|
Eta Orionis
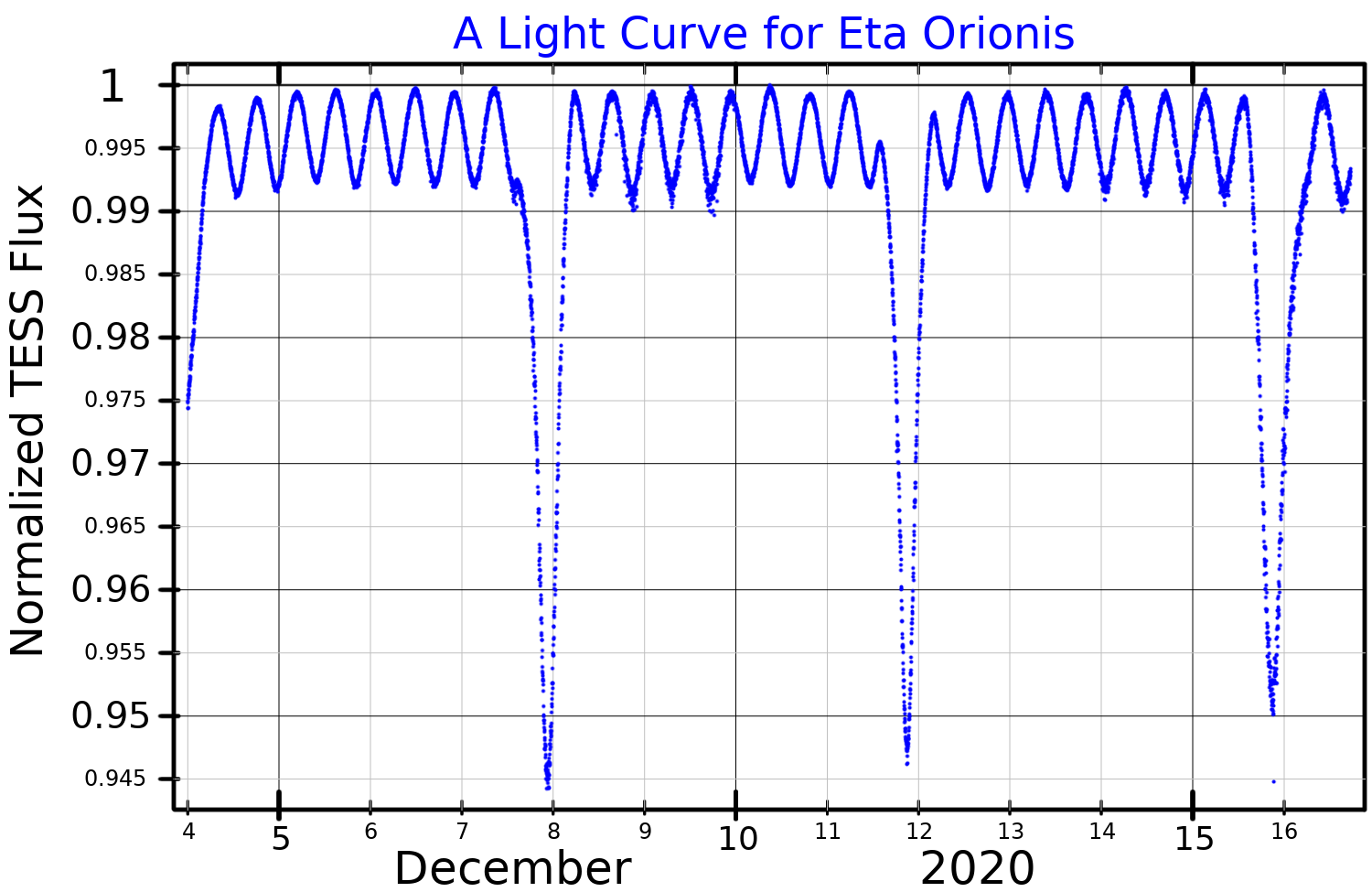
Eta Orionis, Latinized from η Orionis, is a multiple star in the constellation Orion. It lies a little to the west of Orion's Belt between Delta Orionis and Rigel, being closer to Delta Orionis than to Rigel. It lies at a distance of around 1,000 light-years from Earth and is part of the Orion OB1 association. System Eta Orionis is listed in multiple star catalogues as having two companions: a bright component B less than 2″ away; and a faint component C nearly 2′ away. The two are estimated to orbit every 1,800 years. The primary star, Eta Orionis A, is itself a spectroscopic triple star, known from multiple spectral lines with varying radial velocities. The most distant component Ac, has been resolved using speckle interferometry, at a separation of about 0.04″. It orbits the other two in 9.4 years. The two closest stars, Aa and Ab, are separated by only about a tenth of an astronomical unit and orbit in just under eight days. The system lies within the Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speckle Interferometry
Speckle imaging describes a range of high-resolution astronomical imaging techniques based on the analysis of large numbers of short exposures that freeze the variation of atmospheric turbulence. They can be divided into the shift-and-add ("''image stacking''") method and the speckle interferometry methods. These techniques can dramatically increase the resolution of ground-based telescopes, but are limited to bright targets. Explanation The principle of all the techniques is to take very short exposure images of astronomical targets, and then process those so as to remove the effects of astronomical seeing. Use of these techniques led to a number of discoveries, including thousands of binary stars that would otherwise appear as a single star to a visual observer working with a similar-sized telescope, and the first images of sunspot-like phenomena on other stars. Many of the techniques remain in wide use today, notably when imaging relatively bright targets. The resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Draper Catalogue Objects
Henry may refer to: People *Henry (given name) *Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany ** Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: **Henry I of Castile **Henry II of Castile **Henry III of Castile **Henry IV of Castile * Five kings of France, spelt ''Henri'' in Modern French since the Renaissance to italianize the name and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamsteed Objects
John Flamsteed (19 August 1646 – 31 December 1719) was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, ''Catalogus Britannicus'', and a star atlas called ''Atlas Coelestis'', both published posthumously. He also made the first recorded observations of Uranus, although he mistakenly catalogued it as a star, and he laid the foundation stone for the Royal Greenwich Observatory. Life Flamsteed was born in Denby, Derbyshire, England, the only son of Stephen Flamsteed and his first wife, Mary Spadman. He was educated at the free school of Derby and at Derby School, in St Peter's Churchyard, Derby, near where his father carried on a malting business. At that time, most masters of the school were Puritans. Flamsteed had a solid knowledge of Latin, essential for reading the scientific literature of the day, and a love of history, leaving the school in May 1662.Birks, John L. (1999) ''John Flamsteed, the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durchmusterung Objects
In astronomy, Durchmusterung or Bonner Durchmusterung (BD) is an astrometric star catalogue of the whole sky, compiled by the Bonn Observatory in Germany from 1859 to 1903. The name comes from ('run-through examination'), a German word used for a systematic survey of objects or data. The term has sometimes been used for other astronomical surveys, including not only stars, but also the search for other celestial objects. Special tasks include celestial scanning in electromagnetic wavelengths shorter or longer than visible light waves. Original catalog The 44 years of work on the Bonner Durchmusterung (abbreviated BD), initiated by Friedrich Argelander and largely carried out by his assistants, resulted in a catalogue of the positions and apparent magnitudes of approximately 325,000 stars to apparent magnitude 9–10. The catalogue was accompanied by charts plotting the positions of the stars, and was the basis for the ''Astronomische Gesellschaft Katalog'' (AGK) and ''Smithsonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Objects
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceuticals; consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer and dyer Friedrich Weskott. As was common in this era, the company was established as a dyestuffs producer. The versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand their business into other areas, and in 1899 Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. In 1904 Bayer received a trademark for the "Bayer Cross" logo, which was subsequently stamped onto each aspirin tablet, creating an iconic product that is still sold by Bayer. Other commonly known produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algol Variables
ALGOL (; short for "Algorithmic Language") is a family of imperative computer programming languages originally developed in 1958. ALGOL heavily influenced many other languages and was the standard method for algorithm description used by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in textbooks and academic sources for more than thirty years. In the sense that the syntax of most modern languages is "Algol-like", it was arguably more influential than three other high-level programming languages among which it was roughly contemporary: FORTRAN, Lisp, and COBOL. It was designed to avoid some of the perceived problems with FORTRAN and eventually gave rise to many other programming languages, including PL/I, Simula, BCPL, B, Pascal, and C. ALGOL introduced code blocks and the begin...end pairs for delimiting them. It was also the first language implementing nested function definitions with lexical scope. Moreover, it was the first programming language which gave detailed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-type Main-sequence Stars
A B-type main-sequence star (B V) is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type B and luminosity class V. These stars have from 2 to 16 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 10,000 and 30,000 K. B-type stars are extremely luminous and blue. Their spectra have neutral helium, which are most prominent at the B2 subclass, and moderate hydrogen lines. Examples include Regulus and Algol A. This class of stars was introduced with the Harvard sequence of stellar spectra and published in the ''Revised Harvard photometry'' catalogue. The definition of type B-type stars was the presence of non-ionized helium lines with the absence of singly ionized helium in the blue-violet portion of the spectrum. All of the spectral classes, including the B type, were subdivided with a numerical suffix that indicated the degree to which they approached the next classification. Thus B2 is 1/5 of the way from type B (or B0) to type A. Later, however, more refined s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre De Données Astronomiques De Strasbourg
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Jay County, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin **Center (community), Wisconsin *Center Township (other) *Centre Township (other) *Centre Avenue (other) *Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Centre-Val de Loire, formerly Centre, France * Centre (department), H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion's Sword
Orion's Sword is a compact asterism in the constellation Orion. It comprises three stars (42 Orionis, Theta Orionis, and Iota Orionis) and M42, the Orion Nebula, which together are thought to resemble a sword or its scabbard. This group is south of the prominent asterism, Orion's Belt. Fables and old beliefs are in Europe dominated or widely influenced by those of the Greco-Roman narratives. Beyond Europe this grouping is quite widely referenced as a weapon just as the majority of cultures perceived Orion's standout asymmetrical "hourglass" of seven very bright stars as a human. Components Orion Nebula The Orion Nebula consists of one of the nearest (thus in the Milky Way Galaxy), massive molecular clouds (30 - 40 light years in diameter) about 1,300 light years from the solar system. This makes the nebula potentially the closest HII region to Earth, a mass of hydrogen that has been ionized by nearby, hot, young stars. Regions like this are called stellar nurseries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β Cephei Variable
Beta Cephei variables, also known as Beta Canis Majoris stars, are variable stars that exhibit small rapid variations in their brightness due to pulsations of the stars' surfaces, thought due to the unusual properties of iron at temperatures of 200,000 K in their interiors. These stars are usually hot blue-white stars of spectral class B and should not be confused with Cepheid variables, which are named after Delta Cephei and are luminous supergiant stars. Properties Beta Cephei variables are main-sequence stars of masses between about 7 and 20 M_\odot (that is, 7–20 times as massive as the Sun). Among their number are some of the brightest stars in the sky, such as Beta Crucis and Beta Centauri; Spica is also classified as a Beta Cephei variable but mysteriously stopped pulsating in 1970. Typically, they change in brightness by 0.01 to 0.3 magnitudes with periods of 0.1 to 0.3 days (2.4–7.2 hours). The prototype of these variable stars, Beta Cephei, shows variation in apparen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the line of sight to the observer. The word ''magnitude'' in astronomy, unless stated otherwise, usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale dates back to the ancient Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, whose star catalog listed stars from 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined in a way to closely match this historical system. The scale is reverse logarithmic: the brighter an object is, the lower its magnitude number. A difference of 1.0 in magnitude corresponds to a brightness ratio of \sqrt /math>, or about 2.512. For example, a star of magnitude 2.0 is 2.512 times as bright as a star of magnitude 3.0, 6. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |