|
FUJIC
FUJIC was the first electronic digital computer in operation in Japan. It was finished in March 1956, the project having been effectively started in 1949, and was built almost entirely by Dr. Okazaki Bunji. Originally designed to perform calculations for lens design by Fuji, the ultimate goal of FUJIC's construction was to achieve a speed 1,000 times that of human calculation for the same purpose – the actual performance achieved was double that number. Employing approximately 1,700 vacuum tubes, the computer's word length was 33 bits. It had an ultrasonic mercury delay-line memory of 255 words, with an average access time of 500 microseconds. An addition or subtraction was clocked at 100 microseconds, multiplication at 1,600 microseconds, and division at 2,100 microseconds. Used extensively for two years at the Fuji factory in Odawara, it was given later to Waseda University before taking up residence in the National Science Museum of Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FUJIC 1956 National Museum Of Nature And Science 2
FUJIC was the first electronic digital computer in operation in Japan. It was finished in March 1956, the project having been effectively started in 1949, and was built almost entirely by Dr. Okazaki Bunji. Originally designed to perform calculations for lens design by Fujifilm, Fuji, the ultimate goal of FUJIC's construction was to achieve a speed 1,000 times that of human calculation for the same purpose – the actual performance achieved was double that number. Employing approximately 1,700 vacuum tubes, the computer's Word (computer architecture), word length was 33 bits. It had an Ultrasound, ultrasonic mercury delay-line memory of 255 words, with an average access time of 500 microseconds. An addition or subtraction was clocked at 100 microseconds, multiplication at 1,600 microseconds, and division at 2,100 microseconds. Used extensively for two years at the Fuji factory in Odawara, it was given later to Waseda University before takin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
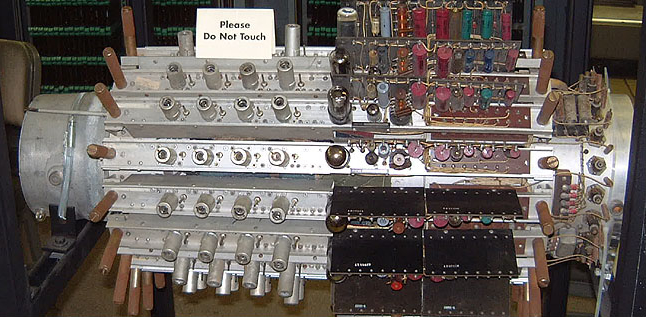
MUSASINO-1
The MUSASINO-1 was one of the earliest electronic digital computers built in Japan. Construction started at the Electrical Communication Laboratories of NTT at Musashino, Tokyo in 1952 and was completed in July 1957. The computer was used until July 1962. Saburo Muroga, a University of Illinois visiting scholar and member of the ILLIAC I team, returned to Japan and oversaw the construction of MUSASINO-1. Using 519 vacuum tubes and 5,400 parametrons, the MUSASINO-1 possessed a magnetic core memory, initially of 32 (later expanded to 256) words. A word was composed of 40 bits, and two instructions could be stored in a single word. Addition time was clocked at 1,350 microseconds, multiplication at 6,800 microseconds, and division time at 26.1 milliseconds. The MUSASINO-1's instruction set was a superset of the ILLIAC I's instructions, so it could generally use the latter's software. However, many of the programs for the ILLIAC used some of the unused bits in the instructions to store ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Vacuum-tube Computers
Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using vacuum-tube logic circuitry. They were preceded by systems using electromechanical relays and followed by systems built from discrete transistors. Some later computers on the list had both vacuum tubes and transistors. This list of vacuum-tube computers is sorted by date put into service: }) are identical, except input-output equipment. Both were used internally. , - , The Wegematic 1000 , , 1960 , , , Improved version of the ALWAC III-E , - , ZRA 1 , , 1960 , , , Built by VEB Carl Zeiss, Jena, German Democratic RepublicSiegmar Gerber: ''Einsatz von Zeiss-Rechnern für Forschung, Lehre und Dienstleistung in Informatik in der DDR – eine Bilanz''. GI-Edition, Bonn 2006, p. 310–318 , - , Minsk-1 , , 1960 , , , Built in Minsk , - , Odra 1001 , , 1960 , , , First computer built by Elwro, Wroclaw, Poland , - , Minsk-1 , , 1960 , , , Built in Minsk , - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube Computers
Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using vacuum-tube logic circuitry. They were preceded by systems using electromechanical relays and followed by systems built from discrete transistors. Some later computers on the list had both vacuum tubes and transistors. This list of vacuum-tube computers is sorted by date put into service: }) are identical, except input-output equipment. Both were used internally. , - , The Wegematic 1000 , , 1960 , , , Improved version of the ALWAC III-E , - , ZRA 1 , , 1960 , , , Built by VEB Carl Zeiss, Jena, German Democratic RepublicSiegmar Gerber: ''Einsatz von Zeiss-Rechnern für Forschung, Lehre und Dienstleistung in Informatik in der DDR – eine Bilanz''. GI-Edition, Bonn 2006, p. 310–318 , - , Minsk-1 , , 1960 , , , Built in Minsk , - , Odra 1001 , , 1960 , , , First computer built by Elwro, Wroclaw, Poland , - , Minsk-1 , , 1960 , , , Built in Minsk , - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word (computer Architecture)
In computing, a word is the natural unit of data used by a particular processor design. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word (the ''word size'', ''word width'', or ''word length'') is an important characteristic of any specific processor design or computer architecture. The size of a word is reflected in many aspects of a computer's structure and operation; the majority of the registers in a processor are usually word-sized and the largest datum that can be transferred to and from the working memory in a single operation is a word in many (not all) architectures. The largest possible address size, used to designate a location in memory, is typically a hardware word (here, "hardware word" means the full-sized natural word of the processor, as opposed to any other definition used). Documentation for older computers with fixed word size commonly states memory sizes in words ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 Hertz, kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating Predation, prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pyth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delay-line Memory
Delay-line memory is a form of computer memory, now obsolete, that was used on some of the earliest digital computers. Like many modern forms of electronic computer memory, delay-line memory was a refreshable memory, but as opposed to modern random-access memory, delay-line memory was sequential-access. Analog delay line technology had been used since the 1920s to delay the propagation of analog signals. When a delay line is used as a memory device, an amplifier and a pulse shaper are connected between the output of the delay line and the input. These devices recirculate the signals from the output back into the input, creating a loop that maintains the signal as long as power is applied. The shaper ensures the pulses remain well-formed, removing any degradation due to losses in the medium. The memory capacity is determined by dividing the time taken to transmit one bit into the time it takes for data to circulate through the delay line. Early delay-line memory systems had ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odawara
is a city in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 188,482 and a population density of 1,700 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . Geography Odawara lies in the Ashigara Plains, in the far western portion of Kanagawa Prefecture at the southwestern tip of the Kantō region. It is bordered by the Hakone Mountains to the north and west, the Sakawa River to the east, and Sagami Bay of the Pacific Ocean to the south. Surrounding municipalities Kanagawa Prefecture * Minamiashigara * Ninomiya * Ōi, Kaisei, Nakai *Hakone, Hakone, Manazuru, Yugawara Climate Odawara has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Odawara is 13.4 °C. The average annual rainfall is 2,144 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 24.2 °C, and lowest in January, at around 2.9&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waseda University
, abbreviated as , is a private university, private research university in Shinjuku, Tokyo. Founded in 1882 as the ''Tōkyō Senmon Gakkō'' by Ōkuma Shigenobu, the school was formally renamed Waseda University in 1902. The university has numerous notable alumni, including nine Prime Minister of Japan, prime ministers of Japan, a number of important figures of Japanese literature, including Haruki Murakami, and many CEOs, including Tadashi Yanai, the CEO of UNIQLO, Nobuyuki Idei, the former CEO of Sony, Takeo Fukui, the former president and CEO of Honda, Norio Sasaki, the former CEO of Toshiba, Lee Kun-hee, the chairman of Samsung Group, Mikio Sasaki, the former chairman of Mitsubishi, and Hiroshi Yamauchi and Shuntaro Furukawa, former and current presidents of Nintendo respectively. Waseda was ranked 26th and 48th globally in the QS Graduate Employability Rankings 2017 and Times Higher Education Alma Mater Index 2017, respectively. Waseda is regarded as one of the most selective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Nature And Science
The is in the northeast corner of Ueno Park in Tokyo. The museum has exhibitions on pre-Meiji period, Meiji science in Japan. It is the venue of the taxidermied bodies of the legendary dogs Hachikō and Taro and Jiro. A life-size blue whale model and a steam locomotive are also on display outside. History file:NMNC02s3200.jpg , Blue whale Life size model. Opened in 1871, it has had several names, including Ministry of Education Museum, Tokyo Museum, Tokyo Science Museum, the National Science Museum of Japan, and the National Museum of Nature and Science as of 2007. It was renovated in the 1990s and 2000s, and offers a wide variety of natural history exhibitions and interactive scientific experiences. It was completed as the main building of the Tokyo Science Museum in September 1931 as part of the reconstruction project after the Great Kanto Earthquake. Neo-Renaissance style. Designed by Kenzo Akitani, an engineer of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)