|
FGF13
Fibroblast growth factor 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FGF13'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth, and invasion. This gene is located to a region associated with Börjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome (BFLS), a syndromal X-linked intellectual disability, which suggests it may be a candidate gene for familial cases of the BFL syndrome. The function of this gene has not yet been determined. Two alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by macrophages; they are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in their function lead to a range of developmental defects. These growth factors typically act as systemic or locally circulating molecules of extracellular origin that activate cell surface receptors. A defining property of FGFs is that they bind to heparin and to heparan sulfate. Thus, some are sequestered in the extracellular matrix of tissues that contains heparan sulfate proteoglycans and are released locally upon injury or tissue remodeling. Families In humans, 23 members of the FGF family have been identified, all of which are ''structurally'' related signaling molecules: * Members FGF1 through FGF10 all bind fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). FGF1 is also known as ''acidic fibroblast growth factor'', and FGF2 is also known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitogen
A mitogen is a small bioactive protein or peptide that induces a cell to begin cell division, or enhances the rate of division (mitosis). Mitogenesis is the induction (triggering) of mitosis, typically via a mitogen. The mechanism of action of a mitogen is that it triggers signal transduction pathways involving mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), leading to mitosis. The cell cycle Mitogens act primarily by influencing a set of proteins which are involved in the restriction of progression through the cell cycle. The G1 checkpoint is controlled most directly by mitogens: further cell cycle progression does not need mitogens to continue. The point where mitogens are no longer needed to move the cell cycle forward is called the "restriction point" and depends on cyclins to be passed.Bohmer et al. "Cytoskeletal Integrity Is Required throughout the Mitogen Stimulation Phase of the Cell Cycle and Mediates the Anchorage-dependent Expression of Cyclin DI". January 1996, Molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Process
Biological processes are those processes that are vital for an organism to live, and that shape its capacities for interacting with its environment. Biological processes are made of many chemical reactions or other events that are involved in the persistence and transformation of life forms. Metabolism and homeostasis are examples. Biological processes within an organism can also work as bioindicators. Scientists are able to look at an individual's biological processes to monitor the effects of environmental changes. Regulation of biological processes occurs when any process is modulated in its frequency, rate or extent. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule. * Homeostasis: regulation of the internal environment to maintain a constant state; for example, sweating to reduce temperature * Organization: being structurally composed of one or more cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome or autophagy, or catabolism). Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two daughter cells. Importantly, cell growth and cell division can also occur independently of one another. During early embryonic development ( cleavage of the zygote to form a morula and blastoderm), cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycle, such as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of developmental biology along with the control of tissue growth and patterning of cellular differentiation. The process controls the organized spatial distribution of cells during the embryonic development of an organism. Morphogenesis can take place also in a mature organism, such as in the normal maintenance of tissue by stem cells or in regeneration of tissues after damage. Cancer is an example of highly abnormal and pathological tissue morphogenesis. Morphogenesis also describes the development of unicellular life forms that do not have an embryonic stage in their life cycle. Morphogenesis is essential for the evolution of new forms. Morphogenesis is a mechanical process involving forces that generate mechanical stress, strain, and moveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
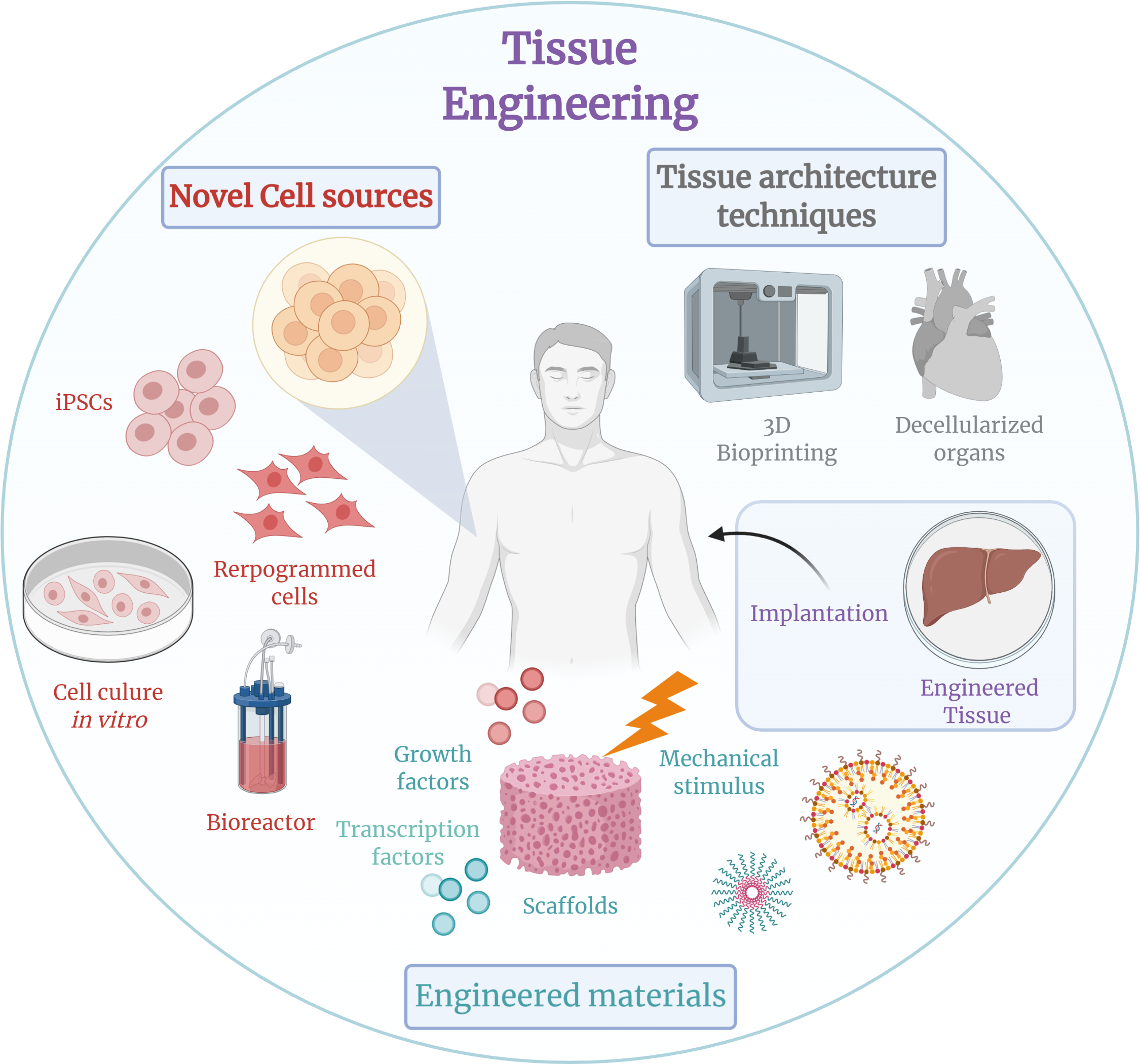
Tissue Repair
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of cells, engineering, materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field of its own. While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e. bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intellectual Disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation,Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significantly impaired intellectual and adaptive functioning. It is defined by an IQ under 70, in addition to deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors that affect everyday, general living. Intellectual functions are defined under DSM-V as reasoning, problem‑solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning from instruction and experience, and practical understanding confirmed by both clinical assessment and standardized tests. Adaptive behavior is defined in terms of conceptual, social, and practical skills involving tasks performed by people in their everyday lives. Intellectual disability is subdivided into syndromic intellectual disability, in which intellectual deficits associated with other medical and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |