|
Esperanto Jubilee Symbol
The Esperanto jubilee symbol ( eo, jubilea simbolo) is a cultural symbol that was created in 1987 to mark the 100th anniversary of Esperanto. Because of its shape, the symbol is sometimes informally called the melon (), egg () or rugby ball (). With a Latin E on one side and a Cyrillic Э (for {{Lang, ru, Эсперанто) on the other, it can be interpreted as being inclusive of East and West. At the time, the Cold War was being waged between the United States and the Soviet Union, and they represented the largest enemies in the world. The desire for a more modern-looking symbol for Esperanto arose when many Esperanto speakers felt that the Esperanto flag appeared too sectarian. Nowadays, many people use the Jubilee Symbol to represent the international Esperanto culture as a whole. For example, the Universal Esperanto Association and Esperanto-USA use it as their symbol. Variations of the symbol involve the addition of a green star, the addition of the text "ESPERAN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jubilea Simbolo
The Esperanto jubilee symbol ( eo, jubilea simbolo) is a cultural symbol that was created in 1987 to mark the 100th anniversary of Esperanto. Because of its shape, the symbol is sometimes informally called the melon (), egg () or rugby ball (). With a Latin E on one side and a Cyrillic Э (for {{Lang, ru, Эсперанто) on the other, it can be interpreted as being inclusive of East and West. At the time, the Cold War was being waged between the United States and the Soviet Union, and they represented the largest enemies in the world. The desire for a more modern-looking symbol for Esperanto arose when many Esperanto speakers felt that the Esperanto flag appeared too sectarian. Nowadays, many people use the Jubilee Symbol to represent the international Esperanto culture as a whole. For example, the Universal Esperanto Association and Esperanto-USA use it as their symbol. Variations of the symbol involve the addition of a green star, the addition of the text "ESPERANT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centennial
{{other uses, Centennial (other), Centenary (other) A centennial, or centenary in British English, is a 100th anniversary or otherwise relates to a century, a period of 100 years. Notable events Notable centennial events at a national or world-level include: * Centennial Exhibition, 1876, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. First official World's Fair in the United States, celebrating the 100th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence in Philadelphia. About 10 million visitors attended, equivalent to about 20% of the population of the United States at the time. The exhibition ran from May 10, 1876, to November 10, 1876. (It included a monorail.) * New Zealand Centennial Exhibition, 1939–1940, celebrated one hundred years since the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi in 1840 and the subsequent mass European settlement of New Zealand. 2,641,043 (2.6 million) visitors attended the exhibition, which ran from 8 November 1939 until 4 May 1940. * 1967 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
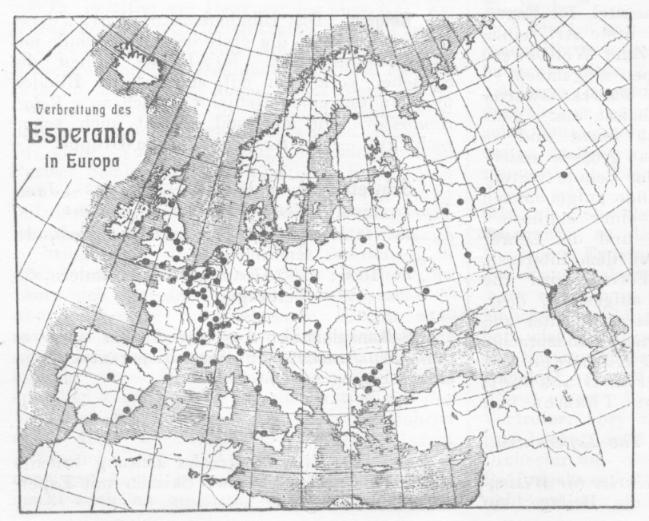
Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, Caucasian languages, Caucasian and Iranian languages, Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin script, Latin and Greek alphabet, Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I of Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race. The Western Bloc was led by the United States as well as a number of other First W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Flag
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Culture
Esperanto culture refers to the shared cultural experience of the Esperantujo, or Esperanto-speaking community. Despite being a constructed language, Esperanto has a history dating back to the late 19th century, and shared socio-cultural norms have developed among its speakers. Some of these can be traced back to the initial ideas of the language's creator, L. L. Zamenhof, Ludwig Zamenhof, including the theory that a global second language would foster international communication. Others have developed over time, as the language has allowed different national and linguistic cultures to blend together. Some Esperanto speakers have also researched the language's ideologies. Esperanto culture also includes art, literature, and music, as well as international celebrations and cultural exchanges such as the Pasporta Servo. Native speakers Native Esperanto speakers are people who have acquired Esperanto as one of their native languages. As of 1996, there were 350 or so attested cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Esperanto Association
The Universal Esperanto Association ( eo, Universala Esperanto-Asocio, UEA), also known as the World Esperanto Association, is the largest international organization of Esperanto speakers, with 5501 individual members in 121 countries and 9215 through national associations (in 2015) and in official relations with the United Nations. In addition to individual members, 70 national Esperanto organizations are affiliated with UEA. Its current president is the professor Duncan Charters. The magazine ''Esperanto'' is the main organ used by UEA to inform its members about everything happening in the Esperanto community. The UEA was founded in 1908 by the Swiss journalist Hector Hodler and others and is now headquartered in Rotterdam, Netherlands. The organization has an office at the United Nations building in New York City. Structure and affiliated organizations According to its 1980 statutes (Statuto de UEA), the Universal Esperanto Association has two kinds of members: * individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto-USA
Esperanto-USA (E-USA) is the largest organization for speakers and supporters of Esperanto in the United States. It was founded in 1952 as the Esperanto League for North America (ELNA) in Sacramento, California. Headquartered in Portland, Maine, Esperanto-USA is a 501(c)3 nonprofit organization and the U.S. affiliate of the Universal Esperanto Association. Phil Dorcas is President of E-USA, and Alexander Vaughn Miller is Vice-President. The organization administers the largest Esperanto-language book service in the Americas. It publishes a bimonthly bulletin '' Usona Esperantisto''. It also publishes reference works about Esperanto. The organization's leadership consists of a president, vice-president, secretary, treasurer, and nine directors; it also has many commissioners responsible for Esperanto-USA's activity in various connections (e.g. audio-visual service; cooperation with libraries; relations with local Esperanto clubs; etc.) Membership is about 650. The youth section ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Association Of Britain
The Esperanto Association of Britain (EAB) is a registered educational charity whose objective is to advance education in and about the international language Esperanto and to preserve and promote the culture and heritage of Esperanto for the educational benefit of the general public. The organisation was established in 1904. Among its activities it publishes, provides and distributes information about the language and organises educational courses, lectures and conferences. It also provides a comprehensive bookshop with material from around the world. Publications In January 1905, the British Esperanto Association launched its official organ, ''The British Esperantist.'' as a monthly publication. The publication was retitled as '' La Brita Esperantisto'' (and for a short while ''LBE'' for 2010 to 2014). The frequency of the publication varied. Initially it was a monthly and later on starting World War II as once every two months. It turned into a quarterly in 1991, then semi-annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Symbols
Esperanto symbols, primarily the Esperanto flag, have seen much consistency over the time of the language's existence (namely in the consistent usage of the colour green), though a few variations in exact flag patterning and symbology exist. The main flag of Esperanto, featuring the ('Green Star'), was adopted in 1905 for use as a symbol of mutual recognition among Esperantists, and is used by most Esperantists. As an alternative to the flag, the '' jubilea simbolo'' ('jubilee symbol') has been more recently proposed (in 1987). History ''Verda Stelo'' Since the earliest days of Esperanto, the colour green has been used as a symbol of mutual recognition, and it appears prominently in all Esperanto symbols. In a letter to ''The British Esperantist'' in 1911, L. L. Zamenhof, the creator of Esperanto, wrote: "It seems to me, that my attention was drawn to the color green by Mr. Richard H. Geoghegan and from that time I began to publish all of my works with green covers . . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)

