|
Eudistoma
''Eudistoma'' is a genus of sea squirts belonging to the class Ascidiacea. It was first described in 1909 by Maurice Caullery. Originally it was thought to be a subgenus of '' Distoma''. ''Eudistoma'' is the most species-rich genus in the family Polycitordae, with 124 valid species as of 2014. They are found in tropical and temperate waters; some species are also found in the Antarctic and subtropical area. Description In 1909 Caullery described ''Eudistoma'' as a subgenus of ''Distoma'' due to the rows of stigmata in the pharynx. In 1917 Ritter and Forsyth described it as a separate genus without explanation. Three subsequent papers published in 1919, 1921 and 1942 all considered it to be a subgenus of ''Polycitor''. ''Eudistoma'' was finally considered a valid genus in 1945 due to "the three rows of pharyngeal slits, long esophagus, flat stomach in the posterior region of the abdomen, very conspicuous longitudinal muscles extending from the pharynx to the end of the abdomen a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudistomin
Eudistomins Eudistomins are β-carboline derivatives, isolated from ascidians (marine tunicates of the family ''Ascidiacea''), like ''Ritterella sigillinoides'', ''Lissoclinum fragile'', or ''Pseudodistoma aureum''. Types of Eudistomin Eudistomin C Eudistomin C is a naturally occurring β-carboline derivative which has been found in the Ascidian, ''Eudistoma Olivaseum.'' Eudistomin C is a cytotoxic molecule; this cytotoxicity is achieved by the Eudistomin C binds onto the 40S or 80S Ribosomal subunits, which inhibits the process of protein translation, leading to cell death. There are cells that are resistance to Eudistomin C's cytotoxicity, and these cells are called Yeast EudiC Resistance mutants (YER). YER mutants have a RPS14A mutation on the cell's uS11 gene, which encodes for the cell's 40S ribosomal subunit. This produces the RPS14A 40S Ribosomal subunit which confers a resistance against Eudistomin C, preventing protein translation inhibition. Eudistomin C has also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplousobranchia
Aplousobranchia is an order of sea squirts in the class Ascidiacea. They are colonial animals, and are distinguished from other sea squirts by the presence of relatively simple pharyngeal baskets. This provides the etymology of their name: in ancient greek, () means "simple". The posterior part of the abdomen contains the heart and gonads, and is typically larger than in other sea squirts. Taxonomy Order Aplousobranchia * Family Clavelinidae Forbes & Hanley 1848 ycnoclavellidae Kott 1990**''Clavelina'' Savigny 1816 [''Bradiclavella'' Zirpolo 1925; ''Chondrostachys'' Macdonald 1858; ''Dendroclavella'' Oka 1927; ''Podoclavella'' Herdman 1890; ''Rhodozona'' Van Name 1902; ''Stereoclavella'' Herdman 1890; ''Synclavella'' Caullery 1900] **''Euclavella'' Kott 1990 **''Nephtheis'' Gould 1856 [''Oxycorynia'' Drasche 1882] **''Pycnoclavella'' Garstang 1891 [''Archiascidia'' Julin 1904] * Family Didemnidae Giard 1872 iplosominae Giard 1872**'' Atriolum'' Kott 1983 **''Clitella'' Kott 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycitoridae
Polycitoridae is a family of tunicates belonging to the order Aplousobranchia. Genera: * '' Archidistoma'' Garstang, 1891 * '' Brevicollus'' Kott, 1990 * '' Cystodytes'' Drasche, 1884 * ''Eucoelium'' Savigny, 1816 * ''Eudistoma'' Caullery, 1909 * ''Exostoma'' Kott, 1990 * '' Millarus'' Monniot & Monniot, 1988 * ''Polycitor'' Renier, 1804 * '' Polycitorella'' Michaelsen, 1924 * ''Rhombifera The Eocrinoidea are an extinct class of echinoderms that lived between the Early Cambrian and Late Silurian periods. They are the earliest known group of stalked, arm-bearing echinoderms, and were the most common echinoderms during the Cambrian. ...'' Pérès, 1956 * '' Salix'' Kott, 2005 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4925722 Aplousobranchia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Emerson Ritter
William Emerson Ritter (November 21, 1856 – January 10, 1944) was an American biologist. Ritter initiated and shaped the Marine Biological Association of San Diego (now Scripps Institution of Oceanography of UC San Diego) and the American Society for the Dissemination of Science (now the Society for Science and the Public and Science News). Innovative and entrepreneurial, with a deep desire for human service, he worked tirelessly to educate people in science thinking. He was the first biologist to propose a theory of systems, and seems to be the originator of the term organicism for biological purposes. Early life William Emerson Ritter was born on a farm on November 21, 1856 in Hampden Township, Columbia County, Wisconsin. His parents, Horatio and Leonora Ritter, moved from New York a few years earlier. The Ritter household included William, his brother Frank, his sisters Mary, Ella, and Flora, and his maternal grandparents, Nathan and Ruby Eason. For the first few years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , Medicinal plant, plants, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxic
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa''). Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of cell fates. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activate a genetic program of controlled cell death (apoptosis). Cells undergoing necrosis typically exhibit rapid swelling, lose membrane integrity, shut down metabolism, and release their contents into the environment. Cells that undergo rapid necrosis in vitro do not have sufficient time or energy to activate apoptotic machinery and will not express apoptotic markers. Apoptosis is characterized by well defined cytological and molecular events including a change i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , |
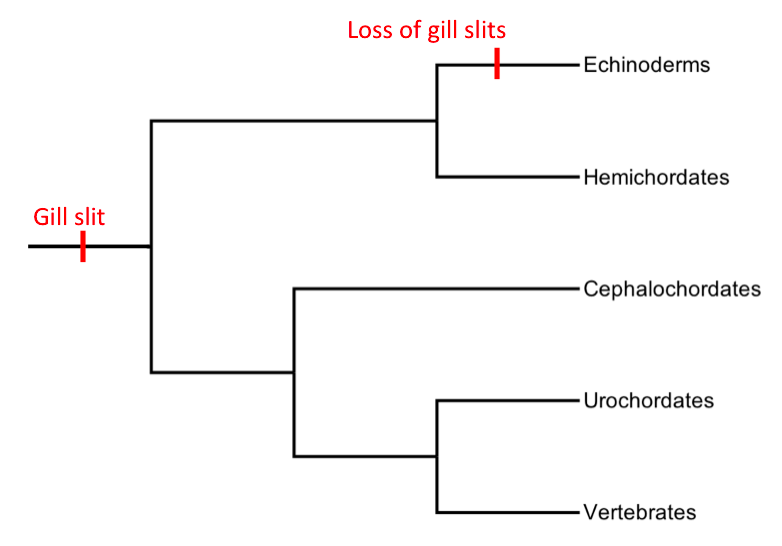
Pharyngeal Slits
Pharyngeal slits are filter-feeding organs found among deuterostomes. Pharyngeal slits are repeated openings that appear along the pharynx caudal to the mouth. With this position, they allow for the movement of water in the mouth and out the pharyngeal slits. It is postulated that this is how pharyngeal slits first assisted in filter-feeding, and later, with the addition of gills along their walls, aided in respiration of aquatic chordates. These repeated segments are controlled by similar developmental mechanisms. Some hemichordate species can have as many as 200 gill slits. Pharyngeal clefts resembling gill slits are transiently present during the embryonic stages of tetrapod development. The presence of pharyngeal arches and clefts in the neck of the developing human embryo famously led Ernst Haeckel to postulate that "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny"; this hypothesis, while false, contains elements of truth, as explored by Stephen Jay Gould in ''Ontogeny and Phylogeny''.. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycitor
''Polycitor'' is a genus of tunicates belonging to the family Polycitoridae. The genus has almost cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The ext .... Species Species: *'' Polycitor adriaticus'' *'' Polycitor africanus'' *'' Polycitor annulus'' *'' Polycitor aurantiacus'' *'' Polycitor calamus'' *'' Polycitor cerasus'' *'' Polycitor circes'' *'' Polycitor clava'' *'' Polycitor columna'' *'' Polycitor crypticus'' *'' Polycitor crystallinus'' *'' Polycitor cuneatus'' *'' Polycitor emergens'' *'' Polycitor epicolon'' *'' Polycitor giganteus'' *'' Polycitor glareosus'' *'' Polycitor luderitzi'' *'' Polycitor nitidus'' *'' Polycitor nubilus'' *'' Polycitor obeliscus'' *'' Polycitor porrecta'' *'' Polycitor profundus'' *'' Polycitor prol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distoma
Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum Platyhelminthes. They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, they can occur also in bile ducts, gallbladder, and liver parenchyma. In these organs, they produce pathological lesions leading to parasitic diseases. They have complex life cycles requiring two or three different hosts, with free-living larval stages in water. Biology The body of liver flukes is leaf-like and flattened. The body is covered with a tegument. They are hermaphrodites having complete sets of both male and female reproductive systems. They have simple digestive systems and primarily feed on blood. The anterior end is the oral sucker opening into the mouth. Inside, the mouth leads to a small pharynx which is followed by an extended intestine that runs through the entire length of the body. The intestine is heavily branched and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |