|
Evgeny Mikhailovich Lifshitz
Evgeny Mikhailovich Lifshitz (russian: Евге́ний Миха́йлович Ли́фшиц; February 21, 1915, Kharkiv, Russian Empire – October 29, 1985, Moscow, Russian SFSR) was a leading Soviet physicist and brother of the physicist Ilya Lifshitz. Work Born into a Ukrainian Jewish family in Kharkov, Kharkov Governorate, Russian Empire (now Kharkiv, Ukraine). Lifshitz is well known in the field of general relativity for coauthoring the BKL conjecture concerning the nature of a ''generic curvature singularity''. , this is widely regarded as one of the most important open problems in the subject of classical gravitation. With Lev Landau, Lifshitz co-authored ''Course of Theoretical Physics'', an ambitious series of physics textbooks, in which the two aimed to provide a graduate-level introduction to the entire field of physics. These books are still considered invaluable and continue to be widely used. Lifshitz was the second of only 43 people ever to pass Landau' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.Kharkiv "never had eastern-western conflicts" ''Euronews'' (23 October 2014) Located in the northeast of the country, it is the largest city of the historic Sloboda Ukraine, Slobozhanshchyna region. Kharkiv is the administrative centre of Kharkiv Oblast and of the surrounding Kharkiv Raion. The latest population is Kharkiv was founded in 1654 as Kharkiv fortress, and after these humble beginnings, it grew to be a major centre of industry, trade and Ukrainian culture in the Russian Empire. At the beginning of the 20th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Member Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki Ramakrishnan ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
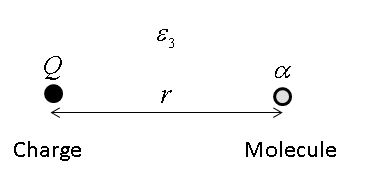
Lifshitz Theory Of Van Der Waals Force
In condensed matter physics and physical chemistry, the Lifshitz theory of van der Waals forces, sometimes called the macroscopic theory of van der Waals forces, is a method proposed by Evgeny Mikhailovich Lifshitz in 1954 for treating van der Waals forces between bodies which does not assume pairwise additivity of the individual intermolecular forces; that is to say, the theory takes into account the influence of neighboring molecules on the interaction between every pair of molecules located in the two bodies, rather than treating each pair independently. Need for a non-pairwise additive theory The van der Waals force between two molecules, in this context, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between them; these forces are primarily electrostatic in nature, and in their simplest form might consist of a force between two charges, two dipoles, or between a charge and a dipole. Thus, the strength of the force may often depend on the net charge, electric dipole moment, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroacoustics
Aeroacoustics is a branch of acoustics that studies noise generation via either turbulent fluid motion or aerodynamic forces interacting with surfaces. Noise generation can also be associated with periodically varying flows. A notable example of this phenomenon is the Aeolian tones produced by wind blowing over fixed objects. Although no complete scientific theory of the generation of noise by aerodynamic flows has been established, most practical aeroacoustic analysis relies upon the so-called ''aeroacoustic analogy'', proposed by Sir James Lighthill in the 1950s while at the University of Manchester. whereby the governing equations of motion of the fluid are coerced into a form reminiscent of the wave equation of "classical" (i.e. linear) acoustics in the left-hand side with the remaining terms as sources in the right-hand side. History The modern discipline of aeroacoustics can be said to have originated with the first publication of Lighthill in the early 1950s, when noise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress–energy–momentum Pseudotensor
In the theory of general relativity, a stress–energy–momentum pseudotensor, such as the Landau–Lifshitz pseudotensor, is an extension of the non-gravitational stress–energy tensor that incorporates the energy–momentum of gravity. It allows the energy–momentum of a system of gravitating matter to be defined. In particular it allows the total of matter plus the gravitating energy–momentum to form a conserved current within the framework of general relativity, so that the ''total'' energy–momentum crossing the hypersurface (3-dimensional boundary) of ''any'' compact space–time hypervolume (4-dimensional submanifold) vanishes. Some people (such as Erwin Schrödinger) have objected to this derivation on the grounds that pseudotensors are inappropriate objects in general relativity, but the conservation law only requires the use of the 4-divergence of a pseudotensor which is, in this case, a tensor (which also vanishes). Also, most pseudotensors are sections of jet bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pergamon Press
Pergamon Press was an Oxford-based publishing house, founded by Paul Rosbaud and Robert Maxwell, that published scientific and medical books and journals. Originally called Butterworth-Springer, it is now an imprint of Elsevier. History The core company, Butterworth-Springer, started in 1948 to bring the "Springer know-how and techniques of aggressive publishing in science"Joe Haines (1988) ''Maxwell'', Houghton Mifflin, p. 137. to Britain. Paul Rosbaud was the man with the knowledge. When Maxwell acquired the company in 1951, Rosbaud held a one-quarter share. They changed the house name to Pergamon Press, using a logo that was a reproduction of a Greek coin from Pergamon. Maxwell and Rosbaud worked together growing the company until May 1956, when, according to Joe Haines, Rosbaud was sacked. When Pergamon Press started it had only six serials and two books. Initially the company headquarters was in Fitzroy Square in West End of London. In 1959, the company moved into He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BKL Conjecture
A Belinski–Khalatnikov–Lifshitz (BKL) singularity is a model of the dynamic evolution of the universe near the initial gravitational singularity, described by an anisotropic, chaotic solution of the Einstein field equation of gravitation. According to this model, the universe is chaotically oscillating around a gravitational singularity in which time and space become equal to zero or, equivalently, the spacetime curvature becomes infinitely big. This singularity is physically real in the sense that it is a necessary property of the solution, and will appear also in the exact solution of those equations. The singularity is not artificially created by the assumptions and simplifications made by the other special solutions such as the Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker, quasi-isotropic, and Kasner solutions. The model is named after its authors Vladimir Belinski, Isaak Khalatnikov, and Evgeny Lifshitz, then working at the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicritical Point
Multicritical points are special points in the parameter space of thermodynamic or other systems with a continuous phase transition. At least two thermodynamic or other parameters must be adjusted to reach a multicritical point. At a multicritical point the system belongs to a universality class different from the "normal" universality class. A more detailed definition requires concepts from the theory of critical phenomena, a branch of physics that reached a very satisfying state in the 1970s. Definition The union of all the points of the parameter space for which the system is critical is called a critical manifold. As an example consider a substance ferromagnetic below a transition temperature T_, and paramagnetic above T_c. The parameter space here is the temperature axis, and the critical manifold consists of the point T_c. Now add hydrostatic pressure P to the parameter space. Under hydrostatic pressure the substance normally still becomes ferromagnetic b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir Effect
In quantum field theory, the Casimir effect is a physical force acting on the macroscopic boundaries of a confined space which arises from the quantum fluctuations of the field. It is named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Casimir, who predicted the effect for electromagnetic systems in 1948. In the same year, Casimir together with Dirk Polder described a similar effect experienced by a neutral atom in the vicinity of a macroscopic interface which is referred to as the Casimir–Polder force. Their result is a generalization of the London– van der Waals force and includes retardation due to the finite speed of light. Since the fundamental principles leading to the London–van der Waals force, the Casimir and the Casimir–Polder force, respectively, can be formulated on the same footing, the distinction in nomenclature nowadays serves a historical purpose mostly and usually refers to the different physical setups. It was not until 1997 that a direct experiment by S. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes classical gravity, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass distributions. Some predictions of general relativity, however, are beyond Newton's law of universal gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invasion, it was the eighth-most populous country in Europe, with a population of around 41 million people. It is also bordered by Belarus to the north; by Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary to the west; and by Romania and Moldova to the southwest; with a coastline along the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and largest city. Ukraine's state language is Ukrainian; Russian is also widely spoken, especially in the east and south. During the Middle Ages, Ukraine was the site of early Slavic expansion and the area later became a key centre of East Slavic culture under the state of Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. The state eventually disintegrated into rival regional powers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Jews In Ukraine
The history of the Jews in Ukraine dates back over a thousand years; Jewish communities have existed in the territory of Ukraine from the time of the Kievan Rus' (late 9th to mid-13th century). Some of the most important Jewish religious and cultural movements, from Hasidism to Zionism, rose either fully or to an extensive degree in the territory of modern Ukraine. According to the World Jewish Congress, the Jewish community in Ukraine constitutes the third-largest in Europe and the fifth-largest in the world. The actions of the Soviet government by 1927 led to a growing antisemitism in the area.Сергійчук, В. Український Крим К. 2001, p.156 Total civilian losses during World War II and the Reichskommissariat Ukraine, German occupation of Ukraine are estimated at seven million. More than one million Soviet Jews, of them around 225,000 in Belarus, were shot and killed by the Einsatzgruppen and by their many local Ukrainian supporters. Most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |