|
Exploration Gateway Platform
The Exploration Gateway Platform was a design concept proposed by Boeing in December 2011 to drastically reduce the cost of Moon, near Earth asteroids (NEAs), or Mars missions by using components already designed to construct a refueling depot and servicing station located at one of the Earth–Moon Lagrange points, L1 or L2. The system claims its cost savings based on an ability to be reused for multiple missions such as a launch platform for deep space exploration, robotic relay station for moon rovers, telescope servicing and a deep space practice platform located outside the Earth's protective radiation belts. The platform would be constructed at the International Space Station (ISS) for testing before being relocated to EM-L1 or EM-L2 via electric or chemical propulsion rockets. Construction The Platform would consist of parts left over from the ISS program. Parts under consideration were Node 4 to form the main connection point, parts from the Space Shuttle's Orbital Mane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zvezda (ISS Module)
''Zvezda'' (russian: Звезда, meaning "star"), ''Salyut'' DOS-8, also known as the ''Zvezda'' Service Module, is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It was the third module launched to the station, and provided all of the station's life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the US Orbital Segment (USOS), as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), which is the Russian part of the ISS. Crew assemble here to deal with emergencies on the station. The module was manufactured in the USSR by RKK Energia, with major sub-contracting work by GKNPTs Khrunichev. ''Zvezda'' was launched on a Proton launch vehicle on 12 July 2000, and docked with the '' Zarya'' module on 26 July 2000. Origins The basic structural frame of ''Zvezda'', known as "DOS-8", was initially built in the mid-1980s to be the core of the '' Mir-2'' space station. This means that ''Zvezda' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
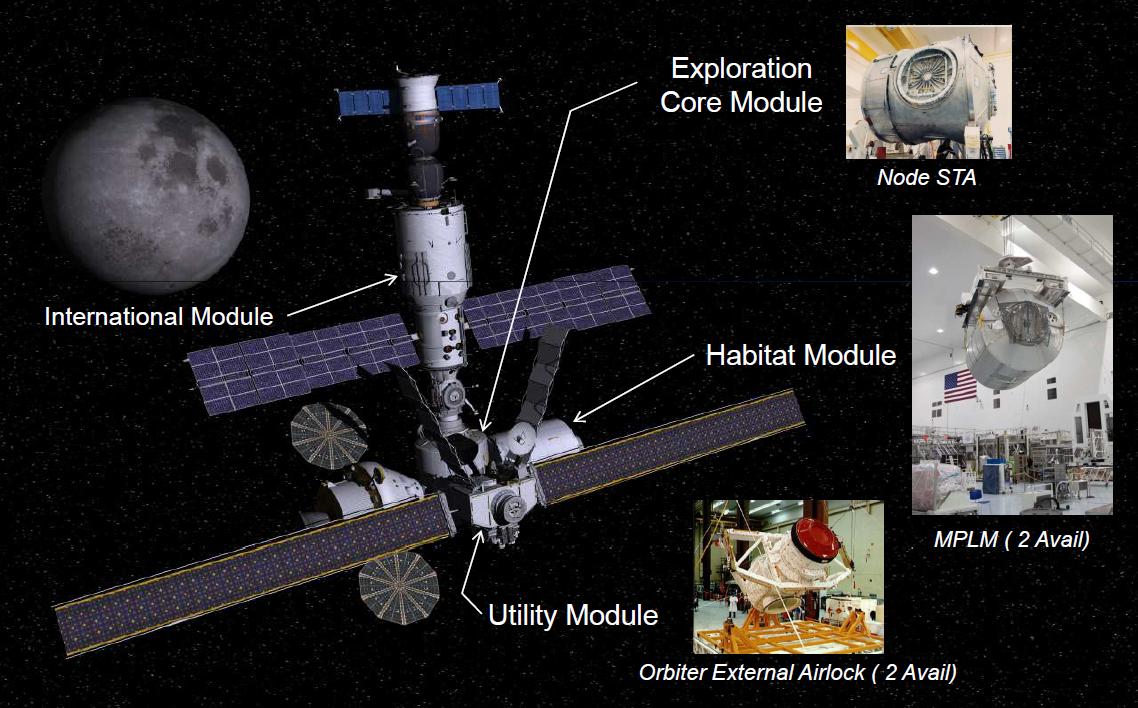
Skylab II
''Skylab II'' was a space station concept proposed in 2013 by the Advanced Concepts Office of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center The George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), located in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama (Huntsville postal address), is the U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. As the largest NASA center, MSFC's first ..., to be located at the Earth-Moon system, Earth-Moon Lagrangian point#L2, L2 Lagrangian point. Proposed by NASA contractor Brand Griffin, ''Skylab II'' would have been constructed as a "wet workshop" using a spent multistage rocket, upper-stage hydrogen fuel tank from the Space Launch System (SLS), much as the ''Skylab'' was originally planned to be built "wet" from the spent bipropellant#Types, bipropellant tanks of the Saturn (rocket family), Saturn S-IVB upper stage. If constructed, ''Skylab II'' would have been the first crewed outpost located beyond the orbit of the Moon. Space station design ''Skyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautilus-X
Nautilus-X (Non-Atmospheric Universal Transport Intended for Lengthy United States Exploration) is a rotating wheel space station concept developed by engineers Mark Holderman and Edward Henderson of the Technology Applications Assessment Team of NASA. The concept was first proposed in January, 2011 for long-duration (1 to 24 months) exo-atmospheric space journeys for a six-person crew. In order to limit the effects of microgravity on human health, the spacecraft would be equipped with a centrifuge. The design was intended to be relatively inexpensive by crewed spaceflight standards, as it was projected to only cost US$3.7 billion. In addition, it was suggested that it might only need 64 months of work. Objectives The original goal of Nautilus-X was to be a stopover to long-term missions for the Moon or Mars. To ease route planning of the whole mission, the station would be placed at the Lagrange point L1 or L2 of the Moon or Mars, depending on which location is to be vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Orbital Station
The Lunar Orbital Station (russian: Лунная Орбитальная Станция, Lunnaya Orbital'naya Stantsiya; LOS) is a proposed Russian space station in orbit around the Moon. The design was presented in 2007 at a conference at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center in Star City. It is one of the two parts of the planned Russian lunar infrastructure, the other part being a base on the surface of the Moon. LOS would have six docking ports, a high-power antenna for communications, maneuvering and attitude control engines, solar panels and a robotic arm. The station components would be launched atop a super heavy version of the Angara rocket. Russia has expressed discontent with its role in the international Lunar Gateway The Lunar Gateway, or simply Gateway, is the first planned extraterrestrial space station in lunar orbit intended to serve as a solar-powered communication hub, science laboratory, and short-term habitation module for government-agency ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Space Habitat
The Deep Space Habitat (DSH) is a series of concepts by NASA that would be used to support crewed exploration missions to the Moon, asteroids, and eventually Mars. Overview Since 2012, numerous iterations of large lunar and Mars transport habitats have been conceived in previous studies to be launched with the upcoming (SLS),[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Launch System
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an American super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle developed by NASA. As of 2022, SLS has the highest payload capacity of any rocket in operational service, as well as the greatest liftoff thrust of any rocket in operation. As the primary launch vehicle of the Artemis moon landing program, SLS is designed to launch the crewed Orion spacecraft on a trans-lunar trajectory. The first uncrewed launch, Artemis 1, took place on 16 November 2022. Development of SLS began in 2011, as a replacement for the retired Space Shuttle as well as the cancelled Ares I and Ares V launch vehicles. As a Shuttle-derived vehicle, the Space Launch System reuses hardware from the Space Shuttle program, including the solid rocket boosters and RS-25 first stage engines. An original flight date of late 2016 was delayed by nearly 6 years. The SLS program has attracted criticism for such delays, high cost, and non-competitive use of Space Shuttle components an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX. The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and payload to a certain altitude, after which the second stage lifts the payload to its ultimate destination. The rocket evolved through several versions. V1.0 flew from 2010–2013, V1.1 flew from 2013–2016, while V1.2 Full Thrust first launched in 2015, encompassing the Block 5 variant, flying since May 2018. The booster is capable of landing vertically to facilitate reuse. This feat was first achieved on flight 20 in December 2015. Since then, SpaceX has successfully landed boosters over 100 times. Individual boosters have flown as many as 15 flights. Both stages are powered by SpaceX Merlin engines, using cryogenic liquid oxygen and rocket-grade kerosene ( RP-1) as propellants. The heaviest payloads flown to geostationary transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle
National Security Space Launch (NSSL) — formerly Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) from 1994 to 2019 — is a program of the United States Space Force (USSF) intended to assure access to space for United States Department of Defense and other United States government payloads. The program is managed by the Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC), specifically the Assured Access to Space Directorate (SSC/AA), in partnership with the National Reconnaissance Office. Started in 1994 as the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle launch system program, the initial program goal was to make government space launches more affordable and reliable, leading to the development of the Boeing Delta IV and Lockheed Martin Atlas V EELV families. As of 2019, these launch vehicles were the primary methods for launching U.S. military satellites, along with the Falcon 9 developed by SpaceX. On 1 March 2019, the program name was changed from EELV to National Security Space Launch (NSSL) to bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BA 330
The B330 (previously known as the Nautilus space complex module and BA 330) was an inflatable space habitat being privately developed by Bigelow Aerospace from 2010 until 2020. The design was evolved from NASA's TransHab habitat concept. B330 will have of internal volume, hence its numeric designation. The craft is intended to support zero-gravity research including scientific missions and manufacturing processes. Beyond its industrial and scientific purposes, however, it has potential as a destination for space tourism and a craft for missions destined for the Moon and Mars. Several test articles were built and tested in various conditions in ground test facilities, but no flight versions were built. Features Compared to their volume-mass ratio, expandable modules offer more living space than traditional rigid modules. For example, the pressurised volume of a B330 module is , compared to of the 15-tonne ISS Destiny module. Thus B330 offers 210% more habitable space, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |