|
Eugene Rosenberg
Eugene Rosenberg ( he, יוג'ין רוזנברג) (October 16, 1935) is a microbiologist at the Faculty of Life Sciences at Tel Aviv University, an expert in the field of applied environmental microbiology, in particular his work on Myxobacteria,Yang, Zhaomin and Penelope I. Higgs (eds.), ''Myxobacteria: Genomics, Cellular and Molecular Biology'' (Portland, OR: Caister Academic Press, 2014) microorganisms to combat pollution (bioremediation), and the Hologenome theory of evolution. Early life and education Rosenberg was born in New York City in 1935, grew up in Los Angeles, and immigrated to Israel in 1970. He received his Bachelor of Science from the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) and his Ph.D. from the Department of Biochemistry at Columbia University, New York (1961). His doctoral thesis, under the supervision of Steven Zamenhof, describes the chemical structures of the capsules of Hemophilus influenzae, types B, E, and F. Rosenberg went on to postdoctoral rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxococcus Xanthus
''Myxococcus xanthus'' is a gram-negative, rod-shaped species of myxobacteria that exhibits various forms of self-organizing behavior in response to environmental cues. Under normal conditions with abundant food, it exists as a predatory, saprophytic single-species biofilm called a swarm. Under starvation conditions, it undergoes a multicellular development cycle. Colony growth A swarm of ''M. xanthus'' is a distributed system, containing millions of bacteria that communicate among themselves in a non-centralized fashion. Simple patterns of cooperative behavior among the members of the colony combine to generate complex group behaviors in a process known as "stigmergy". For example, the tendency for one cell to glide only when in direct contact with another results in the colony forming swarms called "wolf-packs" that may measure up to several inches wide. This behavior is advantageous to the members of the swarm, as it increases the concentration of extracellular digestive enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synbiotics
Synbiotics refer to food ingredients or dietary supplements combining probiotics and prebiotics in a form of synergism, hence synbiotics. The synbiotic concept was first introduced as "mixtures of probiotics and prebiotics that beneficially affect the host by improving the survival and implantation of live microbial dietary supplements in the gastrointestinal tract, by selectively stimulating the growth and/or by activating the metabolism of one or a limited number of health-promoting bacteria, thus improving host welfare". As of 2018, the research on this concept is preliminary, with no high-quality evidence from clinical research that such benefits exist. Synbiotics may be complementary synbiotics, where each component is independently chosen for its potential effect on host health, or synergistic synbiotics, where the prebiotic component is chosen to support the activity of the chosen probiotic. Research is evaluating if synbiotics can be optimized, (known as 'optibiotics') whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is some evidence that probiotics are beneficial for some conditions, but there is little evidence for many of the health benefits claimed for them. The first discovered probiotic was a certain strain of bacillus in Bulgarian yoghurt, called ''Lactobacillus bulgaricus''. The discovery was made in 1905 by Bulgarian physician and microbiologist Stamen Grigorov. The modern-day theory is generally attributed to Russian Nobel laureate Élie Metchnikoff, who postulated around 1907 that yoghurt-consuming Bulgarian peasants lived longer. A growing probiotics market has led to the need for stricter requirements for scientific substantiation of putative benefits conferred by microorganisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are compounds in food that induce the growth or activity of beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. The most common example is in the gastrointestinal tract, where prebiotics can alter the composition of organisms in the gut microbiome. Dietary prebiotics are typically nondigestible fiber compounds that pass undigested through the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract and stimulate the growth or activity of advantageous bacteria in the colon by acting as substrates for them. They were first identified and named by Marcel Roberfroid in 1995. Depending on the jurisdiction, they may have regulatory scrutiny as food additives for the health claims made for marketing purposes. Common prebiotics used in food manufacturing include beta-glucan from oats and inulin from chicory root. Definition The definition of prebiotics and the food ingredients that can fall under this classification, has evolved since its first definition in 1995. In its earliest defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably well-defined habitat which has distinct physio-chemical properties. The term thus not only refers to the microorganisms involved but also encompasses their theatre of activity". In 2020, an international panel of experts published the outcome of their discussions on the definition of the microbiome. They proposed a definition of the microbiome based on a revival of the "compact, clear, and comprehensive description of the term" as originally provided by Whipps ''et al.'', but supplemented with two explanatory paragraphs. The first explanatory paragraph pronounces the dynamic character of the microbiome, and the second explanatory paragraph clearly separates the term ''microbiota'' from the term ''microbiome''. The microbiota consists of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holobiont
A holobiont is an assemblage of a host and the many other species living in or around it, which together form a discrete ecological unit through symbiosis, though there is controversy over this discreteness. The components of a holobiont are individual species or bionts, while the combined genome of all bionts is the hologenome. The holobiont concept was initially introduced by the German theoretical biologist Adolf Meyer-Abich in 1943, and then apparently independently by Dr. Lynn Margulis in her 1991 book ''Symbiosis as a Source of Evolutionary Innovation''. The concept has evolved since the original formulations. Holobionts include the host, virome, microbiome, and any other organisms which contribute in some way to the functioning of the whole. Well-studied holobionts include reef-building corals and humans. Overview A holobiont is a collection of closely associated species that have complex interactions, such as a plant species and the members of its microbiome. Each sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Bleaching
Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to various stressors, such as changes in temperature, light, or nutrients. Bleaching occurs when coral polyps expel the zooxanthellae (dinoflagellates that are commonly referred to as algae) that live inside their tissue, causing the coral to turn white. The zooxanthellae are photosynthetic, and as the water temperature rises, they begin to produce reactive oxygen species. This is toxic to the coral, so the coral expels the zooxanthellae. Since the zooxanthellae produce the majority of coral colouration, the coral tissue becomes transparent, revealing the coral skeleton made of calcium carbonate. Most bleached corals appear bright white, but some are blue, yellow, or pink due to pigment proteins in the coral. The leading cause of coral bleaching is rising ocean temperature due to climate change. A temperature about 1 °C (or 2 °F) above average can cause bleaching. According to the United Nations Environment Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganisms
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
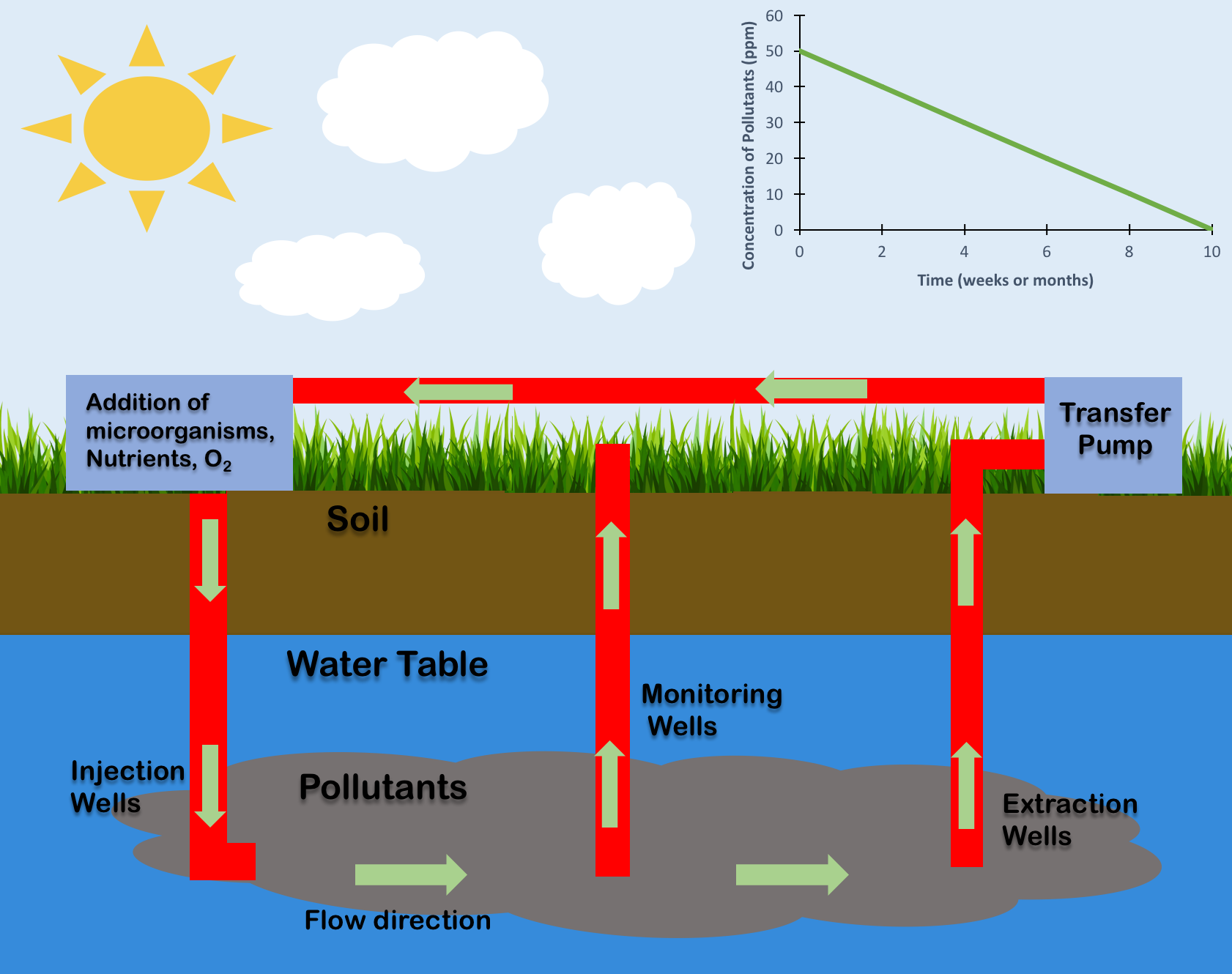
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer considerable advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acinetobacter
''Acinetobacter'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria belonging to the wider class of Gammaproteobacteria. ''Acinetobacter'' species are oxidase-negative, exhibit twitching motility, and occur in pairs under magnification. They are important soil organisms, where they contribute to the mineralization of, for example, aromatic compounds. ''Acinetobacter'' species are a key source of infection in debilitated patients in the hospital, in particular the species ''Acinetobacter baumannii''. Description Species of the genus ''Acinetobacter'' are strictly aerobic, nonfermentative, Gram-negative bacilli. They show mostly a coccobacillary morphology on nonselective agar. Rods predominate in fluid media, especially during early growth. The morphology of ''Acinetobacter'' species can be quite variable in Gram-stained human clinical specimens, and cannot be used to differentiate ''Acinetobacter'' from other common causes of infection. Most strains of ''Acinetobacter'', except some o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Lab
Eugene may refer to: People and fictional characters * Eugene (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Eugene (actress) (born 1981), Kim Yoo-jin, South Korean actress and former member of the singing group S.E.S. * Eugene (wrestler), professional wrestler Nick Dinsmore * Franklin Eugene (producer), American film producer * Gene Eugene, stage name of Canadian born actor, record producer, engineer, composer and musician Gene Andrusco (1961–2000) * Wendell Eugene (1923–2017), American jazz musician Places Canada * Mount Eugene, in Nunavut; the highest mountain of the United States Range on Ellesmere Island United States * Eugene, Oregon, a city ** Eugene, OR Metropolitan Statistical Area ** Eugene (Amtrak station) * Eugene Apartments, NRHP-listed apartment complex in Portland, Oregon * Eugene, Indiana, an unincorporated town * Eugene, Missouri, an unincorporated town Business * Eugene Green Energy Standard, an intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |