|
Ethio-Djibouti Railways
The Ethio-Djibouti Railway (french: Chemin de Fer Djibouto-Éthiopien, C.D.E.; ) is a metre gauge railway in the Horn of Africa that once connected Addis Ababa to the port city of Djibouti. The operating company was also known as the Ethio-Djibouti Railways. The railway was built in 1894–1917 to connect the Ethiopian capital city to French Somaliland. During early operations, it provided landlocked Ethiopia with its only access to the sea. After World War II, the railway progressively fell into a state of disrepair due to competition from road transport. The railway has been mostly superseded by the Addis Ababa–Djibouti Railway, an electrified standard gauge railway that was completed in 2017. The metre gauge railway has been abandoned in central Ethiopia and Djibouti. However, a rehabilitated section is still in operation near the Ethiopia-Djibouti border. As of February 2018, a combined passenger and freight service runs two times a week between the Ethiopian city of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Rail
Various terms are used for passenger railway lines and equipment; the usage of these terms differs substantially between areas: Rapid transit A rapid transit system is an electric railway characterized by high speed (~) and rapid acceleration. It uses passenger railcars operating singly or in multiple unit trains on fixed rails. It operates on separate rights-of-way from which all other vehicular and foot traffic are excluded (i.e. is fully grade-separated from other traffic). It uses sophisticated signaling systems, and high platform loading. Originally, the term ''rapid transit'' was used in the 1800s to describe new forms of quick urban public transportation that had a right-of-way separated from street traffic. This set rapid transit apart from horsecars, trams, streetcars, omnibuses, and other forms of public transport. A variant of the term, ''mass rapid transit (MRT)'', is also used for metro systems in Southeast Asia and Taiwan. Though the term was almost alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Track (rail)
A single-track railway is a railway where trains traveling in both directions share the same track. Single track is usually found on lesser-used rail lines, often branch lines, where the level of traffic is not high enough to justify the cost of constructing and maintaining a second track. Advantages and disadvantages Single track is significantly cheaper to build and maintain, but has operational and safety disadvantages. For example, a single-track line that takes 15 minutes to travel through would have capacity for only two trains per hour in each direction safely. By contrast, a double track with signal boxes four minutes apart can allow up to 15 trains per hour in each direction safely, provided all the trains travel at the same speed. This hindrance on the capacity of a single track may be partly overcome by making the track one-way on alternate days, if the single track is not used for public passenger transit. Long freight trains are a problem if the passing s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Train
A royal train is a set of railway carriages dedicated for the use of the monarch or other members of a royal family. Most monarchies with a railway system employ a set of royal carriages. Australia The various government railway operators of Australia have operated a number of royal trains for members of the Royal Family on their numerous tours of the country. Austria-Hungary The imperial and royal court used the ''k.u.k. Hofsalonzug'' (Imperial and Royal Court Saloon Train). Various versions existed under the rule of Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria. Many of the cars were built by Ringhoffer in Bohemia. The cars were operated and maintained by the Imperial Royal Austrian State Railways. Two cars have survived, one is the dining car kept at the Technical Museum in Prague, and the other is the car of Empress Elisabeth of Austria, which is kept at the Technical Museum in Vienna. Belgium Historic use Some of the historic royal coaches are still preserved, two of which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haile Selassie
Haile Selassie I ( gez, ቀዳማዊ ኀይለ ሥላሴ, Qädamawi Häylä Səllasé, ; born Tafari Makonnen; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia (''Enderase'') for Empress Zewditu from 1916. Haile Selassie is widely considered a defining figure in modern Ethiopian history, and the key figure of Rastafari, a religious movement in Jamaica that emerged shortly after he became emperor in the 1930s. He was a member of the Solomonic dynasty, which claims to trace lineage to Emperor Menelik I, believed to be the son of King Solomon and Makeda the Queen of Sheba. Haile Selassie attempted to modernize the country through a series of political and social reforms, including the introduction of the 1931 constitution, its first written constitution, and the abolition of slavery. He led the failed efforts to defend Ethiopia during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War and spent most of the period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
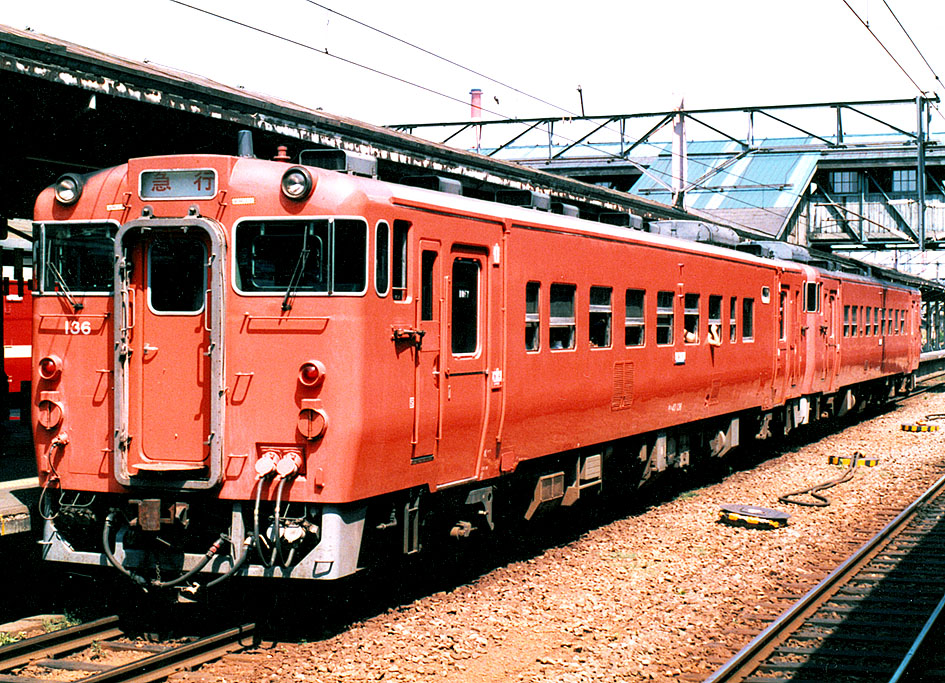
Diesel Multiple Unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple-unit train powered by on-board diesel engines. A DMU requires no separate locomotive, as the engines are incorporated into one or more of the carriages. Diesel-powered single-unit railcars are also generally classed as DMUs. Diesel-powered units may be further classified by their transmission type: diesel–mechanical DMMU, diesel–hydraulic DHMU, or diesel–electric DEMU. Design The diesel engine may be located above the frame in an engine bay or under the floor. Driving controls can be at both ends, on one end, or in a separate car. Types by transmission DMUs are usually classified by the method of transmitting motive power to their wheels. Diesel–mechanical In a diesel–mechanical multiple unit (DMMU), the rotating energy of the engine is transmitted via a gearbox and driveshaft directly to the wheels of the train, like a car. The transmissions can be shifted manually by the driver, as in the great majority of first-gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-called compression-ignition engine (CI engine). This contrasts with engines using spark plug-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine (gasoline engine) or a gas engine (using a gaseous fuel like natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas). Diesel engines work by compressing only air, or air plus residual combustion gases from the exhaust (known as exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)). Air is inducted into the chamber during the intake stroke, and compressed during the compression stroke. This increases the air temperature inside the cylinder to such a high degree that atomised diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber ignites. With the fuel being injected into the air just before combustion, the dispersion of the fuel is une ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel–electric Transmission
A diesel–electric transmission, or diesel–electric powertrain is a transmission system for vehicles powered by diesel engines in road, rail, and marine transport. Diesel–electric transmission is based on petrol–electric transmission, a very similar transmission system used for petrol engines. Diesel–electric transmission is used on railways by diesel–electric locomotives and diesel–electric multiple units, as electric motors are able to supply full torque at 0 RPM. Diesel–electric systems are also used in marine transport, including submarines, and on some land vehicles. Description The defining characteristic of diesel–electric transmission is that it avoids the need for a gearbox, by converting the mechanical force of the diesel engine into electrical energy (through a dynamo), and using the electrical energy to drive traction motors, which propel the vehicle mechanically. The traction motors may be powered directly or via rechargeable batteries, makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsthom
Alstom SA is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer operating worldwide in rail transport markets, active in the fields of passenger transportation, signalling, and locomotives, with products including the AGV, TGV, Eurostar, Avelia and New Pendolino high-speed trains, in addition to suburban, regional and metro trains, and Citadis trams. Alsthom (originally Als-Thom) was formed by a merger between Compagnie Française Thomson-Houston and the electric engineering division of Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques in 1928. Significant later acquisitions included the Constructions Electriques de France (1932), shipbuilder Chantiers de l'Atlantique (1976), and parts of ACEC (Belgium, late-1980s). A merger with parts of the General Electric Company (UK) formed GEC Alsthom in 1989. Throughout the 1990s, the company expanded its holdings in the rail sector, via the acquisition of German rolling stock manufacturer Linke-Hofmann-Busch and Italian rail signalli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Locomotive And Machine Works
Swiss may refer to: * the adjectival form of Switzerland * Swiss people Places * Swiss, Missouri * Swiss, North Carolina *Swiss, West Virginia * Swiss, Wisconsin Other uses *Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports *Swiss International Air Lines ** Swiss Global Air Lines, a subsidiary * Swissair, former national air line of Switzerland *.swiss alternative TLD for Switzerland See also * Swiss made, label for Swiss products * Swiss cheese (other) * Switzerland (other) *Languages of Switzerland, none of which are called "Swiss" *International Typographic Style, also known as Swiss Style, in graphic design *Schweizer (other), meaning Swiss in German *Schweitzer, a family name meaning Swiss in German *Swisse Swisse is a vitamin, supplement, and skincare brand. Founded in Australia in 1969 and globally headquartered in Melbourne, and was sold to Health & Happiness, a Chinese company based in Hong Kong previously known as Biostime Internation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
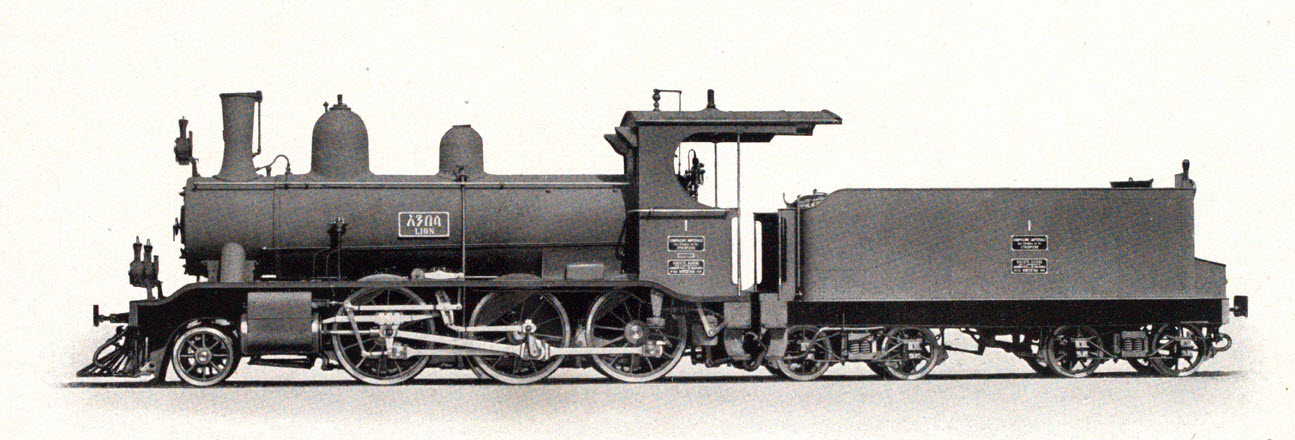
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2M Auf Der Holl Holl-Brücke
M, or m, is the thirteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''em'' (pronounced ), plural ''ems''. History The letter M is derived from the Phoenician Mem, via the Greek Mu (Μ, μ). Semitic Mem is most likely derived from a " Proto-Sinaitic" (Bronze Age) adoption of the "water" ideogram in Egyptian writing. The Egyptian sign had the acrophonic value , from the Egyptian word for "water", ''nt''; the adoption as the Semitic letter for was presumably also on acrophonic grounds, from the Semitic word for "water", '' *mā(y)-''. Use in writing systems The letter represents the bilabial nasal consonant sound in the orthography of Latin as well as in that of many modern languages, and also in the International Phonetic Alphabet. In English, the Oxford English Dictionary (first edition) says that is sometimes a vowel, in words like ''s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIE Nr
CIE may refer to: Organizations * Cambridge International Examinations, an international examination board * Center for International Education at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst * Cleveland Institute of Electronics, a private technical and engineering educational institution * International Commission on Illumination (''Commission internationale de l'éclairage'') * Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire (C.I.E.) * Computability in Europe, an international organization of computability theorists, computer scientists, mathematicians * CIÉ (Córas Iompair Éireann), the Irish state transport authority * Council on Islamic Education * Transportes Aéreos Cielos Andinos, ICAO code: CIE * Civil Information and Educational Section (CIE), General Headquarters, the Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers in Japan (1945–1952) Science and technology * CIE 1931 color space, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces, created by the International Commission on Illu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |