Eta Orionis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Eta Orionis, Latinized from η Orionis, is a
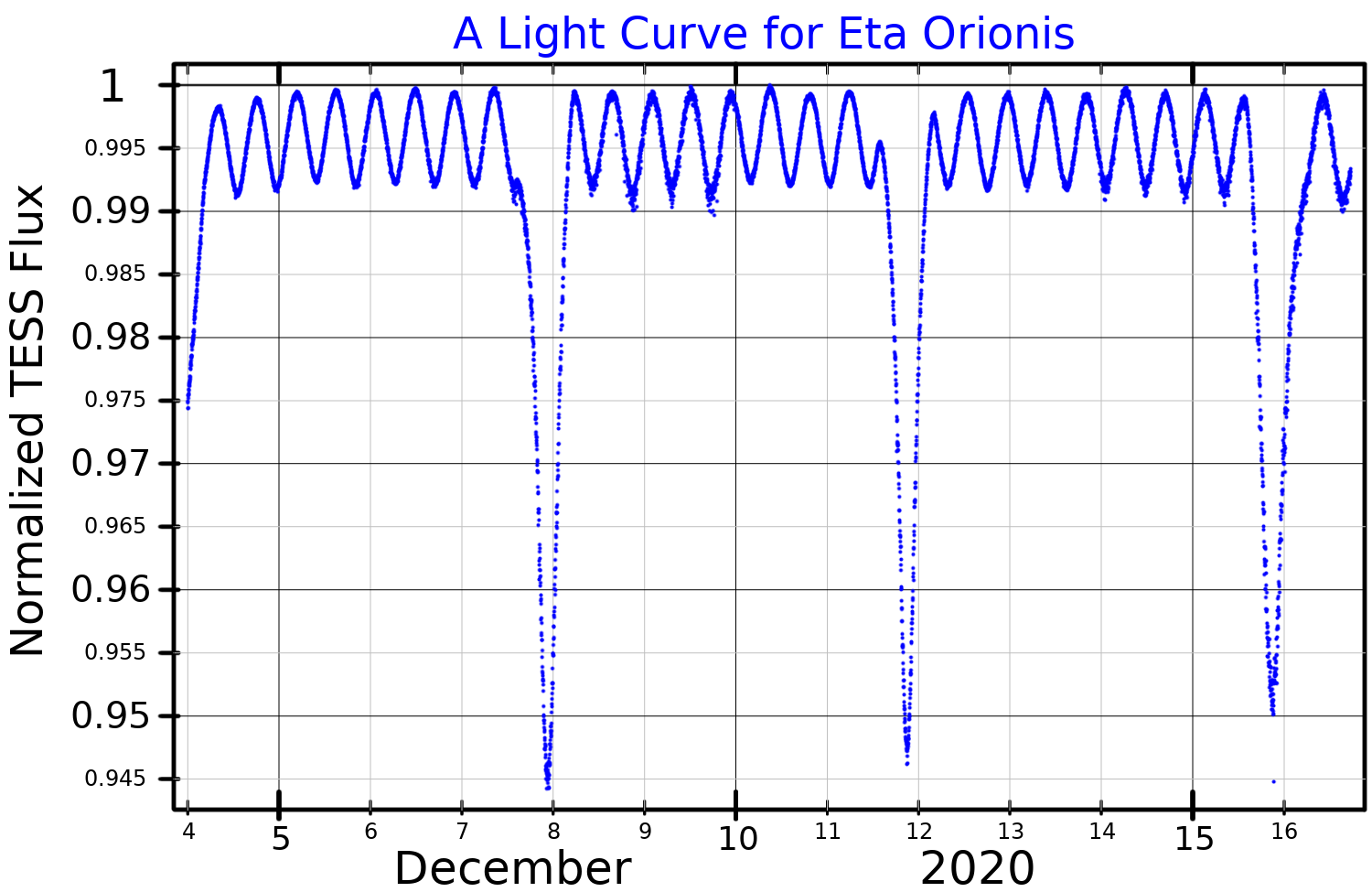 Eta Orionis drops in brightness every four days from a combined
Eta Orionis drops in brightness every four days from a combined
multiple star
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, ...
in the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
Orion. It lies a little to the west of Orion's Belt
Orion's Belt or the Belt of Orion, also known as the Three Kings or Three Sisters, is an asterism in the constellation Orion. It consists of the three bright stars Alnitak
Alnitak is a triple star system in the constellation of ...
between Delta Orionis and Rigel
Rigel is a blue supergiant star in the constellation of Orion. It has the Bayer designation β Orionis, which is Latinized to Beta Orionis and abbreviated Beta Ori or β Ori. Rigel is the brightest and most massive componentand ...
, being closer to Delta Orionis than to Rigel. It lies at a distance of around 1,000 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
and is part of the Orion OB1 association
Orion OB1 (Ori OB1) is a contingent group of several dozen hot giant stars of spectral types O and B in Orion. Associated are thousands of lower-mass stars, and a (smaller but significant) number of protostars. It is part of the larger Orion mo ...
.
System
Eta Orionis is listed in multiple star catalogues as having two companions: a bright component B less than 2″ away; and a faint component C nearly 2′ away. The two are estimated to orbit every 1,800 years. The primary star, Eta Orionis A, is itself aspectroscopic
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wav ...
triple star, known from multiple spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to iden ...
s with varying radial velocities
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the distance or range between the two points. It is equivalent to the vector projection o ...
. The most distant component Ac, has been resolved using speckle interferometry
Speckle imaging describes a range of high-resolution astronomical imaging techniques based on the analysis of large numbers of short exposures that freeze the variation of atmospheric turbulence. They can be divided into the shift-and-add ("'' ...
, at a separation of about 0.04″. It orbits the other two in 9.4 years. The two closest stars, Aa and Ab, are separated by only about a tenth of an astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits t ...
and orbit in just under eight days.
The system lies within the Orion OB1 association, a group of massive stars that includes most of the bright stars of Orion. It is assigned to the oldest and closest part of the association, known as OB1a.
Variability
 Eta Orionis drops in brightness every four days from a combined
Eta Orionis drops in brightness every four days from a combined apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
of 3.31 to about magnitude 3.6. This is due to eclipses between the two closest components, Aa and Ab. The primary and secondary eclipses are very similar, 0.24 and 0.23 magnitudes deep, respectively.
It has also been suggested that component Ab is intrinsically variable with a period of 0.3 days and a very small amplitude. This star has unusual variable spectral lines and lies with the β Cephei variable Beta Cephei variables, also known as Beta Canis Majoris stars, are variable stars that exhibit small rapid variations in their brightness due to pulsations of the stars' surfaces, thought due to the unusual properties of iron at temperatures of 200, ...
instability strip. However, it is now thought that the variable component is either B and Ac, possibly due to an unseen companion or rotational modulation. The actual period is 0.432 days and the 0.3-day period was an alias.
See also
*Orion's Sword Orion's Sword is a compact asterism in the constellation Orion. It comprises three stars (42 Orionis, Theta Orionis, and Iota Orionis) and M42, the Orion Nebula, which together are thought to resemble a sword or its scabbard. This group is so ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Eta Orionis B-type main-sequence stars Algol variables Orion (constellation) Orionis, Eta BD-02 1235 Orionis, 28 035411 0252811788
Events
January–March
* January 1 – The first edition of ''The Times'', previously ''The Daily Universal Register'', is published in London.
* January 2 – Georgia ratifies the United States Constitution, and becomes the fourth U.S ...