|
Ernst Friedrich
Ernst Friedrich (25 February 1894 – 2 May 1967) was a German anarcho-pacifist. Life Childhood and youth Ernst Friedrich was born in Breslau (now Wrocław, Poland) as the 13th child of a cleaning lady and a saddler. After finishing elementary school, he started an apprenticeship as a bookprinter in 1908. Soon after, he quit the apprenticeship and started studying acting. He earned money by working in a factory. He was one of the founders of the Breslau Association for Youth Workers. In 1911, he became a member of the Social Democratic Party of Germany. From 1912 until 1914 he travelled in Denmark, Sweden, Norway and Switzerland. In 1914, he made his acting debut in his hometown and had a performance at the royal theater in Potsdam. World War I He was drafted in World War I and decided to become a conscientious objector A conscientious objector (often shortened to conchie) is an "individual who has claimed the right to refuse to perform military service" on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Friedrich
Ernst Friedrich (25 February 1894 – 2 May 1967) was a German anarcho-pacifist. Life Childhood and youth Ernst Friedrich was born in Breslau (now Wrocław, Poland) as the 13th child of a cleaning lady and a saddler. After finishing elementary school, he started an apprenticeship as a bookprinter in 1908. Soon after, he quit the apprenticeship and started studying acting. He earned money by working in a factory. He was one of the founders of the Breslau Association for Youth Workers. In 1911, he became a member of the Social Democratic Party of Germany. From 1912 until 1914 he travelled in Denmark, Sweden, Norway and Switzerland. In 1914, he made his acting debut in his hometown and had a performance at the royal theater in Potsdam. World War I He was drafted in World War I and decided to become a conscientious objector A conscientious objector (often shortened to conchie) is an "individual who has claimed the right to refuse to perform military service" on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
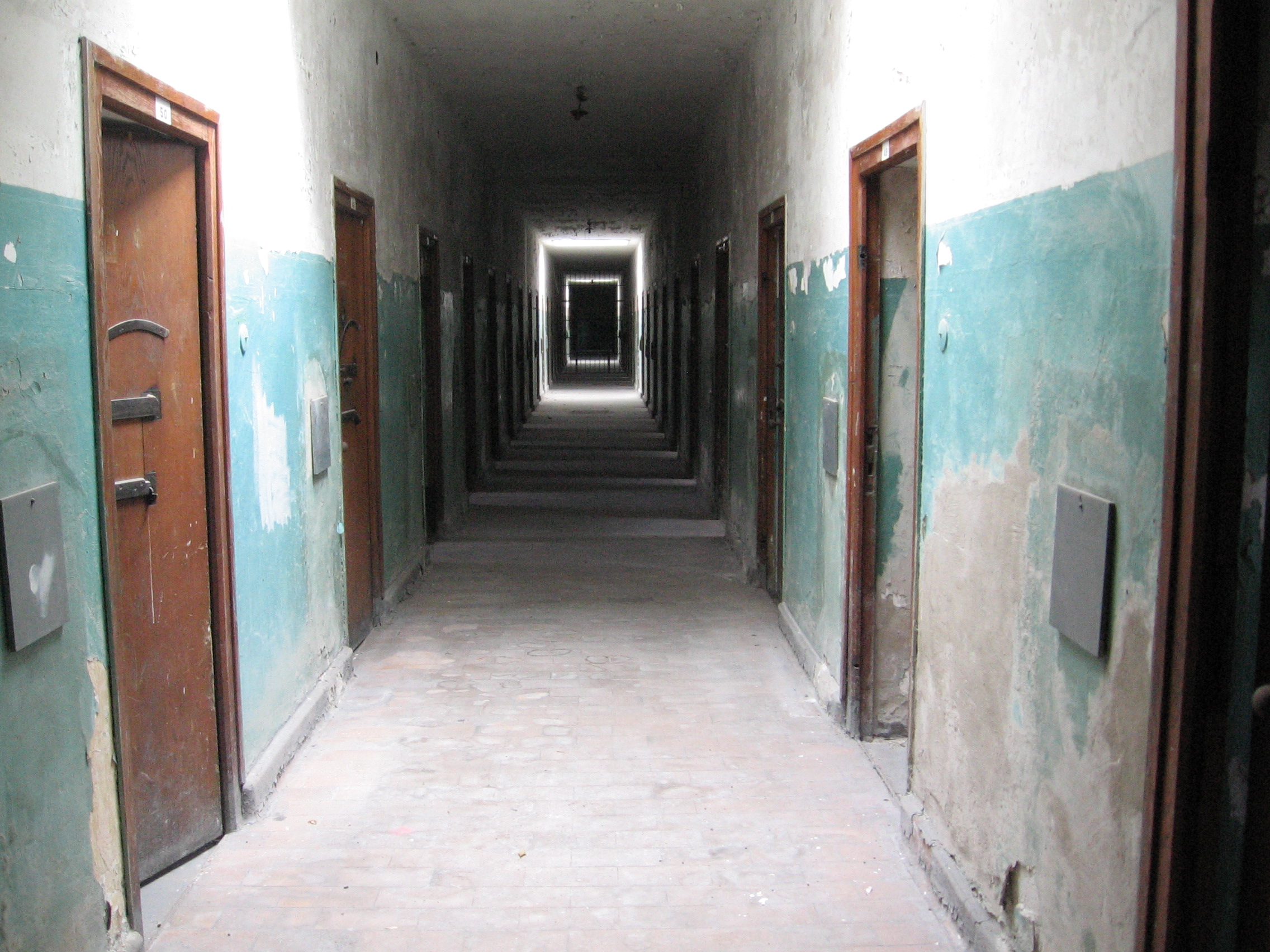
Saint-Cyprien, Pyrénées-Orientales
Saint-Cyprien (; ca, Sant Cebrià de Rosselló) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France. Geography History In the 20th century Saint-Cyprien was the site of a camp housing some 70,000 Republican escapees from Spain at the end of the Spanish Civil War. They were held in very poor conditions, in open spaces enclosed by barbed wire, from which they were not allowed to leave. During the Second World War it was used to intern people before they were sent to extermination camps. Letter from my uncle Government and politics Mayors Population and society Population Sports The main spectator sport in the town is Rugby league, while surfing, snorkeling and boat racing are also popular. See also *Communes of the Pyrénées-Orientales department The Pyrénées-Orientales department is composed of 226 communes. Most of the territory (except for the district of Fenolheda) formed part of the Principality of Catalonia until 1659 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the Fascism, fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its Metropolitan France, territory occupied under harsh terms of the Armistice of 22 June 1940, armistice, it adopted a policy of collaboration with Nazi Germany, which Occupation of France by Nazi Germany, occupied the northern and western portions before occupying the remainder of Metropolitan France in November 1942. Though Paris was ostensibly its capital, the collaborationist Vichy government established itself in the resort town of Vichy in the unoccupied "Free Zone" (), where it remained responsible for the civil administration of France as well as its French colonial empire, colonies. The Third French Republic had begun the war in September 1939 on the side of the Allies of World War II, Allies. On 10 May 1940, it was Invasion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest), is a region of Belgium comprising 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country and is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, but is separate from the Flemish Region (within which it forms an enclave) and the Walloon Region. Brussels is the most densely populated region in Belgium, and although it has the highest GDP per capita, it has the lowest available income per household. The Brussels Region covers , a relatively small area compared to the two other regions, and has a population of over 1.2 million. The five times larger metropolitan area of Brussel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's ability to experience the light within or see "that of God in every one". Some profess a priesthood of all believers inspired by the First Epistle of Peter. They include those with evangelical, holiness, liberal, and traditional Quaker understandings of Christianity. There are also Nontheist Quakers, whose spiritual practice does not rely on the existence of God. To differing extents, the Friends avoid creeds and hierarchical structures. In 2017, there were an estimated 377,557 adult Quakers, 49% of them in Africa. Some 89% of Quakers worldwide belong to ''evangelical'' and ''programmed'' branches that hold services with singing and a prepared Bible message coordinated by a pastor. Some 11% practice ''waiting worship'' or ''unprogramme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichstag Fire
The Reichstag fire (german: Reichstagsbrand, ) was an arson attack on the Reichstag building, home of the German parliament in Berlin, on Monday 27 February 1933, precisely four weeks after Nazi leader Adolf Hitler was sworn in as Chancellor of Germany. Marinus van der Lubbe, a Dutch "council communist", was the apparent culprit; however, Hitler attributed the fire to Communist agitators. He used it as a pretext to claim that Communists were plotting against the German government, and induced President Paul von Hindenburg to issue the Reichstag Fire Decree suspending civil liberties, and pursue a "ruthless confrontation" with the Communists. This made the fire pivotal in the establishment of Nazi Germany. The first report of the fire came shortly after 9:00p.m., when a Berlin fire station received an alarm call. By the time police and firefighters arrived, the Chamber of Deputies (the lower house) was engulfed in flames. The police conducted a thorough search inside the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sturmabteilung
The (; SA; literally "Storm Detachment (military), Detachment") was the original paramilitary wing of the Nazi Party. It played a significant role in Adolf Hitler's rise to power in the 1920s and 1930s. Its primary purposes were providing protection for Nazi rallies and assemblies, disrupting the meetings of opposing parties, fighting against the paramilitary units of the opposing parties, especially the ''Roter Frontkämpferbund'' of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and the ''Reichsbanner Schwarz-Rot-Gold'' of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), and intimidating Romani people, Romani, trade unionists, and especially Jews. The SA were colloquially called Brownshirts () because of the colour of their Uniforms and insignia of the Sturmabteilung, uniform's shirts, similar to Benito Mussolini's blackshirts. The official uniform of the SA was the brown shirt with a brown tie. The color came about because a large shipment of Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck, Lettow-shirts, ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Seizure Of Power
Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the '' Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' (DAP; German Workers' Party). He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Being one of its best speakers, he was made the party leader after he threatened to otherwise leave. In 1920, the DAP renamed itself to the ''Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' – NSDAP (National Socialist German Workers' Party, commonly known as the Nazi Party). Hitler chose this name to win over German workers. Despite the NSDAP being a right-wing party, it had many anti-capitalist and anti-bourgeois elements. Hitler later initiated a purge of these elements and reaffirmed the Nazi Party's pro-business stance. By 1922 Hitler's control over the party was unchallenged. In 1923, Hitler and his supporters attempted a coup to remove the government via force. This seminal event was later called the Beer Hall Putsch. Upon its fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Litten
Hans Achim Litten (19 June 1903 – 5 February 1938) was a German lawyer who represented opponents of the Nazis at important political trials between 1929 and 1932, defending the rights of workers during the Weimar Republic. During one trial in 1931, Litten subpoenaed Adolf Hitler to appear as a witness, and cross-examined him for three hours. Hitler was so rattled by the experience that, years later, he would not allow Litten's name to be mentioned in his presence. In retaliation, Litten was arrested on the night of the Reichstag fire along with other progressive lawyers and leftists. Litten spent the rest of his life in one German concentration camp or another, enduring torture and many interrogations. After five years and a move to Dachau, where his treatment worsened and he was cut off from all outside communication, he committed suicide. A number of memorials to him exist in Germany, but Litten was largely ignored for decades because his politics did not fit comfortably in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Mühsam
Erich Mühsam (6 April 1878 – 10 July 1934) was a German-Jewish antimilitarist anarchist essayist, poet and playwright. He emerged at the end of World War I as one of the leading agitators for a federated Bavarian Soviet Republic, for which he served 5 years in prison. Also a cabaret performer, he achieved international prominence during the years of the Weimar Republic for works which, before Adolf Hitler came to power in 1933, condemned Nazism and satirized the future dictator. Mühsam was tortured and murdered in the Oranienburg concentration camp in 1934. Biography Early life: 1878–1900 The third child born to Siegfried Seligmann Mühsam, a middle-class Jewish pharmacist, Erich Mühsam was born in Berlin on 6 April 1878. Soon after, the family moved to the city of Lübeck. Mühsam was educated at the Katharineum- Gymnasium in Lübeck, a school known for its authoritarian discipline and corporal punishment, which served as the model for several of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Jacoby
Henry Sylvester Jacoby (born 1857, died 1955) was an American educator, born at Springtown, Bucks County, Pennsylvania, He was graduated from Lehigh University in 1877 and during the season of 1878 was connected with the topographical corps of the Pennsylvania Geological Survey. During 1879–85, he was chief draftsman in the United States Engineer's Office in Memphis, Tenn. In 1886, he returned to Lehigh, where until 1890 he was instructor of civil engineering; he then accepted a call to Cornell University, where in 1897 he became professor of bridge engineering. Professor Jacoby was a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and in 1901 presided over the Section on Engineering, with the rank of vice-president, and was president of the Society for the Promotion of Engineering Education in 1915–16. Besides numerous papers on his specialty of bridge engineering, he was the author of: * ''Notes and Problems in Descriptive Geometry'' (1892) * ''Outlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_1982%2C_MiNr_Block_068.jpg)



