|
Evergreen (software)
Evergreen is an open-source integrated library system (ILS), initially developed by the Georgia Public Library Service for Public Information Network for Electronic Services (PINES), a statewide resource-sharing consortium with over 270 member libraries.. Beyond PINES, the Evergreen ILS is deployed worldwide in approximately 1,800 libraries, and is used to power a number of statewide consortial catalogs... .. .SCLENDS Retrieved on 2017-04-14. In 2007, the original Evergreen development team formed a commercial company around the software, Equinox Software, which provides custom support, development, migration, training, and consultation for Evergreen. Equinox Software was later supplanted by the Equinox Open Library Initiative, a non-profit. As of 2014, several more companies and groups also provide support and related services for Evergreen. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Information Network For Electronic Services
The Public Information Network for Electronic Services (or PINES) is the nearly statewide library consortium and its online library catalog of the Georgia Public Library Service. By June 2017, the catalog consisted of books from 284 library facilities in 143 counties across the U.S. state of Georgia with a collection size of 10.6 million items, all of which are searchable by anyone with a PINES library card which can be obtained free of charge from any PINES-participating library. The PINES system effectively turns most of the state of Georgia into one huge library. PINES cardholders are able to request an interlibrary loan from any affiliated library, and the single statewide library card grants access to the hundreds of branches associated with the service. PINES also manages the booking of rooms, the use of remote self-check machines, allows automated search and retrieval, as well as supports RSS and Schema.org standards. PINES developed the open-source software Evergreen, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Interchange Protocol
The Standard Interchange Protocol is a proprietary standard for communication between library computer systems and self-service circulation terminals. Although owned and controlled by 3M, the protocol is published and is widely used by other vendors. Version 2.0 of the protocol, known as "SIP2", is a de facto standard for library self-service applications. History SIP version 1.0 was published by 3M in 1993. The first version of the protocol supported basic check in and check out operations, but had minimal support for more advanced operations. Version 2.0 of the protocol was published in 2006 and added support for flexible, more user-friendly notifications, and for the automated processing of payments for late fees. SIP2 was widely adopted by library automation vendors, including ODILO, Bibliotheca, Nedap, Checkpoint, Envisionware, FE Technologies, Meescan, Redia and open source integrated library system software such as Koha and Evergreen. The standard was the basis for the NI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invenio
Invenio is an open source software framework for large-scale digital repositories that provides the tools for management of digital assets in an institutional repository and research data management systems. The software is typically used for open access repositories for scholarly and/or published digital content and as a digital library. Invenio is initially developed by CERN with both individual and organisational external contributors and is freely available for download. History Prior to July 1, 2006, the package was named CDSware, then renamed CDS Invenio, and now known simply as Invenio. Standards Invenio complies with standards such as the Open Archives Initiative metadata harvesting protocol (OAI-PMH) and uses JSON/JSONSchema as its underlying bibliographic format. Support The service provider TIND Technologies, an official CERN spin-off based in Norway, offers Invenio via a software-as-a-service model. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koha (software)
Koha is an open-source integrated library system (ILS), used world-wide by public, school and special libraries. The name comes from a Māori term for a gift or donation. Features Koha is a web-based ILS, with a SQL database (MariaDB or MySQL preferred) back end with cataloguing data stored in MARC and accessible via Z39.50 or SRU. The user interface is very configurable and adaptable and has been translated into many languages. Koha has most of the features that would be expected in an ILS, including: * Various Web 2.0 facilities like tagging, comment, social sharing and RSS feeds * Union catalog facility * Customizable search * Online circulation * Bar code printing * Patron card creation * Report generation * Patron self registration form through OPAC History Koha was created in 1999 by Katipo Communications for the Horowhenua Library Trust in New Zealand, and the first installation went live in January 2000. From 2000, companies started providing commercial support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people used a browser. The most used browser is Google Chrome, with a 65% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%. A web browser is not the same thing as a search engine, though the two are often confused. A search engine is a website that provides links to other websites. However, to connect to a website's server and display its web pages, a user must have a web browser installed. In some technical contexts, browsers are referred to as user agents. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content from the World Wide Web or from local storage and display it on a user's device. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
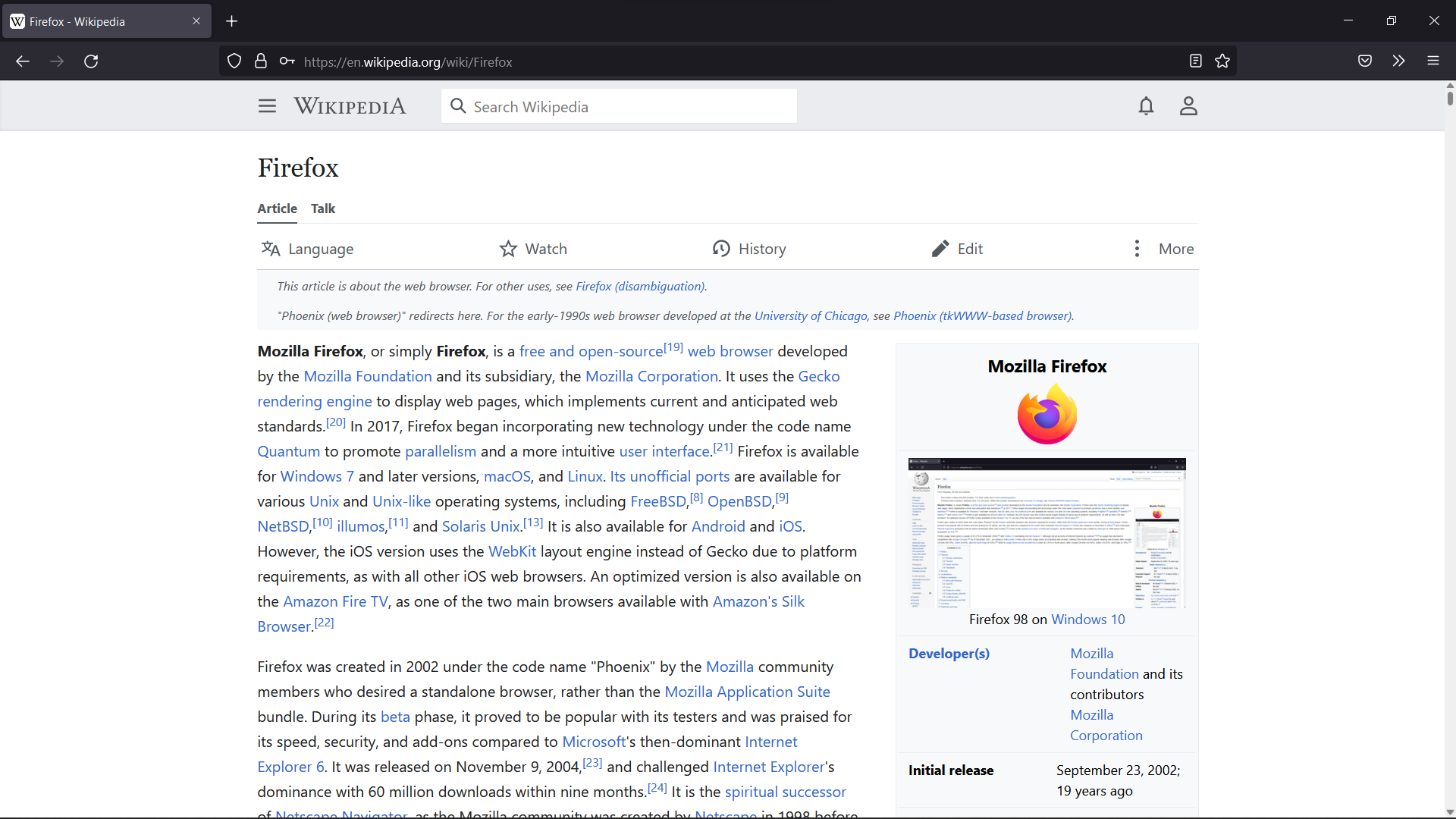
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. In November 2017, Firefox began incorporating new technology under the code name "Quantum" to promote parallelism and a more intuitive user interface. Firefox is available for Windows 7 and later versions, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, illumos, and Solaris Unix. It is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser. Firefox was created in 2002 under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XULRunner
XULRunner is a discontinued, packaged version of the Mozilla platform to enable standalone desktop application development using XUL, developed by Mozilla. It replaced the ''Gecko Runtime Environment'', a stalled project with a similar purpose. The first stable developer preview of XULRunner was released in February 2006, based on the Mozilla 1.8 code base. Mozilla stopped supporting the development of XULrunner in July 2015. XULRunner was a "technology experiment", not a shipped product, meaning there were no official XULRunner releases, only stable builds based on the same code as a corresponding Firefox release. Software architecture XULRunner is a runtime that can be used to bootstrap multiple XUL + XPCOM applications that are equal in capabilities to Firefox and Thunderbird. XULRunner stores a variety of configuration data (bookmarks, cookies, contacts etc.) in internally managed SQLite databases, and even offer an add-on to manage SQLite databases. Uses Mozilla Firefox, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macintosh
The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and software engineers. The current lineup includes the MacBook Air and MacBook Pro laptops, as well as the iMac, Mac Mini, Mac Studio and Mac Pro desktops. Macs run the macOS operating system. The Macintosh 128K, first Mac was released in 1984, and was advertised with the highly-acclaimed 1984 (advertisement), "1984" ad. After a period of initial success, the Mac languished in the 1990s, until co-founder Steve Jobs returned to Apple in 1997. Jobs oversaw the release of many successful products, unveiled the modern Mac OS X, completed the Mac transition to Intel processors, 2005-06 Intel transition, and brought features from the iPhone back to the Mac. During Tim Cook's tenure as CEO, the Mac underwent a period of neglect, but was later reinv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers. Genealogy By marketing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruby (programming Language)
Ruby is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language which supports multiple programming paradigms. It was designed with an emphasis on programming productivity and simplicity. In Ruby, everything is an object, including primitive data types. It was developed in the mid-1990s by Yukihiro "Matz" Matsumoto in Japan. Ruby is dynamically typed and uses garbage collection and just-in-time compilation. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming. According to the creator, Ruby was influenced by Perl, Smalltalk, Eiffel, Ada, BASIC, Java and Lisp. History Early concept Matsumoto has said that Ruby was conceived in 1993. In a 1999 post to the ''ruby-talk'' mailing list, he describes some of his early ideas about the language: Matsumoto describes the design of Ruby as being like a simple Lisp language at its core, with an object system like that of Smalltalk, blocks inspired by higher-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language and first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000 and introduced new features such as list comprehensions, cycle-detecting garbage collection, reference counting, and Unicode support. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision that is not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2 was discontinued with version 2.7.18 in 2020. Python consistently ranks as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |