|
Eugene Island Block 330 Oil Field
Eugene Island block 330 oil field is an oil field in the United States Exclusive Economic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico. It is located southwest of New Orleans, off the Louisiana coast comprising six and a half leased blocks: Eugene Island 313, 314 south, 330, 331, 332, 337 and 338. History In the outer continental shelf lease sale on December 15, 1970 were offered for lease, including Eugene Island blocks. The Block 330 area was acquired by Pennzoil (now part of Royal Dutch Shell). As the Pliocene-Pleistocene sands were considered geochemically immature and wells drilled to the north of Block 330 discovered natural gas, Pennzoil expected to discover a natural gas not oil. The oil field was discovered in March 1971 while drilling the 1 OCS G-2115 well. Approximately at the same time oil was discovered by Royal Dutch Shell in the adjoining block 331. By the end of 1971, two platforms had been installed in the field. The first development well was drilled on Block 330 by Pennzoil' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Heinberg
Richard William Heinberg is an American journalist and educator who has written extensively on energy, economic, and ecological issues, including oil depletion. He is the author of 14 books, and presently serves as the senior fellow at the Post Carbon Institute. Early life Heinberg grew up in St. Joseph, Missouri. His father, William Heinberg, was a chemist and high-school physics and chemistry teacher. Heinberg's interest in science came from his father, but at an early age, he rejected his parents' fundamentalist Christian beliefs. At one point he lived at Colorado's Sunrise Ranch, headquarters of the " Emissaries of Divine Light" group, which Heinberg referred to as "a sort of benign cult." Career After two years in college and a period of personal study, in November 1979 Heinberg became personal assistant to Immanuel Velikovsky. After Velikovsky's death, Heinberg assisted his widow in editing manuscripts. He published his first book in 1989, ''Memories and Visions of Paradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' is an American business-focused, international daily newspaper based in New York City, with international editions also available in Chinese and Japanese. The ''Journal'', along with its Asian editions, is published six days a week by Dow Jones & Company, a division of News Corp. The newspaper is published in the broadsheet format and online. The ''Journal'' has been printed continuously since its inception on July 8, 1889, by Charles Dow, Edward Jones, and Charles Bergstresser. The ''Journal'' is regarded as a newspaper of record, particularly in terms of business and financial news. The newspaper has won 38 Pulitzer Prizes, the most recent in 2019. ''The Wall Street Journal'' is one of the largest newspapers in the United States by circulation, with a circulation of about 2.834million copies (including nearly 1,829,000 digital sales) compared with ''USA Today''s 1.7million. The ''Journal'' publishes the luxury news and lifestyle magazine ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Field
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations. Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence of high heat and pressure in the Earth's crust. Petroleum reservoirs are broadly classified as ''conventional'' and '' unconventional'' reservoirs. In conventional reservoirs, the naturally occurring hydrocarbons, such as crude oil or natural gas, are trapped by overlying rock formations with lower permeability, while in unconventional reservoirs, the rocks have high porosity and low permeability, which keeps the hydrocarbons trapped in place, therefore not requiring a cap rock. Reservoirs are found using hydrocarbon exploration methods. Oil field An oil field is an area of accumulation of liquid oil underground in multiple (potentially linked) reservoirs, trapped as it rises by impermeable rock formations. In industrial terms, an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
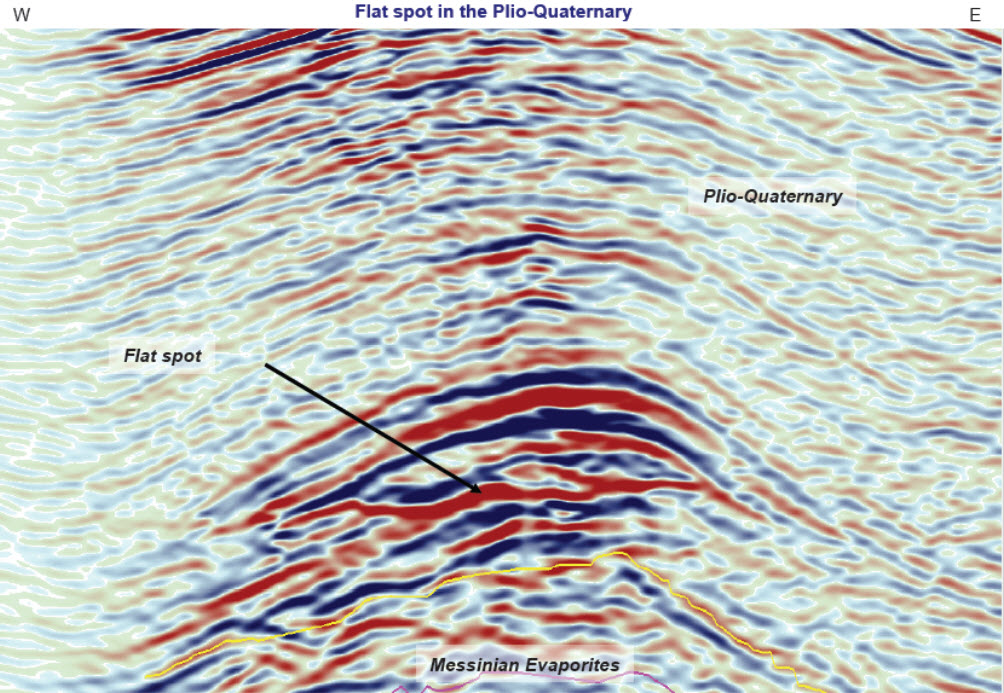
Flat Spot (reflection Seismology)
In reflection seismology, a flat spot is a seismic attribute anomaly that appears as a horizontal reflector cutting across the stratigraphy elsewhere present on the seismic image. Its appearance can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons. Therefore, it is known as a direct hydrocarbon indicator and is used by geophysicists in hydrocarbon exploration. Theory A flat spot can result from the increase in acoustic impedance when a gas-filled porous rock (with a lower acoustic impedance) overlies a liquid-filled porous rock (with a higher acoustic impedance). It may stand out on a seismic image because it is flat and will contrast with surrounding dipping reflections. Caution There are a number of other possible reasons for there being a flat spot on a seismic image. It could be representative of a mineralogical change in the subsurface or an unresolved shallower multiple. Additionally, the interpretation of a flat spot should be attempted after depth conversion to confirm that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bright Spot
In reflection seismology, a bright spot is a local high amplitude seismic attribute anomaly that can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons and is therefore known as a direct hydrocarbon indicator. It is used by geophysicists in hydrocarbon exploration. History Bright spots were not commonly identified until the early 1970s because of the extensive and industry-wide use of automatic gain control, which obscured the amplitude effects of hydrocarbon accumulations. Theory A bright spot primarily results from the increase in acoustic impedance contrast when a hydrocarbon (with a lower acoustic impedance) replaces the brine-saturated zone (with a higher acoustic impedance) that underlies a shale (with a higher acoustic impedance still), increasing the reflection coefficient. The effect decreases with depth because compaction for sands and shales occurs at different rates and the acoustic impedance relationship stated above will not hold after a certain depth/age. Below this depth, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopach Map
An isopach map () illustrates thickness variations within a tabular unit, layer or stratum. Isopachs are contour lines of equal thickness over an area. Isopach maps are utilized in hydrographic survey, stratigraphy, sedimentology, structural geology, petroleum geology and volcanology Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word '' vulcan''. Vulcan was the an .... An isopach map is similar to an isochore map, but these terms actually describe different methods of displaying thickness variations within a layer.Levorsen (1967), p. 596-600 and 616.Tearpock and Bischke (2002), chap. 14. *An isopach map displays lines of equal thickness in a layer where the thicknesses are measured perpendicular to the layer boundaries. Isopach maps are also referred to as True Stratigraphic Thickness (TST) maps.''Isopach maps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithofacies
Lithofacies may refer to: * A mappable subdivision of a designated stratigraphic unit, distinguished from adjacent subdivisions on the basis of lithology; a facies characterized by particular lithologic features * The rock record of any particular sedimentary environment In geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be ..., including both physical and organic characteristics * cf: Lithotope {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |