|
FC-PGA
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package. PGAs are often mounted on printed circuit boards using the through hole method or inserted into a socket. PGAs allow for more pins per integrated circuit than older packages, such as dual in-line package (DIP). PGA variants Plastic Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) packaging was used by Intel for late-model Mendocino core Celeron processors based on Socket 370. Some pre-Socket 8 processors also used a similar form factor, although they were not officially referred to as PPGA. Flip chip A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the die faces downwards on the top of the substrate with the back of the die exposed. This allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium III
The Pentium III (marketed as Intel Pentium III Processor, informally PIII or P3) brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded processors. The most notable differences were the addition of the Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set (to accelerate floating point and parallel calculations), and the introduction of a controversial serial number embedded in the chip during manufacturing. The Pentium III is also a single-core processor. Even after the release of the Pentium 4 in late 2000, the Pentium III continued to be produced with new models introduced until early 2003, and were discontinued in April 2004 for desktop units, and May 2007 for mobile units. Processor cores Similarly to the Pentium II it superseded, the Pentium III was also accompanied by the Celeron brand for lower-end versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 370
Socket 370 (also known as the PGA370 socket) is a CPU socket first used by Intel for Pentium III and Celeron processors to first complement and later replace the older Slot 1 CPU interface on personal computers. The "370" refers to the number of pin holes in the socket for CPU pins. Socket 370 was replaced by Socket 423 in 2000. Overview Socket 370 started as a budget oriented platform for 66 MHz FSB PPGA Mendocino Celeron CPUs in late 1998, as the move to on-die L2 cache removed the need for a PCB design as seen on Slot 1. From late 1999 to late 2000 it was Intel's main desktop socket for 100/133 MHz FSB Coppermine Pentium IIIs. In 2001, the Tualatin Pentium III processors brought changes to the infrastructure which required dedicated Tualatin-compatible motherboards; some manufacturers would indicate this with a blue (instead of white) socket. These late sockets were typically compatible with Coppermine processors, but not older Mendocino Celerons. Some motherboards that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 478
Socket 478, also known as mPGA478 or mPGA478B, is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs. Socket 478 was launched in August 2001 in advance of the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and their Athlon XP processors. Socket 478 was intended to be the replacement for Socket 423, a Willamette-based processor socket which was on the market for only a short time. Socket 478 was phased out with the launch of LGA 775 in 2004. Technical specifications Socket 478 was used for all Northwood Pentium 4 and Celeron processors. It supported the first Prescott Pentium 4 processors and all Willamette Celerons, along with several of the Willamette-series Pentium 4s. Socket 478 also supported the newer Prescott-based Celeron D processors, and early Pentium 4 Extreme Edition processors with 2 MB of L3 CPU cache. Celeron D processors were also available for Socket 478 and were the last CPUs made for the socket. While the Intel mobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers. Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 IA-32 (short for "Intel Architecture, 32-bit", commonly called i386) is the 32-bit version of the x86 instruction set architecture, designed by Intel and first implemented in the 80386 microprocessor in 1985. IA-32 is the first incarnation of ... software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed compared to flagship Intel CPU lines, such as the Pentium or Intel Core (microarchitecture), Core brands. Celeron branded processors often have less CPU cache, cache or intentionally disabled advanced features, with variable impact on performance. While some Celeron designs have achieved strong performance for their segment, most of the Celeron line has exhibited noticeably degraded performance. This has been the primary Market segmentation, justification for the higher cost of other Intel CPU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core CPUs for desktops, laptops and entry-level servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 2008. The production of Netburst processors was active from 2000 until May 21, 2010. All Pentium 4 CPUs are based on the NetBurst microarchitecture. The Pentium 4 '' Willamette'' (180 nm) introduced SSE2, while the '' Prescott'' (90 nm) introduced SSE3. Later versions introduced Hyper-Threading Technology (HTT). The first Pentium 4-branded processor to implement 64-bit was the ''Prescott'' (90 nm) (February 2004), but this feature was not enabled. Intel subsequently began selling 64-bit Pentium 4s using the ''"E0" revision'' of the Prescotts, being sold on the OEM market as the Pentium 4, model F. The E0 revision also adds eXecute Disable (XD) (Intel's name for the NX bit) to Intel 64. Intel's official launch of Intel 64 (under the name EM64T at that time) in mainstream deskt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero Insertion Force
Zero insertion force (ZIF) is a type of IC socket or electrical connector that requires very little (but not literally zero) force for insertion. With a ZIF socket, before the IC is inserted, a lever or slider on the side of the socket is moved, pushing all the sprung contacts apart so that the IC can be inserted with very little force - generally the weight of the IC itself is sufficient and no external downward force is required. The lever is then moved back, allowing the contacts to close and grip the pins of the IC. ZIF sockets are much more expensive than standard IC sockets and also tend to take up a larger board area due to the space taken up by the lever mechanism. Typically, they are only used when there is a good reason to do so. Design A normal integrated circuit (IC) socket requires the IC to be pushed into sprung contacts which then grip by friction. For an IC with hundreds of pins, the total insertion force can be very large (hundreds of newtons), leading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 5
Socket 5 was created for the second generation of Intel P5 Pentium processors operating at speeds from 75 to 133 MHz as well as certain Pentium OverDrive and Pentium MMX processors with core voltage 3.3 V. It superseded the earlier Socket 4. It was released in March 1994. Consisting of 320 pins, this was the first socket to use a staggered pin grid array, or SPGA, which allowed the chip's pins to be spaced closer together than earlier sockets. Socket 5 was replaced by Socket 7 in 1995. External linksDifferences between Socket 5 and Socket 7(archived) See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of AMD microprocessors This article gives a list of AMD microprocessors, sorted by generation and release year. If applicable and openly known, the designation(s) of each processor's core (versions) is (are) listed in parentheses. For an overview over concrete product, y ... References {{earlysock Socket 005 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
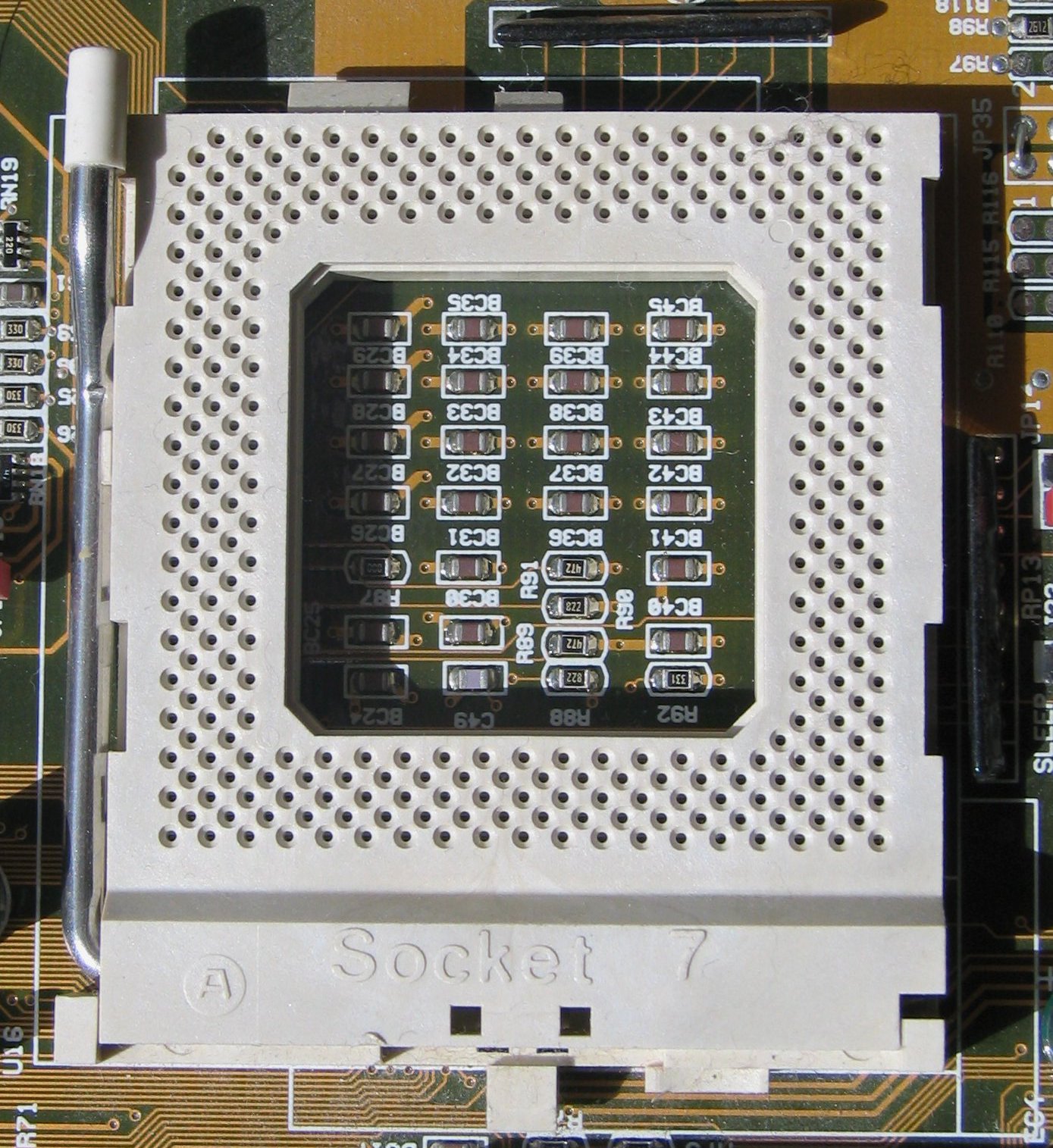
Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. It was released in June 1995. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/ IBM, AMD, IDT and others. Socket 7 was the only socket that supported a wide range of CPUs from different manufacturers and a wide range of speeds. Differences between Socket 5 and Socket 7 are that Socket 7 has an extra pin and is designed to provide dual split rail voltage, as opposed to Socket 5's single voltage. However, not all motherboard manufacturers supported the dual voltage on their boards initially. Socket 7 is backwards compatible; a Socket 5 CPU can be inserted and used on a Socket 7 motherboard. Processors that used Socket 7 are the AMD K5 and K6, the Cyrix 6x86 and 6x86MX, the IDT WinChip, the Intel P5 Pentium (2.5–3.5 V, 75–200 MHz), the Pentium MMX (166–23 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 8
The Socket 8 CPU socket was used exclusively with the Intel Pentium Pro and Pentium II Overdrive computer processors. Intel discontinued Socket 8 in favor of Slot 1 with the introduction of the Pentium II and Slot 2 with the release of the Pentium II Xeon in 1999. Technical specifications Socket 8 is a unique rectangular CPGA socket with 387 pins. It supports FSB speeds ranging from 60 to 66 MHz, a voltage from 3.1 or 3.3V, and support for the Pentium Pro and the Pentium II OverDrive CPUs. Socket 8 also has a unique pin arrangement pattern. One part of the socket has pins in a PGA grid, while the other part uses a SPGA grid. Intel did not return to rectangular sockets until the launch of LGA 1700 in late 2021. Intel Pentium II Overdrive Engineering Sample.jpg, An engineering sample of the Pentium II Overdrive CPU showing the bottom of the unit. KL Socket8 Slot1 Adapter.jpg, Socket 8 to Slot 1 adapter See also *List of Intel microprocessors This generational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD Phenom II X6 1090T (HDT90ZFBK6DGR) CPU-pins PNr°0295
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufactured its own processors, the company later outsourced its manufacturing, a practice known as going fabless, after GlobalFoundries was spun off in 2009. AMD's main products include microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, graphics processors, and FPGAs for servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded system applications. History First twelve years Advanced Micro Devices was formally incorporated by Jerry Sanders, along with seven of his colleagues from Fairchild Semiconductor, on May 1, 1969. Sanders, an electrical engineer who was the director of marketing at Fairchild, had, like many Fairchild executives, grown frustrated with the increasing lack of support, opportunity, and flexibility within the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice (group)
In geometry and group theory, a lattice in the real coordinate space \mathbb^n is an infinite set of points in this space with the properties that coordinate wise addition or subtraction of two points in the lattice produces another lattice point, that the lattice points are all separated by some minimum distance, and that every point in the space is within some maximum distance of a lattice point. Closure under addition and subtraction means that a lattice must be a subgroup of the additive group of the points in the space, and the requirements of minimum and maximum distance can be summarized by saying that a lattice is a Delone set. More abstractly, a lattice can be described as a free abelian group of dimension n which spans the vector space \mathbb^n. For any basis of \mathbb^n, the subgroup of all linear combinations with integer coefficients of the basis vectors forms a lattice, and every lattice can be formed from a basis in this way. A lattice may be viewed as a regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few integrated circuits using Very-Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) greatly reduced the cost of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_CPU-pins_PNr°0295.jpg)


_(JPG).jpg)