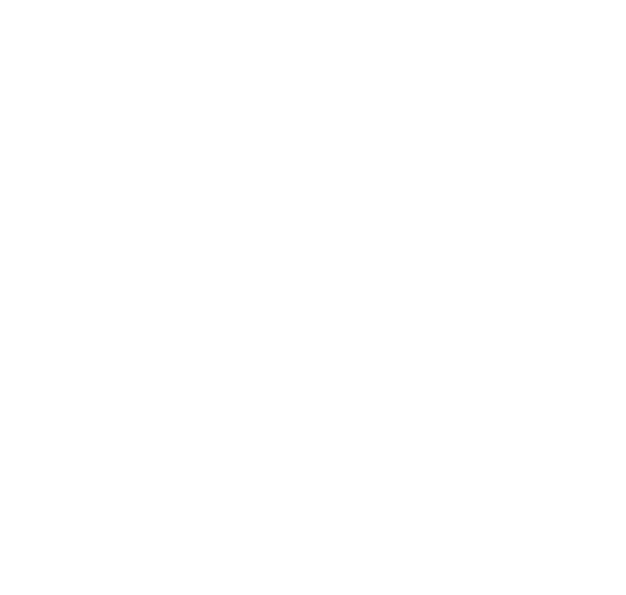
Roman Republic Empire Map
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of Roman civilization *Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter written by Paul, found in the New Testament of the Christian Bible *Ar-Rum (), the 30th sura of the Quran. Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music *Romans (band), a Japanese pop group *Roman (album), ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 *Roman (EP), ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *"Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio *Roman (film), ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film *Romans (2013 film), ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film *Romans (2017 film), ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film *The Romans (Doctor Who), ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic War (376–382)
The Gothic War of 376–382 was one of several Gothic Wars in Roman history in which the Goths fought against the Roman Empire. This particular conflict included the catastrophic Roman defeat at the Battle of Adrianople, which is commonly seen as a cause of the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, decline of the Western Roman Empire, although its significance is widely debated. Background In the summer of 376, a massive number of Goths arrived on the Danube River, the border of the Roman Empire, requesting asylum from the Huns. There were two groups: the Thervings led by Fritigern and Alavivus and the Greuthungi led by Alatheus and Saphrax. Eunapius states their number as 200,000 including civilians, but Peter Heather estimates that the Thervings may have had only 10,000 warriors and 50,000 people in total, with the Greuthungi about the same size. ''The Cambridge Ancient History'' places modern estimates at around 90,000 people. Noel Lenski accepts Eunapius' number as approximating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English essayist, historian, and politician. His most important work, ''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1789, is known for the quality and irony of its prose, its use of primary sources, and its polemical Criticism of religion, criticism of organized religion. Early life: 1737–1752 Edward Gibbon was born in 1737, the son of Edward Gibbon (died 1770), Edward and Judith Gibbon, at Lime Grove in the town of Putney, Surrey. He had five brothers and one sister, all of whom died in infancy. His grandfather, also named Edward, had lost his assets as a result of the South Sea Company, South Sea bubble stock-market collapse in 1720 but eventually regained much of his wealth. Gibbon's father thus inherited a substantial estate. His paternal grandmother, Catherine Acton, was granddaughter of Sir Walter Acton, 2nd Baronet. Gibbon described himself as "a puny child, neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodization has since been widely accepted. Late antiquity represents a cultural sphere that covered much of the Mediterranean world, including parts of Europe and the Near East.Brown, Peter (1971), ''The World of Late Antiquity (1971), The World of Late Antiquity, AD 150-750''Introduction Late antiquity was an era of massive political and religious transformation. It marked the origins or ascendance of the three major monotheistic religions: Christianity, rabbinic Judaism, and Islam. It also marked the ends of both the Western Roman Empire and the Sasanian Empire, the last Persian empire of antiquity, and the beginning of the early Muslim conquests, Arab conquests. Meanwhile, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire became a milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a loosely delimited region comprising the easternmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, and well as the adjoining land—often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea. It includes the southern half of Turkey's main region, Anatolia; its smaller Hatay Province; the island of Cyprus; the Greek Dodecanese islands; and the countries of Egypt, Israel, Jordan, State of Palestine, Palestine, Syria and Lebanon. Its broadest uses can encompass the Libyan Sea (thus Libya), the Aegean Sea (thus East Thrace, European Turkey and the mainland and islands of Greece), and the Ionian Sea (thus southern Albania in Southeast Europe) and can extend west to Italy's farthest south-eastern coasts. Jordan is climatically and economically part of the region. Regions The eastern Mediterranean region is commonly interpreted in two ways: *The Levant, including its historically tied neighboring countries, Balkans and islands of Greece. *The Syria (region), region of Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeno (emperor)
Zeno (; ; – 9 April 491) was Eastern Roman emperor from 474 to 475 and again from 476 to 491. His reign was plagued by domestic revolts and religious dissension, but was more successful on the foreign front. He is credited with further stabilizing the Eastern empire, while the Western Roman Empire fell following the deposition of Romulus Augustulus. Born in Isauria, Zeno was known as Tarasis before adopting his Greek name and becoming an ally of Emperor Leo I (emperor), Leo I, who saw the Isaurian general as an important counterweight against the Germanic leader Aspar. In 466, he married Leo I's daughter, Ariadne (empress), Ariadne, with whom he had a son, Leo II (emperor), Leo. On the death of Leo I in 474, Zeno's seven-year-old son took the throne as Leo II, with Zeno made co-emperor shortly after. Leo II died of an illness later that year, leaving Zeno as the sole emperor. Despite his early success in making peace with the Vandals, Zeno was an unpopular emperor due to his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Roman Emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. Modern historians distinguish this later phase of the Roman Empire as Byzantine due to the imperial seat moving from Rome to Byzantium, the Empire's integration of Christianity, and the predominance of Greek instead of Latin. The Byzantine Empire was the direct legal continuation of the eastern half of the Roman Empire following the division of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romulus Augustulus
Romulus Augustus (after 511), nicknamed Augustulus, was Roman emperor of the Western Roman Empire, West from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476. Romulus was placed on the imperial throne while still a minor by his father Orestes (father of Romulus Augustulus), Orestes, the , for whom he served as little more than a figurehead. After a rule of ten months, the barbarian general Odoacer defeated and killed Orestes and deposed Romulus. As Odoacer did not proclaim any successor, Romulus is typically regarded as the last Western Roman emperor, his deposition marking the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, end of the Western Roman Empire as a political entity. The deposition of Romulus Augustulus is also sometimes used by historians to mark the transition from Classical antiquity, antiquity to the medieval period. Very few records survive of Romulus's reign. There are no known policies, laws or inscriptions of significance of the emperor, which leaves the impression that he was a shado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odoacer
Odoacer ( – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a barbarian soldier and statesman from the Middle Danube who deposed the Western Roman child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became the ruler of Italy (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustulus is traditionally understood as marking the end of the Western Roman Empire. Although he held power over Italy, he also represented himself as the client of the Eastern Roman Emperor in Constantinople, Zeno. He was referred to not only as a king (), but also as commander (), or using the Roman honorific patrician, granted by Zeno. Odoacer himself used the title of king in the only surviving official document that emanated from his chancery, and it was also used by the consul Basilius. He had the support of the Roman Senate and was able to distribute land to his followers without much opposition. Unrest among his soldiers led to violence in 477–478, but no such disturbances occurred during the later p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of the Roman Empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of ''Germani'' involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of ''Germania'' was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term ''Germani ''is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE. Different ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |