|
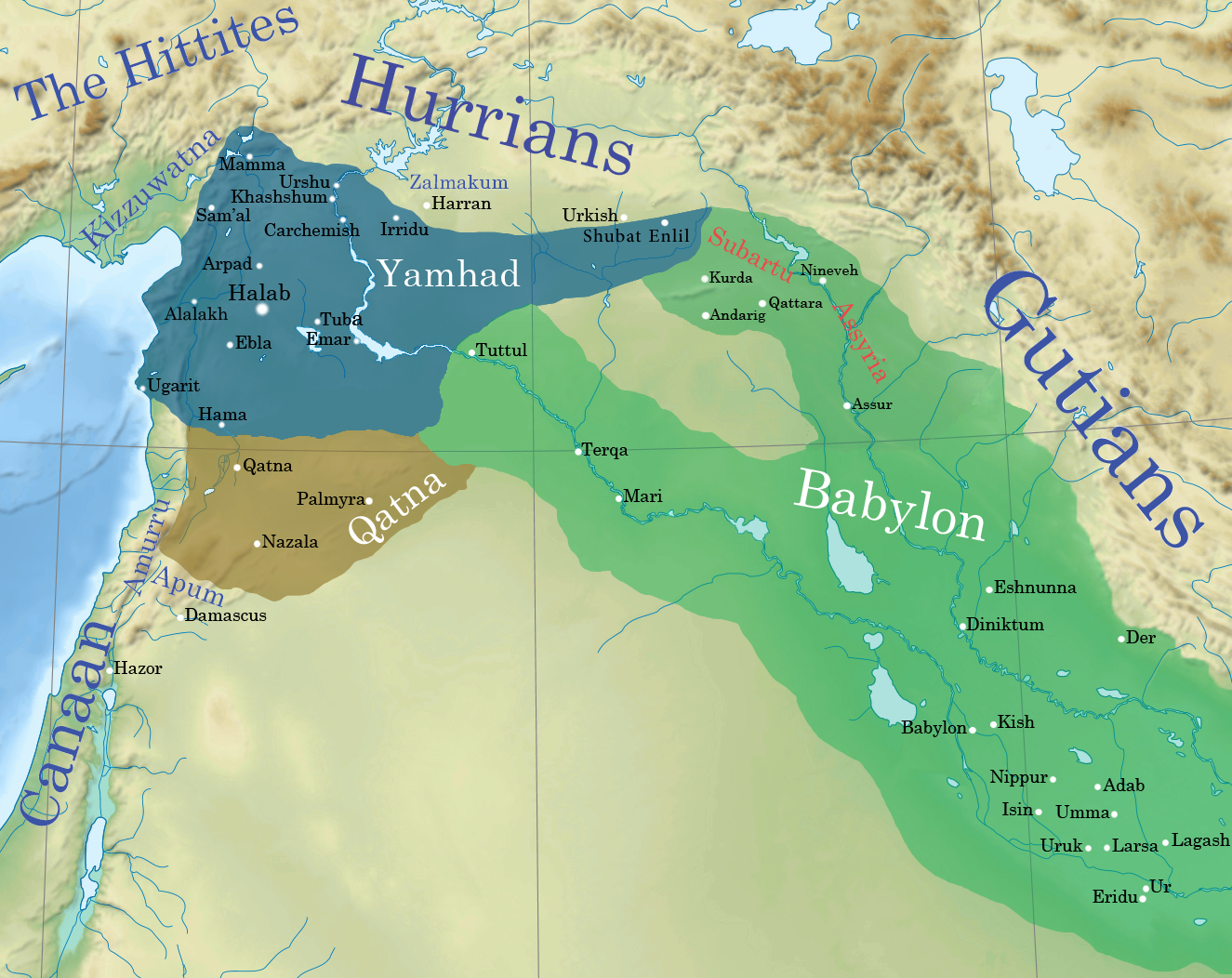
Esnunna
Eshnunna (modern Tell Asmar in Diyala Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian (and later Akkadian Empire, Akkadian) city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Although situated in the Diyala River, Diyala Valley north-west of Sumer proper, the city nonetheless belonged securely within the Sumerian cultural milieu. It is sometimes, in archaeological papers, called Ashnunnak or Tuplias,. The tutelary deity of the city was Tishpak (Tišpak) (having replaced Ninazu) though other gods, including Sin (mythology), Sin, Adad, and Inanna of Kititum were also worshiped there. The personal goddess of the rulers were Belet-Šuḫnir and Belet-Terraban. History Early Bronze Inhabited since the Jemdet Nasr period, around 3000 BC, Eshnunna was a major city during the Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia), Early Dynastic period of Mesopotamia. It is known, from cuneiform records and excavations, that the city was oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishbi-Erra
Ishbi-Erra (Akkadian: d''iš-bi-ir₃-ra'') was the founder of the dynasty of Isin, reigning from ''c.'' 2017 — ''c.'' 1986 BC on the middle chronology or 1953 BC — ''c.'' 1920 BC on the short chronology. Ishbi-Erra was preceded by Ibbi-Sin of the third dynasty of Ur in ancient Lower Mesopotamia, and then succeeded by Šu-ilišu. According to the Weld-Blundell Prism,WB 444, the Weld-Blundell prism, r. 33. Išbi-erra reigned for 33 years and this is corroborated by the number of his extant year-names. While in many ways this dynasty emulated that of the preceding one, its language was Akkadian as the Sumerian language had become moribund in the latter stages of the third dynasty of Ur. Biography At the outset of his career, Ishbi-Erra was an official working for Sumerian King Ibbi-Sin, the last king of the third dynasty of Ur. Ishbi-Erra was described as a man of Mari,Tablet UM 7772. either his origin or the city for which he was assigned. His progress is recorded in lette ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copal
Copal is tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree ''Protium copal'' (Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includes resinous substances in an intermediate stage of polymerization and hardening between "gummier" resins and amber. Copal that is partly mineralized is known as copaline. It is available in different forms; the hard, amber-like yellow copal is a less expensive version, while the milky white copal is more expensive. Etymology The word "copal" is derived from the Nahuatl language word , meaning "incense". History and uses Subfossil copal is well known from New Zealand (kauri gum from ''Agathis australis'' (Araucariaceae)), Japan, the Dominican Republic, Colombia, and Madagascar. It often has inclusions and is sometimes sold as "young amber". When it is treated or enhanced in an autoclave (as is sometimes done to industrialized Baltic amber) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, jet, and pearl) are also used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some soft minerals are used in jewelry because of their luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. Rarity and notoriety are other characteristics that lend value to gemstones. Apart from jewelry, from earliest antiquity engraved gems and hardstone carvings, such as cups, were major luxury art forms. A gem expert is a gemologist, a gem maker is called a lapidarist or gemcutter; a diamond cutter is called a diamantaire. Characteristics and classification The traditional classification in the West, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elam
Elam (; Linear Elamite: ''hatamti''; Cuneiform Elamite: ; Sumerian: ; Akkadian: ; he, עֵילָם ''ʿēlām''; peo, 𐎢𐎺𐎩 ''hūja'') was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of modern-day Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems from the Sumerian transliteration ''elam(a)'', along with the later Akkadian ''elamtu'', and the Elamite ''haltamti.'' Elamite states were among the leading political forces of the Ancient Near East. In classical literature, Elam was also known as Susiana ( ; grc, Σουσιανή ''Sousiānḗ''), a name derived from its capital Susa. Elam was part of the early urbanization of the Near East during the Chalcolithic period (Copper Age). The emergence of written records from around 3000 BC also parallels Sumerian history, where slightly earlier records have been found. In the Old Elamite period ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shutruk-Nakhunte
Šutruk-Nakhunte was king of Elam from about 1184 to 1155 BC (middle chronology), and the second king of the Shutrukid Dynasty. Elam amassed an empire that included most of Mesopotamia and western Iran. Under his command, Elam defeated the Kassites and established the short-lived Elamite Empire, conquered within about 40 years by Nebuchadnezzar I of Babylon, in 1120 BC. Šutruk-Nakhunte was married to the daughter of a Kassite king named Meli-Šipak. Inscription on the Naram-Sin victory stele Shutruk-Nahhunte is known by an inscription that he added to the Victory Stele of Naram-Sin, itself dated about one millennium earlier to circa 2250 BC. His inscription appears on the top right corner of the stele, on the depiction of a mountainous cone, and was written in Elamite by Shutruk-Nahhunte himself: In popular culture Shutruk-Nakhunte gained a small public exposition in Ethan Canin's short story "The Palace Thief", and its adaptation in the 2002 film ''The Emperor's C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammurabi
Hammurabi (Akkadian: ; ) was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from to BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered Elam and the city-states of Larsa, Eshnunna, and Mari. He ousted Ishme-Dagan I, the king of Assyria, and forced his son Mut-Ashkur to pay tribute, bringing almost all of Mesopotamia under Babylonian rule. Hammurabi is best known for having issued the Code of Hammurabi, which he claimed to have received from Shamash, the Babylonian god of justice. Unlike earlier Sumerian law codes, such as the Code of Ur-Nammu, which had focused on compensating the victim of the crime, the Law of Hammurabi was one of the first law codes to place greater emphasis on the physical punishment of the perpetrator. It prescribed specific penalties for each crime and is among the first codes to establish the presumption of innocence. Although its penalties are extremely harsh by modern s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siwe-Palar-Khuppak
Siwe-Palar-Khuppak was the ''Sukkalmah'' (ruler) of Elam from around 1778 to 1745 B.C.E. Around 1767 B.C.E, Siwe-Palar-Khuppak formed a coalition with Zimri-Lim of Mari and Hammurabi of Babylon. He led this coalition against Eshnunna, conquering it and imposed direct rule from his ''sukkal'' Kudu-zulush in Susa. This coalition turned against him as he attempted to expand his power into Babylon. Hammurabi, allied with Zimri-Lim, expelled the Elamite's forces from Eshnunna One of his generals was Kunnam of Elam Kunnam also often called Kunnam of Elam was a military expedition leader of the kingdom of Elam in the 18th century BC. He was part of a military campaign into Mesopotamia and is mainly known from cuneiform letters found at Mari, a Syrian city st ... who appears in many letters found at Mari. In a clay tablet, Siwe-Palar-Khuppak refers to himself as "Governor of Elam" and "Enlarger of the Empire". It is speculated that the tablet was made after Siwe-Palar-Khuppak's defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zimri-Lim
__NOTOC__ Zimri-Lim (Akkadian: ''Zi-im-ri Li-im'') was king of Mari c. 1775–1761 BCE. Zimri-Lim was the son or grandson of Iakhdunlim, but was forced to flee to Yamhad when his father was assassinated by his own servants during a coup. He had a tenuous relationship with Andarig, with whom he battled and allied with occasionally. The city was occupied by Shamshi-Adad I, the king of Ekallatum, who put his own son Yasmah-Adad on the throne. Shortly after the death of Shamshi-Adad I, Zimri-Lim returned from exile and was able to oust Yasmah-Adad from power with the help of Yarimlim, the king of Yamhad. There is an Akkadian literary text, written in the early years of his reign, entitled The Epic of Zimri-Lim. Zimri-Lim ruled Mari for about thirteen years, and campaigned extensively to establish his power in the neighboring areas along the Euphrates and the Khabur valley. He extended his palace in the city, which was possibly the largest at the time, containing over 260 rooms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamshi-Adad I
Shamshi-Adad ( akk, Šamši-Adad; Amorite: ''Shamshi-Addu''), ruled 1808–1776 BC, was an Amorite warlord and conqueror who had conquered lands across much of Syria, Anatolia, and Upper Mesopotamia.Some of the Mari letters addressed to Shamsi-Adad by his son can be found in the Mari Letters section of Rise Shamshi-Adad I inherited the throne in Ekallatum from Ila-kabkabu (fl. c. 1836 BC – c. 1833 BC). Ila-kabkabu is mentioned as the father of Shamshi-Adad I in the "Assyrian King List" (AKL); a similar name (not necessarily the same figure) is listed in the preceding section of the AKL among the “kings whose fathers are known”. However, Shamshi-Adad I did not inherit the Assyrian throne from his father but was instead a conqueror. Ila-kabkabu had been an Amorite king not of Assur (Aššur) (in Assyria) but of Ekallatum. According to the '' Mari Eponyms Chronicle'', Ila-kabkabu seized Shuprum (c. 1790 BC), then Shamshi-Adad I “entered his father's house” (Shamshi-Adad I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia Male Worshiper 2750-2600 B
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran, Syria and Turkey. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrian people, Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of recorded history, written history () to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (). Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naram-Suen Of Eshnunna
Naram-Suen (also transcribed Narām-Sîn, Naram-Sin) was a king who ruled over Eshnunna for at least nine years during the later 19th century BCE, during its brief time of political power. He is known to be the son of Ipiq-Adad II, king of Eshnunna, and a contemporary of Shamshi-Adad I, king of the Kingdom of Upper Mesopotamia. An inscription praying for the king's peace was found in Kythira. References See also *Naram-Sin of Akkad *Naram-Sin of Assyria Naram-Sin, or Narām-Sîn or –Suen, inscribed in cuneiform on contemporary seal impressions as d''na-ra-am-''dEN.ZU, had been the "waklum" (ugula, Overseer) or "'' Išši’ak Aššur''" (énsi d''a-šùr'', Steward of Ashur) of the city-state ... Kings of Eshnunna {{AncientNearEast-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |