|
FACTS Ubt 2
A flexible alternating current transmission system (FACTS) is a system composed of static equipment used for the alternating current (AC) transmission of electrical energy. It is meant to enhance controllability and increase power transfer capability of the network. It is generally a power electronics-based system. FACTS is defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as "a power electronic based system and other static equipment that provide control of one or more AC transmission system parameters to enhance controllability and increase power transfer capability". According to Siemens, "FACTS Increase the reliability of AC grids and reduce power delivery costs. They improve transmission quality and efficiency of power transmission by supplying inductive or reactive power to grid. Technology Shunt compensation In shunt compensation, power system is connected in shunt (parallel) with the FACTS. It works as a controllable current source. Shunt comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify '' current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa. In certain applications, like guitar amplifiers, different waveforms are used, such as triangular waves or square waves. Audio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Synchronous Series Compensator
A static synchronous series compensator (SSSC) is a type of flexible AC transmission system which consists of a solid-state voltage source inverter coupled with a transformer that is connected in series with a transmission line. This device can inject an almost sinusoidal voltage in series with the line. This injected voltage could be considered as an inductive or capacitive reactance, which is connected in series with the transmission line. This feature can provide controllable voltage compensation. In addition, SSSC is able to reverse the power flow by injecting a sufficiently large series reactive compensating voltage. See also * Active power filter * Static synchronous compensator (STATCOM), a similar shunt-connected device * Unified power flow controller, a combination of SSSC and STATCOM * Dynamic voltage restoration Dynamic voltage restoration (DVR) is a method of overcoming voltage sags and swells that occur in electrical power distribution. These are a problem beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HVDC
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) transmission systems. Most HVDC links use voltages between 100 kV and 800 kV. However, a 1,100 kV link in China was completed in 2019 over a distance of with a power capacity of 12 GW. With this dimension, intercontinental connections become possible which could help to deal with the fluctuations of wind power and photovoltaics. HVDC allows power transmission between AC transmission systems that are not synchronized. Since the power flow through an HVDC link can be controlled independently of the phase angle between source and load, it can stabilize a network against disturbances due to rapid changes in power. HVDC also allows the transfer of power between grid systems running at different frequencies, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
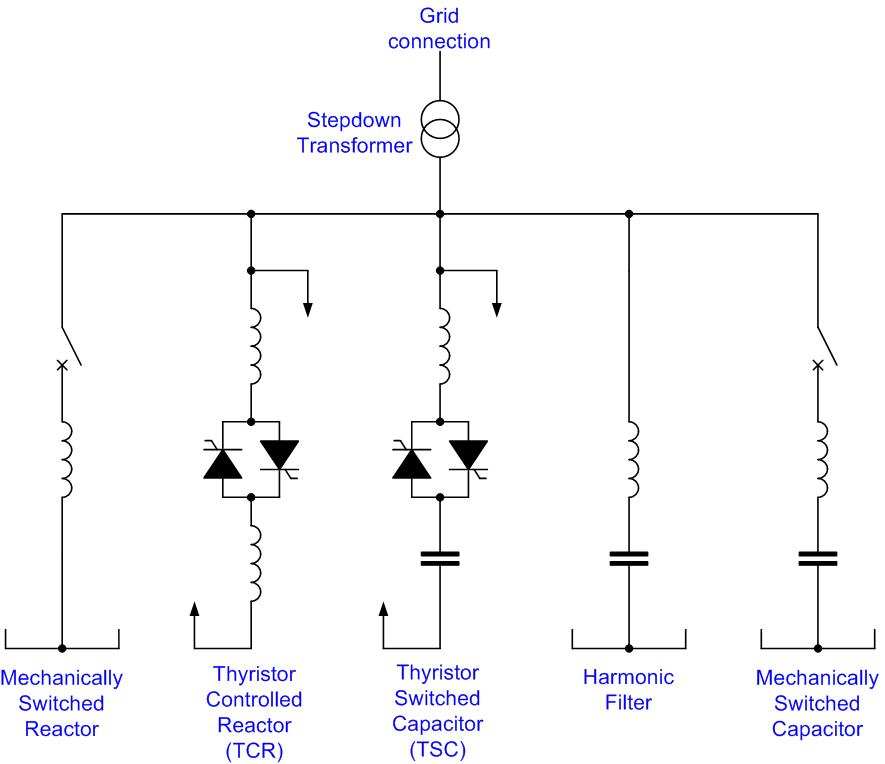
Static VAR Compensator
A static VAR compensator (SVC) is a set of electrical devices for providing fast-acting reactive power on high-voltage electricity transmission networks. SVCs are part of the flexible AC transmission system device family, regulating voltage, power factor, harmonics and stabilizing the system. A static VAR compensator has no significant moving parts (other than internal switchgear). Prior to the invention of the SVC, power factor compensation was the preserve of large rotating machines such as synchronous condensers or switched capacitor banks. The SVC is an automated impedance matching device, designed to bring the system closer to unity power factor. SVCs are used in two main situations: * Connected to the power system, to regulate the transmission voltage ("transmission SVC") * Connected near large industrial loads, to improve power quality ("industrial SVC") In transmission applications, the SVC is used to regulate the grid voltage. If the power system's reactive load is capac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
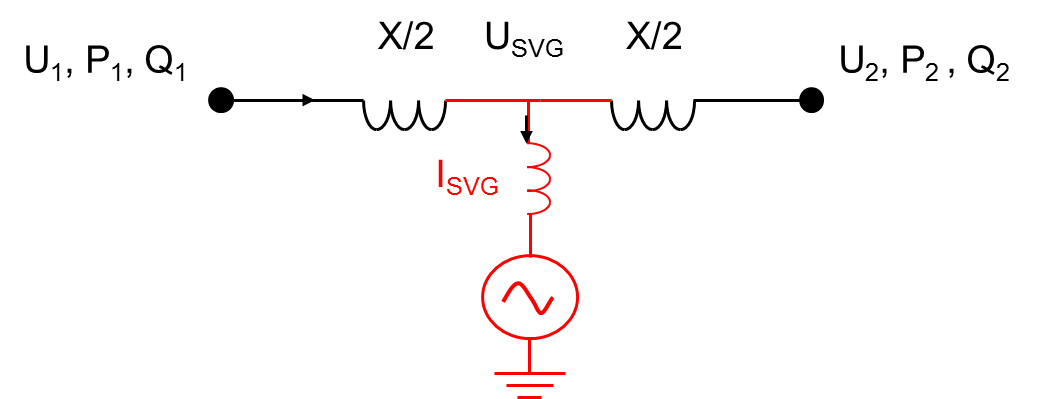
STATCOM
A static synchronous compensator (STATCOM), originally known as a static synchronous condenser (STATCON), is a regulating device shunt-connected to alternating current electricity transmission network. It is based on a power electronics voltage-source converter and can act as either a source or sink of reactive AC power to an electricity network. If connected to a source of power it can also provide active AC power. It is a member of the FACTS family of devices, that became possible in 1990s due to availability of powerful gate turn-off thyristors (GTO). STATCOM is inherently modular and electable. These compensators can also be used to reduce voltage fluctuations. History and uses A prototype 1 MVAr STATCON was described in a report by Empire State Electric Energy Research Corporation in 1987. The first production 100 MVAr STATCON made by Westinghouse Electric was installed at the Tennessee Valley Authority Sullivan substation in 1995 and was quickly retired due to obsolesce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FACTS Shunt Compensation1
A flexible alternating current transmission system (FACTS) is a system composed of static equipment used for the alternating current (AC) transmission of electrical energy. It is meant to enhance controllability and increase power transfer capability of the network. It is generally a power electronics-based system. FACTS is defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as "a power electronic based system and other static equipment that provide control of one or more AC transmission system parameters to enhance controllability and increase power transfer capability". According to Siemens, "FACTS Increase the reliability of AC grids and reduce power delivery costs. They improve transmission quality and efficiency of power transmission by supplying inductive or reactive power to grid. Technology Shunt compensation In shunt compensation, power system is connected in shunt (parallel) with the FACTS. It works as a controllable current source. Shunt comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductor Reactor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a coil. When the current flowing through the coil changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces an electromotive force (''emf'') (voltage) in the conductor, described by Faraday's law of induction. According to Lenz's law, the induced voltage has a polarity (direction) which opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors oppose any changes in current through them. An inductor is characterized by its inductance, which is the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of inductance is the henry (H) named for 19th century American scientist Joseph Henry. In the measurement of magnetic circuits, it is equivalent to . Inductors have values that typically ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the '' condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)