|
Eulogy Of King Prasat Thong
''Eulogy of King Prasat Thong'' is a long poem in Thai language, Thai, composed during the king’s reign (1629–1656) by a senior noble. It is the first Thai poem which is specifically a royal panegyric and titled as such. It recounts the main events of the reign, including the building and renaming of the Chakkawat Phaichaiyon audience hall, adjustment of the calendar, a grand almsgiving, and a military parade and festival, all also described in the Ayutthaya Kingdom#Royal Chronicles of Ayutthaya, Royal Chronicles of Ayutthaya. It also states that Prasat Thong, King Prasat Thong is a Bodhisattva, bodhisatta, destined to become the tenth in a sequence of ten future Ten Bodhisattas, Buddhas beginning with Maitreya, Metteyya. This claim is currently found in no other document. The sole manuscript, which was discovered in the 1980s, was copied in 1747/8 and is clearly incomplete. An annotated edition, including a facsimile of the original, was prepared by Buntuean Siworaphot and publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nirvana (Buddhism)
Nirvana (Sanskrit: निर्वाण, '; Pali: ') is "blowing out" or "quenching" of the activities of the worldly mind and its related suffering. Nirvana is the goal of the Hinayana and Theravada Buddhist paths, and marks the soteriological release from worldly suffering and rebirths in '' saṃsāra''. Nirvana is part of the Third Truth on "cessation of '' dukkha''" in the Four Noble Truths,_and_the_"''summum_bonum.html" ;"title="Four Noble Truths: BUDDHIST PHILOSOPHY Encycl ..., and the "''summum bonum">Four Noble Truths: BUDDHIST PHILOSOPHY Encycl ..., and the "''summum bonum'' of Buddhism and goal of the Noble Eightfold Path, Eightfold Path." In the Buddhist tradition, nirvana has commonly been interpreted as the extinction of the "three fires", or "three poisons", greed (''raga''), aversion (''dvesha'') and ignorance ('' moha''). When these ''fires'' are extinguished, release from the cycle of rebirth ('' saṃsāra'') is attained. Nirvana has also been claimed by so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damrong Rajanubhab
Prince Tisavarakumarn, the Prince Damrong Rajanubhab (Thai: ; Full transcription is "Somdet Phrachao Borommawongthoe Phra-ongchao Ditsawarakuman Kromphraya Damrongrachanuphap" (สมเด็จพระเจ้าบรมวงศ์เธอ พระองค์เจ้าดิศวรกุมาร กรมพระยาดำรงราชานุภาพ)) (21 June 1862 – 1 December 1943) was the founder of the modern Thai educational system as well as the modern provincial administration. He was an autodidact, a (self-taught) historian, and one of the most influential Thai intellectuals of his time. Born as ''Phra Ong Chao Tisavarakumarn'' (พระองค์เจ้าดิศวรกุมาร; "Prince Tisavarakumarn"), a son of King Mongkut with Consort Chum (เจ้าจอมมารดาชุ่ม; Chao Chom Manda Chum), a lesser royal wife; he initially learned Thai and Pali from private tutors, and English at the Royal School with Mr. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eulogy Of King Narai
''Eulogy of King Narai'' is a poem in Thai, composed during the reign of King Narai (1656–1688). It is a major example of the Thai genre of royal panegyrics. The identity of the author is uncertain. The poem relates the key events of the reign, the king’s power, his palace at Lopburi, the beauties of the forest, and an elephant hunt. Dating and authorship ''Eulogy of King Narai'' ( th, โคลงเฉลิมพระเกียรติสมเด็จพระนารายณ์มหาราช), ''Khlong chaloem phrakiat somdet phra narai maharat'', is a poem in Thai. The poem was probably composed in the early 1680s as no event after 1680 is mentioned in the text. As with most old Thai literature, the author is not identified. Some authorities attribute authorship to Luang Si Mahosot, while others including Winai Pongsripian favour Phra Maharatchakhru, a head of the Brahman department, and author of several other poetic works. Significance The royal panegyric is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
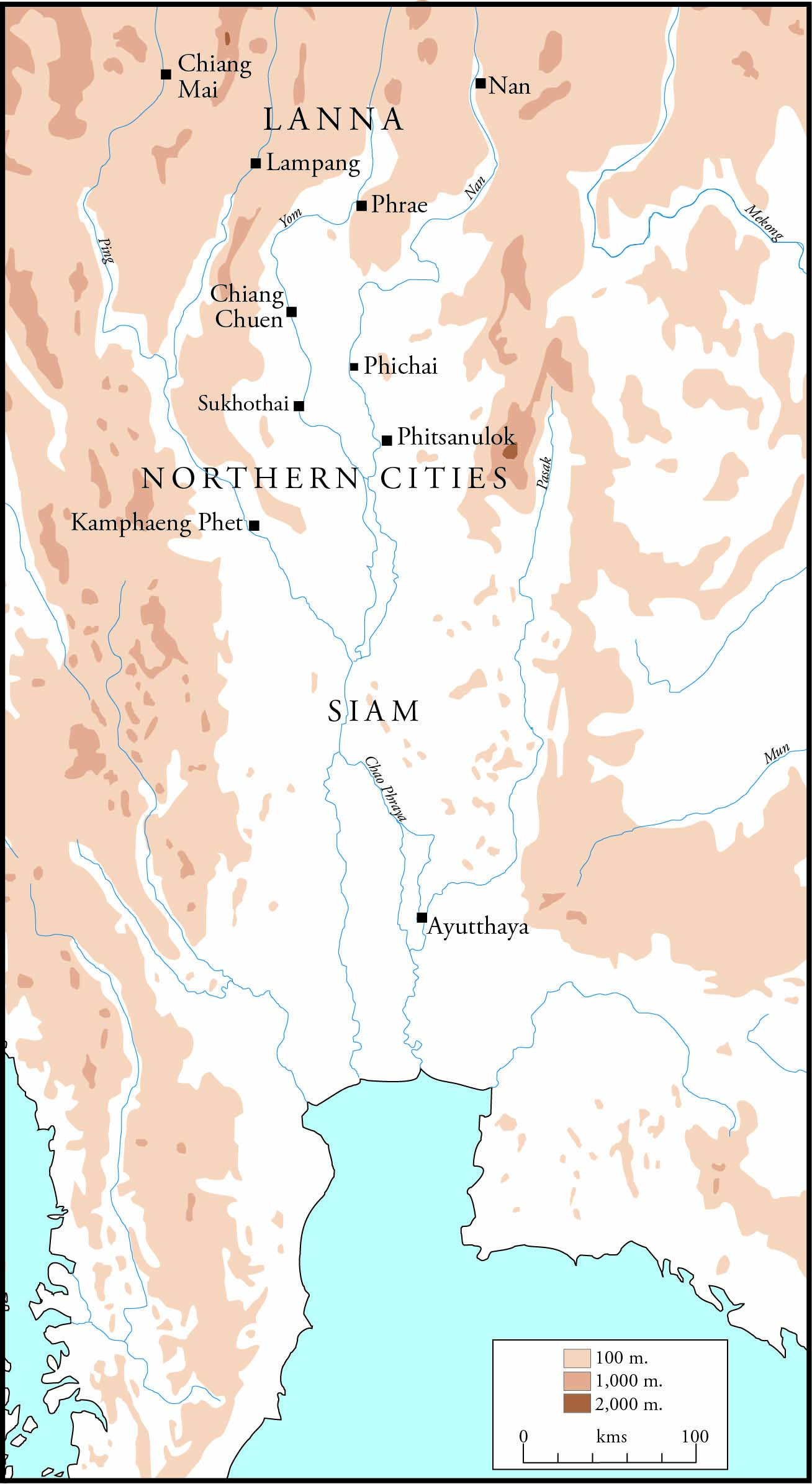
Yuan Phai
''Yuan Phai'' ( th, ยวนพ่าย, also known as ''Lilit Yuan Phai'', , see below for details), "Defeat of the Yuan," is a historical epic poem in the Thai language about rivalry between Ayutthaya and Lanna culminating in a battle that took place in 1474/5 AD at the place then called Chiang Cheun at Si Satchanalai. The Yuan are the people of Lanna or Yonok, then an independent kingdom in the upper reaches of the Chao Phraya River basin with a capital at Chiang Mai. The poem was written to celebrate King Boromma Trailokanat of Ayutthaya (r. 1448-1488), the victor. The poem was probably written soon after the battle. It counts among only a handful of works of Thai literature from the Early Ayutthaya era that have survived, and may be still in its original form, without later revisions. The main body of the poem consists of 1,180 lines in a variant of the ''khlong'' ( th, โคลง) meter. The poem is considered important as a source of historical information, as an exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prashasti
''Prashasti'' (IAST: Praśasti, Sanskrit for "praise") is an Indian genre of inscriptions composed by poets in praise of their rulers. Most date from the 6th century CE onwards. Written in the form of poetry or ornate prose, the ''prashastis'' stereotypically constructed a genealogy, the ruler's attributes, eulogize victories, piety and typically ended with one or more announcements of generous gifts and rewards he has given. They differ from the so-called "Cultic" genre of Indian inscriptions which praise a deity, religious founder (Buddha, Tirthankara, sub-tradition of Hinduism), guru, or sages then typically announces gifts or donations to a monastery, school, temple or a generous cause. In some epigraphic literature, a ''prashasti'' is considered synonymous with a ''kirti'' or ''purva'', and is related to the word ''kirtana'' which implies "songs and praises of" someone or a deity. The ''prashastis'' generally contained ornate titles, links to mythical legends or comparison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panegyric
A panegyric ( or ) is a formal public speech or written verse, delivered in high praise of a person or thing. The original panegyrics were speeches delivered at public events in ancient Athens. Etymology The word originated as a compound of grc, παν- 'all' (the form taken by the word πᾶν, neuter of πᾶς 'all', when that is used as a prefix) and the word grc, ἄγυρις, ágyris 'assembly' (an Aeolic dialect form, corresponding to the Attic or Ionic form grc, ἀγορά, agorá). Compounded, these gave grc, πανήγυρις, panḗgyris 'general or national assembly, especially a festival in honour of a god' and the derived adjective grc, πανηγυρικός, panēgyrikós 'of or for a public assembly or festival'. In Hellenistic Greek the noun came also to mean 'a festal oration, laudatory speech', and the adjective 'of or relating to a eulogy, flattering'. The noun grc, πανήγυρις, panḗgyris had been borrowed into Classical Latin by around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lan Xang
existed as a unified kingdom from 1353 to 1707. For three and a half centuries, Lan Xang was one of the largest kingdoms in Southeast Asia. The meaning of the kingdom's name alludes to the power of the kingship and formidable war machine of the early kingdom. The kingdom is the precursor for the country of Laos and the basis for its national historic and cultural identity. Historical overview Origins The geography Lan Xang would occupy had been originally settled by indigenous Austroasiatic-speaking tribes, such as Khmuic peoples and Vietic peoples which gave rise to the Bronze Age cultures in Ban Chiang (today part of Isan, Thailand) and the Đông Sơn culture as well as Iron Age peoples near Xiangkhoang Plateau on the Plain of Jars, Funan, and Chenla (near Vat Phou in Champasak Province). The Han dynasty's chronicles of the southward expansion of the Han dynasty provide the first written accounts of Tai–Kadai speaking peoples or ''Ai Lao'' who inhabited the areas o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Ava
The Kingdom of Ava ( my, အင်းဝခေတ်, ) was the dominant kingdom that ruled upper Burma (Myanmar) from 1364 to 1555. Founded in 1365, the kingdom was the successor state to the petty kingdoms of Myinsaing, Pinya and Sagaing that had ruled central Burma since the collapse of the Pagan Empire in the late 13th century. Like the small kingdoms that preceded it, Ava may have been led by Bamarised Shan kings who claimed descent from the kings of Pagan.Htin Aung 1967: 84–103Phayre 1883: 63–75 Scholars debate that the Shan ethnicity of Avan kings comes from mistranslation, particularly from a record of the Avan kings' ancestors ruling a Shan village in central Burma prior to their rise or prominence.Aung-Thwin 2010: 881–901 History The kingdom was founded by Thado Minbya in 1364Coedès 1968: 227 following the collapse of the Sagaing and Pinya Kingdoms due to raids by the Shan States to the north. In its first years of existence, Ava, which viewed itself a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Meru
Mount Meru (Sanskrit/Pali: मेरु), also known as Sumeru, Sineru or Mahāmeru, is the sacred five-peaked mountain of Hindu, Jain, and Buddhist cosmology and is considered to be the centre of all the physical, metaphysical and spiritual universes. There is no clear identification of Mount Meru with a particular geophysical location. Many famous Buddhist, Jain, and Hindu temples have been built as symbolic representations of this mountain. The "Sumeru Throne" 須彌座 xūmízuò style base is a common feature of Chinese pagodas. The highest point (the finial bud) on the pyatthat, a Burmese-style multi-tiered roof, represents Mount Meru. Etymology Etymologically, the proper name of the mountain is Meru (Sanskrit: Meru), to which is added the approbatory prefix su-, resulting in the meaning "excellent Meru" or "wonderful Meru". ''Meru'' is also the name of the central bead in a mālā. In other languages In other languages, Mount Meru is pronounced: * Assamese: � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indra
Indra (; Sanskrit: इन्द्र) is the king of the devas (god-like deities) and Svarga (heaven) in Hindu mythology. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. volumes/ref> Indra's myths and powers are similar to other Indo-European deities such as Jupiter, Perun, Perkūnas, Zalmoxis, Taranis, Zeus, and Thor, part of the greater Proto-Indo-European mythology. Indra is the most referred deity in the ''Rigveda''. He is celebrated for his powers, and as the one who killed the great evil (a malevolent type of asura) named Vritra, who obstructed human prosperity and happiness. Indra destroys Vritra and his "deceiving forces", and thereby brings rains and sunshine as the saviour of mankind. He is also an important deity worshipped by the Kalash people, indicating his prominence in ancient Hinduism. Indra's significance diminishes in the post-Vedic Indian literature, but he still plays an important role in various m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)