|
Eozostrodon
''Eozostrodon'' is an extinct morganucodont mammaliaform. It lived during the Rhaetian stage of the Late Triassic. ''Eozostrodon'' is known from disarticulated bones from Wales and South West England and estimated to have been less than in head-body length, slightly smaller than the similar-proportioned ''Megazostrodon''. ''Eozostrodon'' was described on the basis of two teeth discovered in a quarry near Frome in Somerset, England, each originally assigned to separate species ''E. parvus'' and ''E. problematicus''. The latter was synonymized in 1971. The identity of and status of ''Eozostrodon'' is controversial. Kühne considered ''Eozostrodon'' to be "one and the same" with ''Morganucodon'' which he described, albeit after the published description of ''Eozostrodon'', claiming "...for a number of good reasons ''Morganucodon'' ought to be used, the name of ''Eozostrodon'' being used for sentimental reasons only or because of ignorance." Jenkins and Crompton in 1979 argued ''Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morganucodon
''Morganucodon'' ("Glamorgan tooth") is an early mammaliaform genus that lived from the Late Triassic to the Middle Jurassic. It first appeared about 205 million years ago. Unlike many other early mammaliaforms, ''Morganucodon'' is well represented by abundant and well preserved (though in the vast majority of cases disarticulated) material. Most of this comes from Glamorgan in Wales (''Morganucodon watsoni''), but fossils have also been found in Yunnan Province in China (''Morganucodon oehleri'') and various parts of Europe and North America. Some closely related animals (''Megazostrodon'') are known from exquisite fossils from South Africa. The name comes from a Latinization of ''Morganuc'', the name for South Glamorgan in the Domesday Book, the county of Wales where it was discovered by Walter Georg Kühne,Walter G. Kühne, "On a Triconodont tooth of a new pattern from a Fissure-filling in South Glamorgan", ''Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London'', volume 119 (1949� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morganucodont
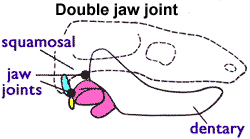
Morganucodonta ("Glamorgan teeth") is an extinct order of basal Mammaliaformes, a group including crown-group mammals (Mammalia) and their close relatives. Their remains have been found in Southern Africa, Western Europe, North America, India and China. The morganucodontans were probably insectivorous and nocturnal, though like eutriconodonts some species attained large sizes and were carnivorous. Nocturnality is believed to have evolved in the earliest mammals in the Triassic (called the nocturnal bottleneck) as a specialisation that allowed them to exploit a safer, night-time niche, while most larger predators were likely to have been active during the day (though some dinosaurs, for example, were nocturnal as well). Anatomy and biology Morganucodontans had a double jaw articulation made up of the dentary-squamosal joint as well as a quadrate-articular one. This implies that they also retained one of their postdentary bones: the articular. There is a trough at the back of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morganucodonts
Morganucodonta ("Glamorgan teeth") is an extinct order of basal Mammaliaformes, a group including crown-group mammals (Mammalia) and their close relatives. Their remains have been found in Southern Africa, Western Europe, North America, India and China. The morganucodontans were probably insectivorous and nocturnal, though like eutriconodonts some species attained large sizes and were carnivorous. Nocturnality is believed to have evolved in the earliest mammals in the Triassic (called the nocturnal bottleneck) as a specialisation that allowed them to exploit a safer, night-time niche, while most larger predators were likely to have been active during the day (though some dinosaurs, for example, were nocturnal as well). Anatomy and biology Morganucodontans had a double jaw articulation made up of the dentary-squamosal joint as well as a quadrate-articular one. This implies that they also retained one of their postdentary bones: the articular. There is a trough at the back of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth distal to the canines, preceded by deciduous molars. Morphology There is always one large buccal cusp, especially so in the mandibular first premolar. The lower seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of England
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic England
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archosaurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic Synapsids Of Europe
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaetian Life
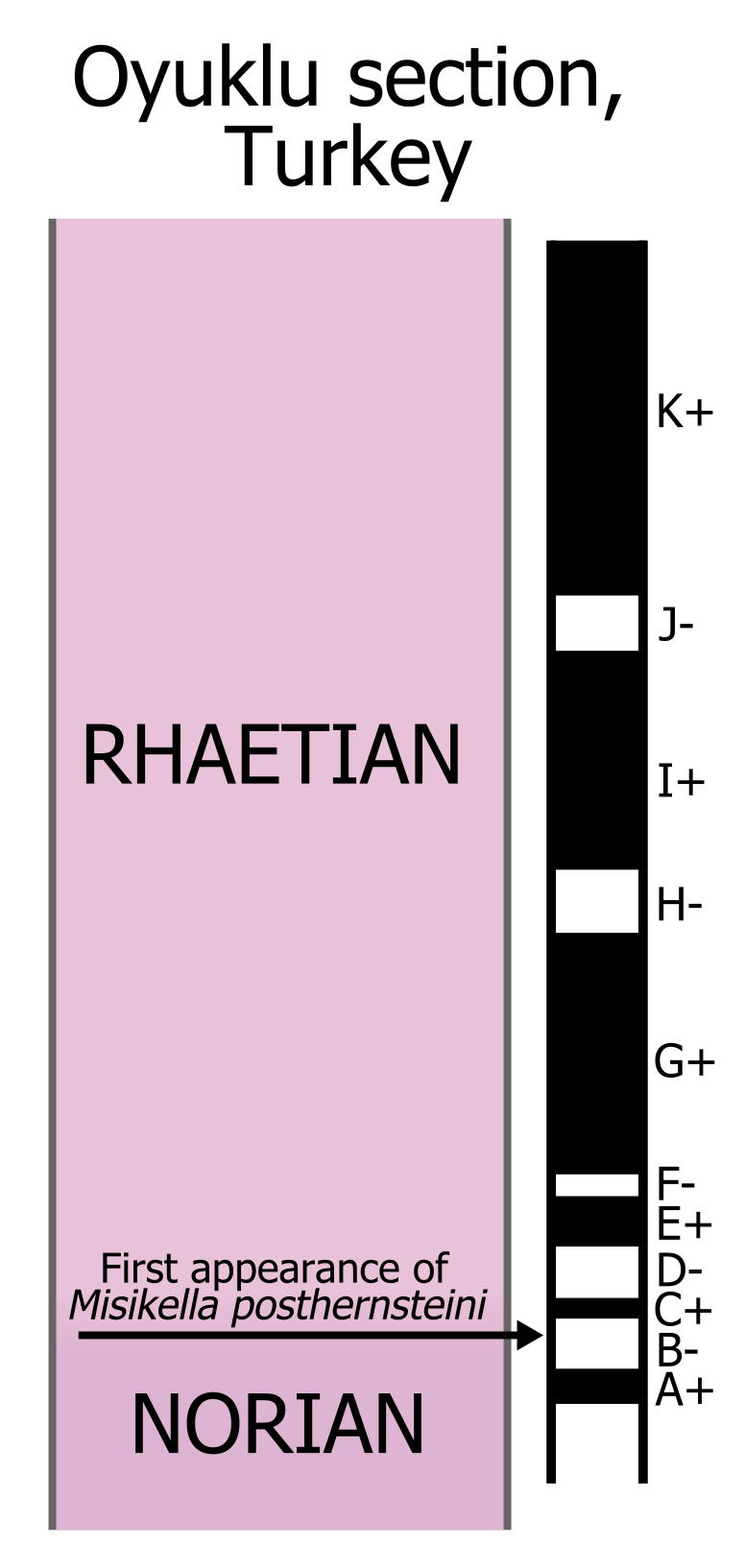
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age of the Jurassic). The base of the Rhaetian lacks a formal GSSP, though candidate sections include Steinbergkogel in Austria (since 2007) and Pignola-Abriola in Italy (since 2016). The end of the Rhaetian (and the base of the overlying Hettangian Stage) is more well-defined. According to the current ICS (International Commission on Stratigraphy) system, the Rhaetian ended ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). In 2010, the base of the Rhaetian (i.e. the Norian-Rhaetian boundary) was voted to be defined based on the first appearance of '' Misikella posthernsteini'', a marine conodont. However, there is still much debate over the age of this boundary, as well as the evolution of ''M. posthernsteini''. The most comprehensive source of precise ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Cynodont Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Rex Parrington
Francis Rex Parrington (20 February 1905 – 17 April 1981) was a British vertebrate palaeontologist and comparative anatomist at the University of Cambridge. A Fellow of the Royal Society, he was director of the Cambridge University Museum of Zoology and past president of the zoology section of the British Association for the Advancement of Science. Early life Francis Rex Parrington was born on 20 February 1905 in Bromborough near Neston in Cheshire, the youngest of three children of brewery owner Frank Harding Parrington and his wife Bessie Harding. After the death of his father in 1907, his mother remarried and 'Rex' Parrington was brought up in Central Liverpool, where his stepfather was a general practitioner. His interest in natural history developed in childhood, and he collected wildflowers, beetles, and fossils. In 1920, his family moved to North Wales, where he could freely explore his interests in the natural world. He was educated at the Merchant Taylors' School in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age of the Jurassic). The base of the Rhaetian lacks a formal GSSP, though candidate sections include Steinbergkogel in Austria (since 2007) and Pignola-Abriola in Italy (since 2016). The end of the Rhaetian (and the base of the overlying Hettangian Stage) is more well-defined. According to the current ICS (International Commission on Stratigraphy) system, the Rhaetian ended ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). In 2010, the base of the Rhaetian (i.e. the Norian-Rhaetian boundary) was voted to be defined based on the first appearance of '' Misikella posthernsteini'', a marine conodont. However, there is still much debate over the age of this boundary, as well as the evolution of ''M. posthernsteini''. The most comprehensive source of precise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |