|
Fête De La Fédération
The (; ) was a massive holiday festival held throughout Kingdom of France, France in 1790 in honour of the French Revolution, celebrating the Revolution itself, as well as national unity. It commemorated the revolution and events of 1789 which had culminated in a new form of national government, a constitutional monarchy led by a representative National Constituent Assembly (France), Assembly. The inaugural ''fête'' of 1790 was set for 14 July, to coincide with the first anniversary of the storming of the Bastille, although that is not what was celebrated. At this relatively calm stage of the Revolution, many people considered France's period of political struggle to be over. This thinking was encouraged by the constitutional monarchist ''Monarchiens''. The first ''fête'' was designed with a role for King Louis XVI that would respect and maintain his royal status, while emphasizing his new role as the citizen king of the incipient French classical liberalism, liberal constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fête De La Fédération 1790, Musée De La Révolution Française - Vizille
In the United Kingdom and some of Crown colony, its former colonies, a fête or fete is a public festival organised to raise money for a charity, typically held outdoors. It generally includes entertainment and the sale of goods and refreshments. Fetes are typically held annually, in the summer months. Village fêtes Village fêtes are common in Britain. These are usually outdoor shows held on village greens or recreation grounds with a variety of activities. They are organised by an ad hoc committee of volunteers from organisations like religious groups or residents' associations. Fêtes can also be seen in former British colonies. In Australia, fêtes are often held yearly by schools and sometimes churches to raise funds. Attractions seen at village fêtes include Tombola (raffle), tombolas, raffles, bowling for a pig, Coconut shy, coconut shies, bat a rat, bat a rat stalls, White elephant sale, white elephant stalls, cakes, and home produce such as jams and pickles. Competiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Seine
The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern France. Its drainage basin is in the Paris Basin (a geological relative lowland) covering most of northern France. It rises at Source-Seine, northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre (and Honfleur on the left bank). It is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen, from the sea. Over 60 percent of its length, as far as Burgundy (region), Burgundy, is negotiable by large barges and most tour boats, and nearly its whole length is available for recreational boating; Bateaux Mouches, excursion boats offer sightseeing tours of the river banks in the capital city, Paris. There are 37 List of bridges in Paris#Seine, bridges in Paris across the Seine (the most famous of which are the Pont Alexandre III and the Pont Neuf) and dozens List of crossings of the River Seine, more outside the city. A notable bridge, which is also the last along the course of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette (; ; Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last List of French royal consorts, queen of France before the French Revolution and the establishment of the French First Republic. She was the wife of Louis XVI. Born Archduchess Maria Antonia of Austria, she was the penultimate child and youngest daughter of Empress Maria Theresa and Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Francis I. She married Louis Auguste, Dauphin of France, in May 1770 at age 14, becoming the Dauphine of France. On 10 May 1774, her husband ascended the throne as Louis XVI, and she became queen. As queen, Marie Antoinette became increasingly a target of criticism by opponents of the domestic and foreign policies of Louis XVI and those opposed to the monarchy in general. The French accused her of being profligate, promiscuous, having illegitimate children, and harboring sympathies for France's perceived enemies, including her native Habsburg monarchy, Austria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Popular Monarchy
Popular monarchy is a term used by Kingsley Martin (1936) for monarchical titles referring to a people rather than a territory.. This was the norm in classical antiquity and throughout much of the Middle Ages, and such titles were retained in some of the monarchies of 19th- and 20th-century Europe. During the French Revolution, Louis XVI had to change his title to indicate he was "king of the French" rather than "king of France", paralleling the title of "king of the Franks" (''rex Francorum'') used in medieval France. Currently, Belgium has the only explicit popular monarchy, the formal title of its king being ''King of the Belgians'' rather than ''King of Belgium''. List of royal and imperial titles See also *Revolutions of 1830 *'' Pater Patriae'' Notes {{DEFAULTSORT:Popular Monarchy Monarchy Monarchy A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gilbert Du Motier, Marquis De Lafayette
Marie-Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert du Motier de La Fayette, Marquis de La Fayette (; 6 September 1757 – 20 May 1834), known in the United States as Lafayette (), was a French military officer and politician who volunteered to join the Continental Army, led by General George Washington, in the American Revolutionary War. Lafayette was ultimately permitted to command Continental Army troops in the decisive Siege of Yorktown in 1781, the Revolutionary War's final major battle, which secured American independence. After returning to France, Lafayette became a key figure in the French Revolution of 1789 and the July Revolution of 1830 and continues to be celebrated as a hero in both France and the United States. Lafayette was born into a wealthy land-owning family in Chavaniac in the province of Auvergne in south-central France. He followed the family's martial tradition and was commissioned an officer at age 13. He became convinced that the American revolutionary cause was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
French Constitution Of 1791
The French Constitution of 1791 () was the first written constitution in France, created after the collapse of the absolute monarchy of the . One of the basic precepts of the French Revolution was adopting constitutionality and establishing popular sovereignty. Drafting process Early efforts Following the Tennis Court Oath, the National Assembly began the process of drafting a constitution as its primary objective. The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, adopted on 26 August 1789 eventually became the preamble of the constitution adopted on 3 September 1791. The Declaration offered sweeping generalizations about rights, liberty, and sovereignty. A twelve-member Constitutional Committee was convened on 14 July 1789 (coincidentally the day of the Storming of the Bastille). Its task was to do much of the drafting of the articles of the constitution. It included originally two members from the First Estate (Champion de Cicé, Archbishop of Bordeaux and Tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bishop Of Autun
The Diocese of Autun (–Chalon-sur-Saône–Mâcon–Cluny) (Latin: ''Diocesis Aeduensis'', ''Dioecesis Augustodunensis (–Cabillonensis–Matisconensis–Cluniacensis)''; French: ''Diocèse d'Autun (–Chalon-sur-Saône–Mâcon–Cluny)''), more simply known as the Diocese of Autun, is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in France. The diocese comprises the entire Department of Saone et Loire, in the Region of Bourgogne. The diocese was suffragan to the Archdiocese of Lyon under the Ancien Régime, and the Bishop of Autun held the post of Vicar of the Archbishop. The bishopric of Chalon-sur-Saône (since Roman times) and (early medieval) bishopric of Mâcon, also suffragans of Lyon, were united to Autun after the French Revolution by the Concordat signed by First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte and Pope Pius VII. For a short time, from 1802 to 1822, the enlarged diocese of Autun was suffragan to the Archbishop of Besançon. In 1822, however, Autun was again subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Maurice De Talleyrand
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (James (wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/ǵerh₂-">ĝer-, where the ĝ is a palatal consonant, meaning "to rub; to be old; grain." An old man has been worn away and is now grey with age. In some Slavic languages, the name ''Drago (given name), Drago'' (and variants: ''Dragom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
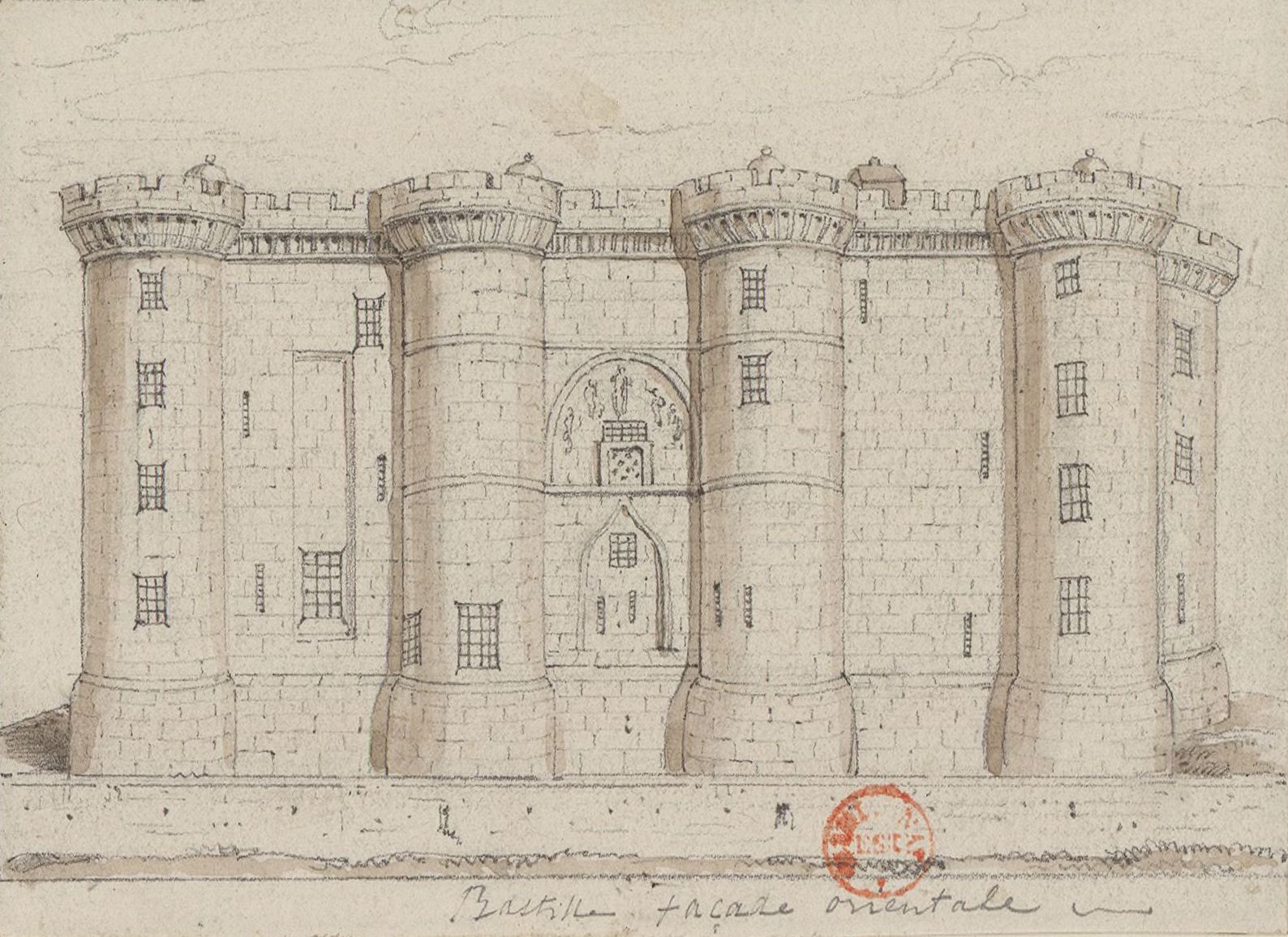
The Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions of the Burgu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |