|
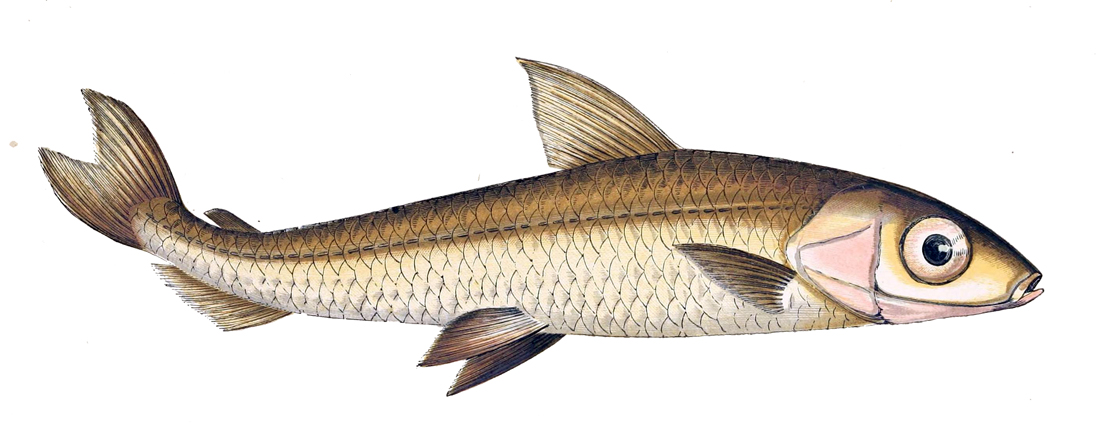
Euteleostei
Euteleostei, whose members are known as euteleosts, is a clade of bony fishes within Teleostei that evolved some 240 million years ago. It is divided into Protacanthopterygii (including the salmon and dragonfish) and Neoteleostei (including the lanternfish, lizardfish, oarfish, and Acanthopterygii). The cladogram is based on Near et al. (2012) and Betancur-Rodriguez et al. 2016. They explored the phylogeny and divergence times of every major lineage, analysing the DNA sequences of 9 unlinked genes. They calibrated (set actual values for) branching times in this tree from 36 reliable measurements of absolute time from the fossil A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ... record. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1378777 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomiati
Stomiati is a group of teleost fish belonging to the cohort (group) Euteleostei, which is a group of bony fishes within the infra-class Teleostei that evolved ~240 million years ago. Teleostei is a group of ray-finned fishes with the exception of primitive bichirs, sturgeons, paddlefishes, freshwater garfishes, and bowfins. The cohort of Euteleostei is divided into two smaller groups: the Protacanthopterygii and the Neoteleostei. Stomiati happen to be descendants of the Protacanthopterygii, and contains the order of Osmeriformes and Stomiiformes (Betancur-R, et al.). Stomiati is one of five major euteleost lineages that were recently placed in one monophyly, a group of organisms all descending from one common ancestor. The five being a clade formed by Esociformes and Salmoniformes; second being the Stomiatii consisting of only Osmeriformes and Stomiiformes; Argentiniformes (excludes Alepocephaliformes); Galaxiiformes (excludes '' Lepidogalaxias''); and Neotelestei. Stomiati ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomiiformes
Stomiiformes is an order of deep-sea ray-finned fishes of very diverse morphology. It includes, for example, dragonfishes, lightfishes (Gonostomatidae and Phosichthyidae), loosejaws, marine hatchetfishes and viperfishes. The order contains 4 families (5 according to some authors) with more than 50 genera and at least 410 species. As usual for deep-sea fishes, there are few common names for species of the order, but the Stomiiformes as a whole are often called dragonfishes and allies or simply stomiiforms. The scientific name means "''Stomias''-shaped", from '' Stomias'' (the type genus) + the standard fish order suffix "-formes". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek ''stóma'' (στόμᾶ, "mouth") + Latin ''forma'' ("external form"), the former in reference to the huge mouth opening of these fishes. Description and ecology Members of this order are mostly pelagic fishes living in deep oceanic waters. Their distribution around the world's oceans is very wide, ranging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
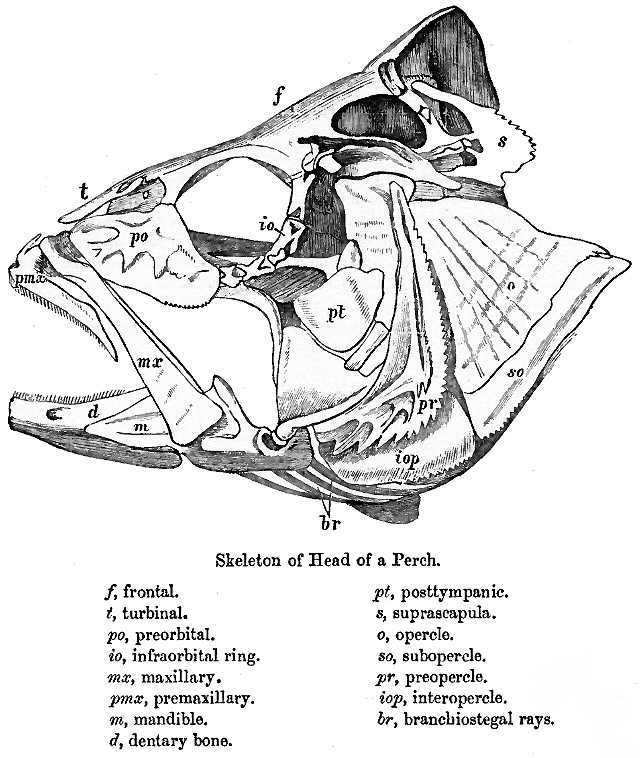
Teleostei
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest class (biology), infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all neontology, extant species of fish. Teleosts are arranged into about 40 order (biology), orders and 448 family (biology), families. Over 26,000 species have been described. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over , to the minute male anglerfish ''Photocorynus spiniceps'', just long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses. The difference between teleosts and other bony fish lies mainly in their jaw bones; teleosts have a movable premaxilla and corresponding modifications in the jaw musculature which make it possible for them to cranial kinesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protacanthopterygii
Protacanthopterygii is a ray-finned fish taxon ranked as a superorder of the infraclass Teleostei. They inhabit both marine and freshwater habitats. They appear to have evolved in the Cretaceous or perhaps late Jurassic, originating probably roughly 150 million years ago; fossils of them and the closely related Otocephala are known from throughout the Cretaceous.Encyclopædia Britannica Online (2009): Annotated classification – Superorder Protacanthopterygii. ''In:'Fish Version of 2009-APR-22. Retrieved 2009-SEP-28. Characteristics and origin The Protacanthopterygii contain a number of moderately advanced teleosts. Anatomical and other traits commonly found in this superorder are: more than 24 vertebrae, epicentral cartilages, one supraorbital bone, and a mesocoracoid, an adipose fin, and (often prominent) glossohyal teeth. However, they usually lack a protrusible upper jaw, a gular plate, and proximal forking of the intermuscular bones. Most members of this taxon are rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ateleopodidae
The jellynose fishes or tadpole fishes are the small order Ateleopodiformes. This group of ray-finned fish is monotypic, containing a single family Ateleopodidae. It has about a dozen species in four genera, but these enigmatic fishes are in need of taxonomic revision. The scientific name means "''Ateleopus''-shaped", from ''Ateleopus'' (the type genus) + the standard fish order suffix "-formes". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek ''atelēs'' (ἀτελής, "imperfect") + ''pous'' (πούς, "foot") + Latin ''forma'' ("external form"), the Greek part in reference to the reduced pectoral and ventral fins of the jellynoses. Description and ecology Jellynoses are deep-water, bottom-dwelling, marine fishes. They are known from the Caribbean Sea, eastern Atlantic, the western and central Indopacific, and the Pacific coast of Central America.Olney (1998), Nelson (2006): p.213 Their skeletons are largely cartilage (hence "jellynose"), although they are true teleosts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myctophiformes
The Myctophiformes are an order of ray-finned fishes consisting of two families of deep-sea marine fish, most notably the highly abundant lanternfishes (Myctophidae). The blackchins (Neoscopelidae) contain six species in three genera, while the bulk of the family belongs to the Myctophidae, with over 30 genera and some 252 species.Nelson (2006): p.223 The scientific name ultimately derives from Ancient Greek ''myktér'' (μυκτήρ, "nose") + ''óphis'' (ὄφῖς, "serpent") + Latin ''forma'' ("external form"), the Greek part in reference to the long, slender, and heavy-headed shape of these fishes. Description and ecology These smallish fishes inhabit the pelagic and benthopelagic zones of the deep sea. They are laterally compressed and usually have photophores (light organs). The eyes are large, in some decidedly huge, and generally directed straight sideways. The mouth also quite large and located at the tip of the snout; its gape extends to below the eyes or even be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulopiformes
Aulopiformes is a diverse order of marine ray-finned fish consisting of some 15 extant and several prehistoric families with about 45 genera and over 230 species. The common names grinners, lizardfishes and allies, or aulopiforms are sometimes used for this group. The scientific name means "''Aulopus''-shaped", from ''Aulopus'' (the type genus) + the standard fish order suffix "-formes". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek ''aulós'' (αὐλός, "flute" or "pipe") + Latin ''forma'' ("external form"), the former in reference to the elongated shape of many aulopiforms.FishBase (2000) They are grouped together because of common features in the structure of their gill arches. Indeed, many authors have considered them so distinct as to warrant separation in a monotypic superorder of the Teleostei, under the name Cyclosquamata. However, monotypic taxa are generally avoided by modern taxonomists if not necessary, and in this case a distinct superorder seems indeed unwarra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoteleostei
The Neoteleostei is a large clade of bony fish that includes the Ateleopodidae (jellynoses), Aulopiformes (lizardfish), Myctophiformes (lanternfish), Polymixiiformes (beardfish), Percopsiformes (Troutperches), Gadiformes (cods), Zeiformes (dories), Lampriformes (oarfish, opah, ribbonfish), and the populous clade of the Acanthopterygii which includes the Beryciformes (squirrelfish) and the Percomorpha (many families such as the tuna, seahorses, gobies, cichlids, flatfish, wrasse, perches, anglerfish The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence ..., pufferfish). References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1977650 Fish superorders Euteleostei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Smelt
The Argentiniformes are an order of ray-finned fish whose distinctness was recognized only fairly recently. In former times, they were included in the Osmeriformes (typical smelt and allies) as suborder Argentinoidei. That term refers only to the suborder of marine smelts and barreleyes in the classification used here, with the slickheads and allies being the Alepocephaloidei. These suborders were treated as superfamilies Argentinoidea and Alepocephaloidea, respectively, when the present group was still included in the Osmeriformes. They contain six or seven families with almost 60 genera and at least 228 species. A common name for the group is marine smelts and allies, but this is rather misleading since the " freshwater" smelts of the Osmeridae also live predominantly in the ocean. FishBase (2006)Order Osmeriformes Version of 2006-OCT-09. Retrieved 2009-SEP-28. pp. 190-194 Description and ecology The Argentiniformes are smallish silvery or dark and generally bathypelagic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esociformes
The Esociformes () are a small order of ray-finned fish, with two families, Umbridae and Esocidae. The pikes of genus '' Esox'' give the order its name. This order is closely related to the Salmoniformes, the two comprising the superorder Protacanthopterygii, and are often included in their order. The esociform fishes first appeared in the mid-Cretaceous — early products of the Euteleostei radiation of that time. Today, they are found in weed-choked freshwater habitats in North America and northern Eurasia. Esocidae The three extant esocid genera ('' Esox'', '' Novumbra'', and ''Dallia'') together comprise a holarctic distribution. Two additional genera have been described from fossils dating to the Cretaceous of North America. Umbridae ''Umbra'' remains the only extant species in this family, and can be found in eastern North America and Europe. Three additional genera have been described from fossils dating from the Paleocene of Europe; however, genetic studies on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentiniformes
The Argentiniformes are an order of ray-finned fish whose distinctness was recognized only fairly recently. In former times, they were included in the Osmeriformes (typical smelt and allies) as suborder Argentinoidei. That term refers only to the suborder of marine smelts and barreleyes in the classification used here, with the slickheads and allies being the Alepocephaloidei. These suborders were treated as superfamilies Argentinoidea and Alepocephaloidea, respectively, when the present group was still included in the Osmeriformes. They contain six or seven families with almost 60 genera and at least 228 species. A common name for the group is marine smelts and allies, but this is rather misleading since the "freshwater" smelts of the Osmeridae also live predominantly in the ocean.FishBase (2006)Order Osmeriformes Version of 2006-OCT-09. Retrieved 2009-SEP-28. pp. 190-194 Description and ecology The Argentiniformes are smallish silvery or dark and generally bathypelagic oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmo Salar (crop)
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and in rivers that flow into it. Most populations are anadromous, hatching in streams and rivers but moving out to sea as they grow where they mature, after which the adults seasonally move upstream again to spawn. When the mature fish re-enter rivers to spawn, they change in colour and appearance. Some populations of this fish only migrate to large lakes, and are "landlocked", spending their entire lives in freshwater. Such populations are found throughout the range of the species. Unlike Pacific species of salmon, ''S. salar'' is iteroparous, which means it can survive spawning and return to sea to repeat the process again in another year. Such individuals can grow to extremely large sizes, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |