|
Euphratean Society
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf. Etymology The Ancient Greek form ''Euphrátēs'' ( grc, Εὐφράτης, as if from Greek εὖ "good" and φράζω "I announce or declare") was adapted from Old Persian 𐎢𐎳𐎼𐎠𐎬𐎢 ''Ufrātu'', itself from Elamite 𒌑𒅁𒊏𒌅𒅖 ''ú-ip-ra-tu-iš''. The Elamite name is ultimately derived from a name spelt in cuneiform as 𒌓𒄒𒉣 , which read as Sumerian is "Buranuna" and read as Akkadian is "Purattu"; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean the same. In Akkadian the river was called ''Pura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
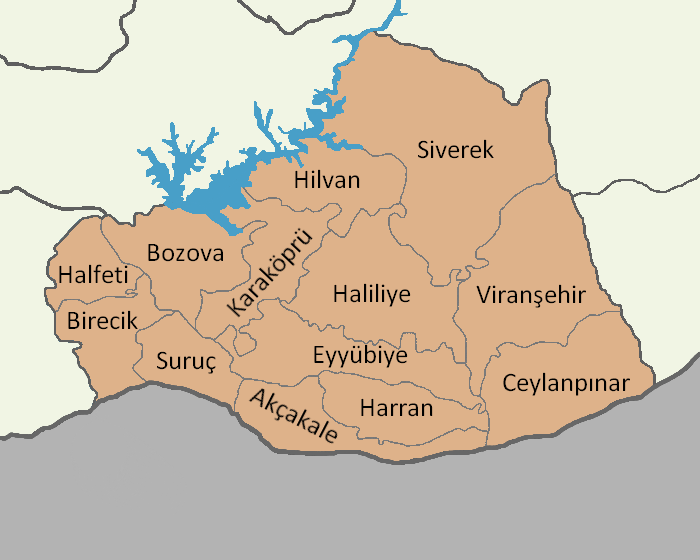
Şanlıurfa Province
Şanlıurfa Province ( tr, Şanlıurfa ili; ku, Parêzgeha Rihayê) or simply Urfa Province is a province in southeastern Turkey. The city of Şanlıurfa is the capital of the province which bears its name. The population is 1,845,667 (2014). The province is considered part of Turkish Kurdistan and has a Kurds, Kurdish majority with a significant Arabs, Arab and Turkish people, Turkish minority. Districts Şanlıurfa province is divided into 13 Districts of Turkey, districts (capital district in bold): * Urfa (Central district. In 2014 it was split into three districts: Eyyübiye, Haliliye and Karaköprü.) * Akçakale * Birecik * Bozova * Ceylanpınar * Halfeti * Harran * Hilvan * Siverek * Suruç * Viranşehir Geography Area 18,584 km2 (7,173 sq. miles), the largest province of Southeast Anatolia with: * Adıyaman to the north; * Syria to the south; * Mardin and Diyarbakır to the east; * Gaziantep to the west; Şanlıurfa includes several major components of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habbaniyah
Al Habbaniyah or Habbaniya ( ar, ٱلْحَبَّانِيَّة, ''al-Ḥabbānīyah'') is a city 85 km (53 mi) west of Baghdad in Al-Anbar Province, in central Iraq. A military airfield, RAF Habbaniya, was the site of a battle in 1941, during World War II. Lake Habbaniyah is also nearby. History On 25 May 1941, Second Battalion of the Fourth Gurkha Rifles (2/4 GR), forming part of 10 Indian Infantry Division, was airlifted to reinforce and secure Habbaniyah, which was a Royal Air Force airfield under threat from Iraqi ground troops and the German Luftwaffe, located in Mosul, and Baghdad. It has 74,217 citizens. Assyrians from Naqadeh and Urmia, Iran, settled to the city in the early 20th century after Sayfo The Sayfo or the Seyfo (; see below), also known as the Assyrian genocide, was the mass slaughter and deportation of Assyrian / Syriac Christians in southeastern Anatolia and Persia's Azerbaijan province by Ottoman forces and some Kurdish t .... Climate Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balikh River
The Balikh River ( ar, نهر البليخ) is a perennial river that originates in the spring of Ain al-Arous near Tell Abyad in the Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests ecoregion. It flows due south and joins the Euphrates at the modern city of Raqqa. The Balikh is the second largest tributary to the Euphrates in Syria, after the Khabur River. It is an important source of water and large sections have recently been subjected to canalization. Geography The primary source of the Balikh River is the karstic spring of Ain al-Arous, just south of the Syria–Turkey border. Additionally, the Balikh receives water from a number of periodical streams and wadis that drain the Harran Plain to the north, as well as the plains to the west and east of the river valley. These streams are the Jullab, the Wadi Qaramogh, and the Wadi al-Kheder. A few kilometres south of Ain al-Arous, the Balikh is joined by the channel of the Jullab. This small river rises from sprin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris–Euphrates River System
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia which discharges into the Persian Gulf. Its principal rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates along with smaller tributaries. From their sources and upper courses in the mountains of eastern Turkey, the rivers descend through valleys and gorges to the uplands of Syria and northern Iraq and then to the alluvial plain of central Iraq. Other tributaries join the Tigris from sources in the Zagros Mountains to the east. The rivers flow in a south-easterly direction through the central plain and combine at Al-Qurnah to form the Shatt al-Arab and discharge into the Persian Gulf. The rivers and their tributaries drain an area of 879,790 km2, including almost the entire area of Iraq as well as portions of Turkey, Syria, Iran, and Kuwait. The region has historical importance as part of the Fertile Crescent region, in which Mesopotamian civilization is believed to have first emerged. Geography The Tigris–Euphra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basra Governorate
Basra Governorate ( ar, محافظة البصرة ), also called Basra Province, is a Governorates of Iraq, governorate in southern Iraq, bordering Kuwait to the south and Iran to the east. The capital is the city of Basra, located in the Basrah District, Basrah district. Other districts of Basra include Al-Qurna District, Al-Qurna, Al-Zubair District, Al-Zubair, Al-Midaina District, Al-Midaina, Shatt Al-Arab District, Shatt Al-Arab, Abu Al-Khaseeb District, Abu Al-Khaseeb and Al-Faw District, Basra Governorate, Al-Faw located on the Persian Gulf. It is the only governorate with a coastline. History In 1920, after the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I, the United Kingdom took over the former Subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman vilayets of Basra Vilayet (Ottoman Empire), Basra, Baghdad Province, Ottoman Empire, Baghdad and Mosul Province, Ottoman Empire, Mosul which had together formed the historical region of ''Irak Arabi'' or ''Babylonia, Irak Babeli'', and cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Qurnah
Al-Qurnah (Kurnah or Qurna, meaning connection/joint in Arabic) is a town in southern Iraq about 74 km northwest of Basra, that lies within the conglomeration of Nahairat. Qurna is located at the confluence point of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers to form the Shatt al-Arab waterway. Local folklore holds Qurnah to have been the original site of biblical paradise, the Garden of Eden and location of the Tree of Knowledge. History Local folklore holds Qurnah to have been the site of the Garden of Eden and the location of a city built by general Seleucus Nicator I. An ancient tree is celebrated locally and shown to the tourists as the actual Tree of Knowledge of the Bible. The tree died some time ago and replacement trees were planted. The tomb of Ezra is also described to be nearby and found further upstream on the river Tigris. In 1855, Al Qurnah was the site of the Qurnah Disaster, in which local tribes attacked and sank a convoy of a ship and rafts carrying 240 cases of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shatt Al-Arab
The Shatt al-Arab ( ar, شط العرب, lit=River of the Arabs; fa, اروندرود, Arvand Rud, lit=Swift River) is a river of some in length that is formed at the confluence of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the town of al-Qurnah in the Basra Governorate of southern Iraq. The southern end of the river constitutes the Iran–Iraq border down to its mouth, where it discharges into the Persian Gulf. The Shatt al-Arab varies in width from about at Basra to at its mouth. It is thought that the waterway formed relatively recently in geological time, with the Tigris and Euphrates originally emptying into the Persian Gulf via a channel further to the west. Kuwait's Bubiyan Island is part of the Shatt al-Arab delta. The Karun, a tributary which joins the waterway from the Iranian side, deposits large amounts of silt into the river; this necessitates continuous dredging to keep it navigable. The area used to hold the largest date palm forest in the world. In the mid-1970s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keban
Keban is a town of Elazığ Province of Turkey. It is the seat of Keban District.İlçe Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 19 December 2022. Its population is 4,022 (2021). In the local elections 2019 the independent Fethiye Atlı was elected as Mayor. Keban is at the west of Elazığ Province and 46 km. away from province center. At the east of Keban, there is Elazığ Province. At west, Arapgir District of Malatya Province, at north there is Çemişgezek District of Tunceli Province, at northwest, Ağın District, at south, Baskil province. There is the second biggest dam of Turkey, |
Karasu (Euphrates)
The Karasu (Turkish for 'black water') or Western Euphrates is a long river in eastern Turkey, one of the two sources of the Euphrates. It has a length of about 450 km. To the ancient Greeks the river was known as the (''Telebóas''). Course The river rises on the Dumlu Dağ in Erzurum Province, and drains the plains around the city of Erzurum. It is joined by the Serçeme River, then flows west through Erzincan Province, turning south, then west and receiving the tributary Tuzla Su. Between Erzincan and Kemah it is joined by the Gönye River and passes through a rocky gorge. Near the small town of Kemaliye it receives its last tributary, the Çaltı Çayı, before turning sharply southeast to flow through a deep canyon into the Keban Dam Lake on the Euphrates. Before construction of the Keban Dam the Karasu joined the Murat River 10 km above the dam site and 13 km above the town of Keban. History It is thought likely that the river Harpasos mentioned b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murat River
The Murat River, also called Eastern Euphrates ( tr, Murat Nehri, , hy, Արածանի, translit=Aratsani), is a major source of the Euphrates River. The Ancient Greeks and Romans used to call the river ''Arsanias'' ( gr, Ἀρσανίας). It originates near Mount Ararat north of Lake Van, in Eastern Turkey, and flows westward for through mountainous area. Before the construction of the Keban Dam, the Murat River joined the Karasu River or Western Euphrates north of the dam site and north of the town of Keban. In Muş Province, the river is interrupted by the Alpaslan-1 Dam, which was completed in 2009. The Alpaslan-2 Dam was completed in 2021 and is located downstream of Alpaslan-1. The river merges into the reservoir of the Keban Dam, at one time Turkey's largest dam, which was completed in 1974 and provides electrical power. In Bingöl and Elazığ provinces, Kalehan Energy has four dams planned for the river: from upstream to downstream, the Upper Kaleköy Dam, Lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hīt
Hīt, also spelled ''Heet'' ( ar, هيت), ancient name ''Is'', is an Iraqi city in Al-Anbar province. Hīt lies northwest of Ramadi, the provincial capital. Straddling the Euphrates River, the city of Hīt was originally a small walled town surrounded by a halt moat and built on two mounds on the site of the ancient city of Is. In ancient times, the town was known for its bitumen wells; bitumen from the wells was used in the construction of Babylon over 3,000 years ago, and for tasks such as caulking boats. Hīt also became a frontier fortress for Assyria. Now, Hīt is a marketplace for agricultural produce. Oil pipelines to the Mediterranean Sea cross the Euphrates there. It was regarded as the head of navigation on the river before the decline in river traffic. Hit marks the beginning of the high sedimentary plain on the Euphrates, and it contains a number of hot springs. The city of Heet is also famous for its ancient yet still functioning water wheels (also known as ''nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasiriyah
Nasiriyah ( ar, ٱلنَّاصِرِيَّة; United States Board on Geographic Names, BGN: ''An Nāşirīyah''; also spelled ''Nassiriya'' or ''Nasiriya'') is a city in Iraq. It is on the lower Euphrates River, Euphrates, about south-southeast of Baghdad, near the ruins of the ancient city of Ur. It is the capital of the Dhi Qar Governorate. Its population in 2003 was about 560,000, making it the fourth-largest city in Iraq. It had a diverse population of Muslims, Mandaeans and Jews in the early 20th century;Field Museum of Natural History, 1940, p. 258. today its inhabitants are predominantly Shia muslims. Nasiriyah was founded by the Muntafiq tribe in the late 19th century during the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman era. It has since become a major hub for transportation. Nasiriyah is the center of a Date palm#Dates, date-growing area. The city's cottage industries include boat-building, carpentry and silver working. The city museum has a large collection of Sumerian, Assyrian, Babyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

