|
Equating
Test equating traditionally refers to the statistical process of determining comparable scores on different forms of an exam.Kolen, M.J., & Brennan, R.L. (1995). Test Equating. New York: Spring. It can be accomplished using either classical test theory or item response theory. In item response theory, ''equating'' is the process of placing scores from two or more parallel test forms onto a common score scale. The result is that scores from two different test forms can be compared directly, or treated as though they came from the same test form. When the tests are not parallel, the general process is called linking. It is the process of equating the units and origins of two scales on which the abilities of students have been estimated from results on different tests. The process is analogous to equating degrees Fahrenheit with degrees Celsius by converting measurements from one scale to the other. The determination of comparable scores is a by-product of equating that results from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchor Test
In psychometrics, an anchor test is a common set of test items administered in combination with two or more alternative forms of the test with the aim of establishing the equivalence of the test scores on the alternative forms. The purpose of the anchor test is to provide a baseline for an equating Test equating traditionally refers to the statistical process of determining comparable scores on different forms of an exam.Kolen, M.J., & Brennan, R.L. (1995). Test Equating. New York: Spring. It can be accomplished using either classical test ... analysis between different forms of a test.Kolen, M.J., & Brennan, R.L. (1995). Test Equating. New York: Spring. Anchor test is one type of psychological assessment tool to measure an individual's knowledge or cognitive ability by testing the same areas in different ways. In psychometrics, to develop assessment tools that are reliable for testing certain skills and abilities are what most Psychometricists are interested in. Anchor tests a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grading On A Curve
A norm-referenced test (NRT) is a type of Test (student assessment), test, Educational assessment, assessment, or evaluation which yields an estimate of the position of the tested individual in a predefined population, with respect to the trait being measured. Assigning scores on such tests may be described as relative grading, marking on a curve (British English, BrE) or grading on a curve (American English, AmE, Canadian English, CanE) (also referred to as curved grading, bell curving, or using grading curves). It is a method of assigning grades to the students in a class in such a way as to obtain or approach a pre-specified distribution (probability), distribution of these grades having a specific mean and derivation properties, such as a normal distribution (also called Gaussian distribution). The term "curve" refers to the Normal distribution, bell curve, the graphical representation of the probability density of the normal distribution, but this method can be used to achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exam
An examination (exam or evaluation) or test is an educational assessment intended to measure a test-taker's knowledge, skill, aptitude, physical fitness, or classification in many other topics (e.g., beliefs). A test may be administered verbally, on paper, on a computer-adaptive testing, computer, or in a predetermined area that requires a test taker to demonstrate or perform a set of skills. Tests vary in style, rigor and requirements. There is no general consensus or invariable standard for test formats and difficulty. Often, the format and difficulty of the test is dependent upon the educational philosophy of the instructor, subject matter, class size, policy of the educational institution, and requirements of accreditation or governing bodies. A test may be administered formally or informally. An example of an informal test is a reading test administered by a parent to a child. A formal test might be a final examination administered by a teacher in a classroom or an IQ te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Test Theory
Classical test theory (CTT) is a body of related psychometric theory that predicts outcomes of psychological testing such as the difficulty of items or the ability of test-takers. It is a theory of testing based on the idea that a person's observed or obtained score on a test is the sum of a true score (error-free score) and an error score. Generally speaking, the aim of classical test theory is to understand and improve the reliability of psychological tests. ''Classical test theory'' may be regarded as roughly synonymous with ''true score theory''. The term "classical" refers not only to the chronology of these models but also contrasts with the more recent psychometric theories, generally referred to collectively as item response theory, which sometimes bear the appellation "modern" as in "modern latent trait theory". Classical test theory as we know it today was codified by Novick (1966) and described in classic texts such as Lord & Novick (1968) and Allen & Yen (1979/2002). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
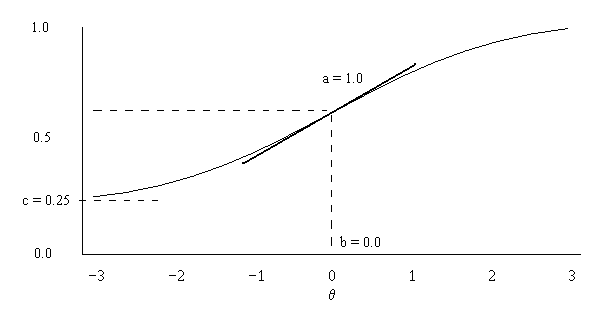
Item Response Theory
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT) (also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring abilities, attitudes, or other variables. It is a theory of testing based on the relationship between individuals' performances on a test item and the test takers' levels of performance on an overall measure of the ability that item was designed to measure. Several different statistical models are used to represent both item and test taker characteristics. Unlike simpler alternatives for creating scales and evaluating questionnaire responses, it does not assume that each item is equally difficult. This distinguishes IRT from, for instance, Likert scaling, in which ''"''All items are assumed to be replications of each other or in other words items are considered to be parallel instruments".A. van Alphen, R. Halfens, A. Hasman and T. Imbos. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-stakes Testing
A high-stakes test is a test with important consequences for the test taker. Passing has important benefits, such as a high school diploma, a scholarship, or a license to practice a profession. Failing has important disadvantages, such as being forced to take remedial classes until the test can be passed, not being allowed to drive a car, or difficulty finding employment. The use and misuse of high-stakes tests are a controversial topic in public education, especially in the United States and U.K., where they have become especially popular in recent years, used not only to assess school-age students but in attempts to increase teacher accountability. Definitions In common usage, a high-stakes test is any test that has major consequences or is the basis of a major decision. Under a more precise definition, a high-stakes test is any test that: * is a single, defined assessment, * has a clear line drawn between those who pass and those who fail, and * has direct consequences for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval Scale
Level of measurement or scale of measure is a classification that describes the nature of information within the values assigned to variables. Psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens developed the best-known classification with four levels, or scales, of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. This framework of distinguishing levels of measurement originated in psychology and is widely criticized by scholars in other disciplines. Other classifications include those by Mosteller and Tukey, and by Chrisman. Stevens's typology Overview Stevens proposed his typology in a 1946 ''Science'' article titled "On the theory of scales of measurement". In that article, Stevens claimed that all measurement in science was conducted using four different types of scales that he called "nominal", "ordinal", "interval", and "ratio", unifying both " qualitative" (which are described by his "nominal" type) and "quantitative" (to a different degree, all the rest of his scales). The conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Distribution
In statistics, the frequency (or absolute frequency) of an event i is the number n_i of times the observation has occurred/recorded in an experiment or study. These frequencies are often depicted graphically or in tabular form. Types The cumulative frequency is the total of the absolute frequencies of all events at or below a certain point in an ordered list of events. The (or empirical probability) of an event is the absolute frequency normalized by the total number of events: : f_i = \frac = \frac. The values of f_i for all events i can be plotted to produce a frequency distribution. In the case when n_i = 0 for certain i, pseudocounts can be added. Depicting frequency distributions A frequency distribution shows us a summarized grouping of data divided into mutually exclusive classes and the number of occurrences in a class. It is a way of showing unorganized data notably to show results of an election, income of people for a certain region, sales of a product within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude and sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the ''arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is the ''sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the mean, or expected value, of the underlying distribution, the ''population mean'' (denoted \mu or \mu_x).Underhill, L.G.; Bradfield d. (1998) ''Introstat'', Juta and Company Ltd.p. 181/ref> Outside probability and statistics, a wide range of other notions of mean are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter '' s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation of a popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
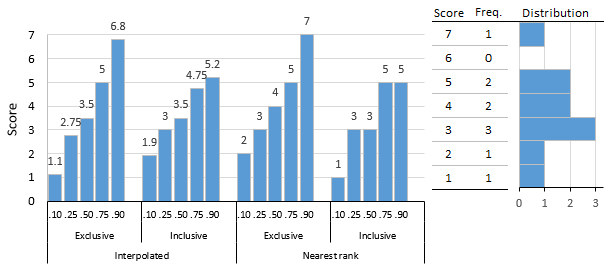
Percentile
In statistics, a ''k''-th percentile (percentile score or centile) is a score ''below which'' a given percentage ''k'' of scores in its frequency distribution falls (exclusive definition) or a score ''at or below which'' a given percentage falls (inclusive definition). For example, the 50th percentile (the median) is the score below which 50% of the scores in the distribution are found (by the "exclusive" definition), or at or below which 50% of the scores are found (by the "inclusive" definition). Percentiles are expressed in the same unit of measurement as the input scores; for example, if the scores refer to human weight, the corresponding percentiles will be expressed in kilograms or pounds. The percentile score and the '' percentile rank'' are related terms. The percentile rank of a score is the percentage of scores in its distribution that are less than it, an exclusive definition, and one that can be expressed with a single, simple formula. Percentile scores and perce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |