|
Epiglottic Cartilage
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food into the lungs, forcing the swallowed liquids or food to go along the oesophagus toward the stomach instead. It is thus the valve that diverts passage to either the trachea or the oesophagus. The epiglottis is made of elastic cartilage covered with a mucous membrane, attached to the entrance of the larynx. It projects upwards and backwards behind the tongue and the hyoid bone. The epiglottis may be inflamed in a condition called epiglottitis, which is most commonly due to the vaccine-preventable bacteria ''Haemophilus influenzae''. Dysfunction may cause the inhalation of food, called aspiration, which may lead to pneumonia or airway obstruction. The epiglottis is also an important landmark for intubation. The epiglottis has been identifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
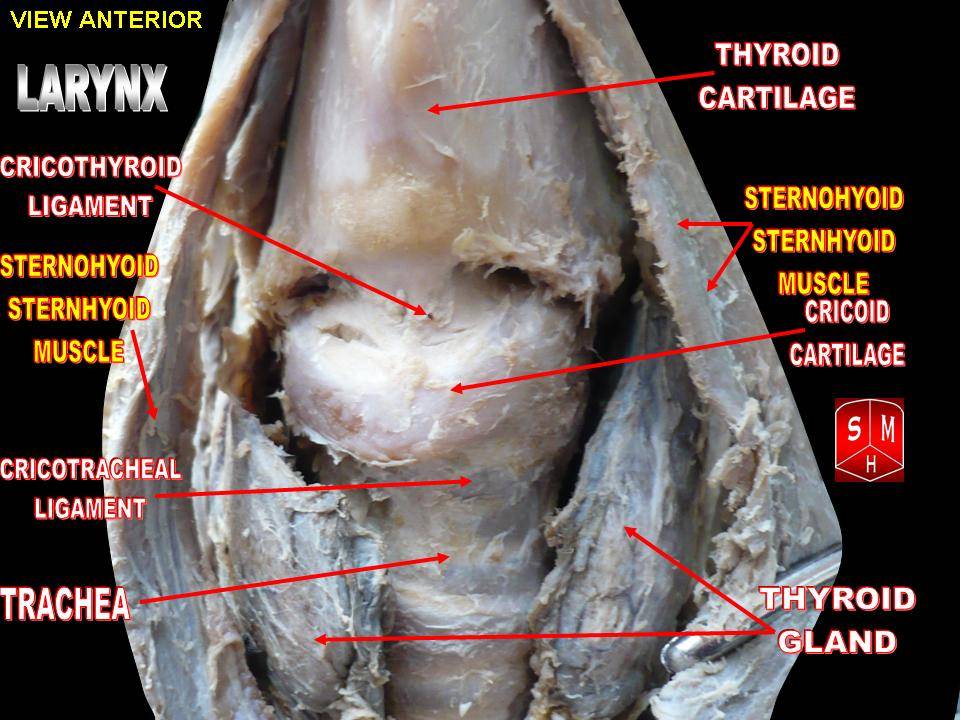
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottis
The glottis is the opening between the vocal folds (the rima glottidis). The glottis is crucial in producing vowels and voiced consonants. Etymology From Ancient Greek ''γλωττίς'' (glōttís), derived from ''γλῶττα'' (glôtta), variant of ''γλῶσσα'' (glôssa, "tongue"). Function Phonation As the vocal folds vibrate, the resulting vibration produces a "buzzing" quality to the speech, called voice or voicing or pronunciation. Sound production that involves moving the vocal folds close together is called ''glottal''. English has a voiceless glottal transition spelled "h". This sound is produced by keeping the vocal folds spread somewhat, resulting in non-turbulent airflow through the glottis. In many accents of English the glottal stop (made by pressing the folds together) is used as a variant allophone of the phoneme (and in some dialects, occasionally of and ); in some languages, this sound is a phoneme of its own. Skilled players of the Australian di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), immunoglobulins (especially IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Amphibians, fish, snails, slugs, and some other invertebrates also produce external mucus from their epidermis as protection against pathogens, and to help in movement and is also produced in fish to li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair of mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columnar Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithelial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-keratinized Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of naming epithelia according to the cell type at the surface. In the deeper layers, the cells may be columnar or cuboidal. There are no intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced before the basement membrane is exposed. It forms the outermost layer of the skin and the inner lining of the mouth, esophagus and vagina. In the epidermis of skin in mammals, reptiles, and birds, the layer of keratin in the outer layer of the stratified squamous epithelial surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiglottic Vallecula
The epiglottic valleculae are paired spaces between the root of the tongue and anterior surface of the epiglottis. Each vallecula is bordered medially by the median glossoepiglottic fold and laterally by the lateral glossoepiglottic fold. The valleculae can collect saliva to prevent initiation of the swallowing reflex. The vallecula is an important reference landmark used during intubation of the trachea. The procedure requires the blade-tip of a Macintosh-style laryngoscope Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ge ... to be placed as far as possible into the vallecula in order to facilitate directly visualizing the glottis. Additional Images File:Slide10vvv.JPG, Epiglottic vallecula References * Human head and neck Human throat {{respiratory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryepiglottic Fold
The aryepiglottic folds are triangular folds of mucous membrane of the larynx. They enclose ligamentous and muscular fibres. They extend from the lateral borders of the epiglottis to the arytenoid cartilages, hence the name 'aryepiglottic'. They contain the aryepiglottic muscles and form the upper borders of the quadrangular membrane. They have a role in growling as a form of phonation. They may be narrowed and cause stridor, or be shortened and cause laryngomalacia. Structure The aryepiglottic folds are triangular. They are narrow in front, wide behind, and slope obliquely downward and backward. They originate from the lateral borders of the epiglottis. They insert into the arytenoid cartilages. In front, they are bounded by the epiglottis. Behind, they are bounded by the apices of the arytenoid cartilages, the corniculate cartilages, and the interarytenoid notch. Within the posterior part of each aryepiglottic fold exists a cuneiform cartilage which forms whitish promine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arytenoid Cartilage
The arytenoid cartilages () are a pair of small three-sided pyramids which form part of the larynx. They are the site of attachment of the vocal cords. Each is pyramidal or ladle-shaped and has three surfaces, a base, and an apex. The arytenoid cartilages allow for movement of the vocal cords by articulating with the cricoid cartilage. It may be affected by arthritis, dislocations, or sclerosis. Structure The arytenoid cartilages are part of the posterior part of the larynx. Surfaces The posterior surface is triangular, smooth, concave, and gives attachment to the arytenoid muscle and transversus. The antero-lateral surface is somewhat convex and rough. On it, near the apex of the cartilage, is a rounded elevation (colliculus) from which a ridge (crista arcuata) curves at first backward and then downward and forward to the vocal process. The lower part of this crest intervenes between two depressions or foveæ, an upper, triangular, and a lower oblong in shape; the latter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroepiglottic Ligament
The thyroepiglottic ligament is an intrinsic ligament of the larynx. It connects the stalk of the epiglottis to the angle formed by the two laminæ of the thyroid cartilage, a short distance below the superior thyroid notch The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the ''laryngeal skeleton'', the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx (only the cricoid cartilage .... References Ligaments of the head and neck {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Cartilage
The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the ''laryngeal skeleton'', the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx (only the cricoid cartilage encircles it). Structure The thyroid cartilage is a hyaline cartilage structure that sits in front of the larynx and above the thyroid gland. The cartilage is composed of two halves, which meet in the middle at a peak called the laryngeal prominence, also called the Adam's apple. In the midline above the prominence is the superior thyroid notch. A counterpart notch at the bottom of the cartilage is called the inferior thyroid notch. The two halves of the cartilage that make out the outer surfaces extend obliquely to cover the sides of the trachea. The posterior edge of each half articulates with the cricoid cartilage inferiorly at a joint called the cricothyroid joint. The most posterior part of the cartilage also has two projection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)